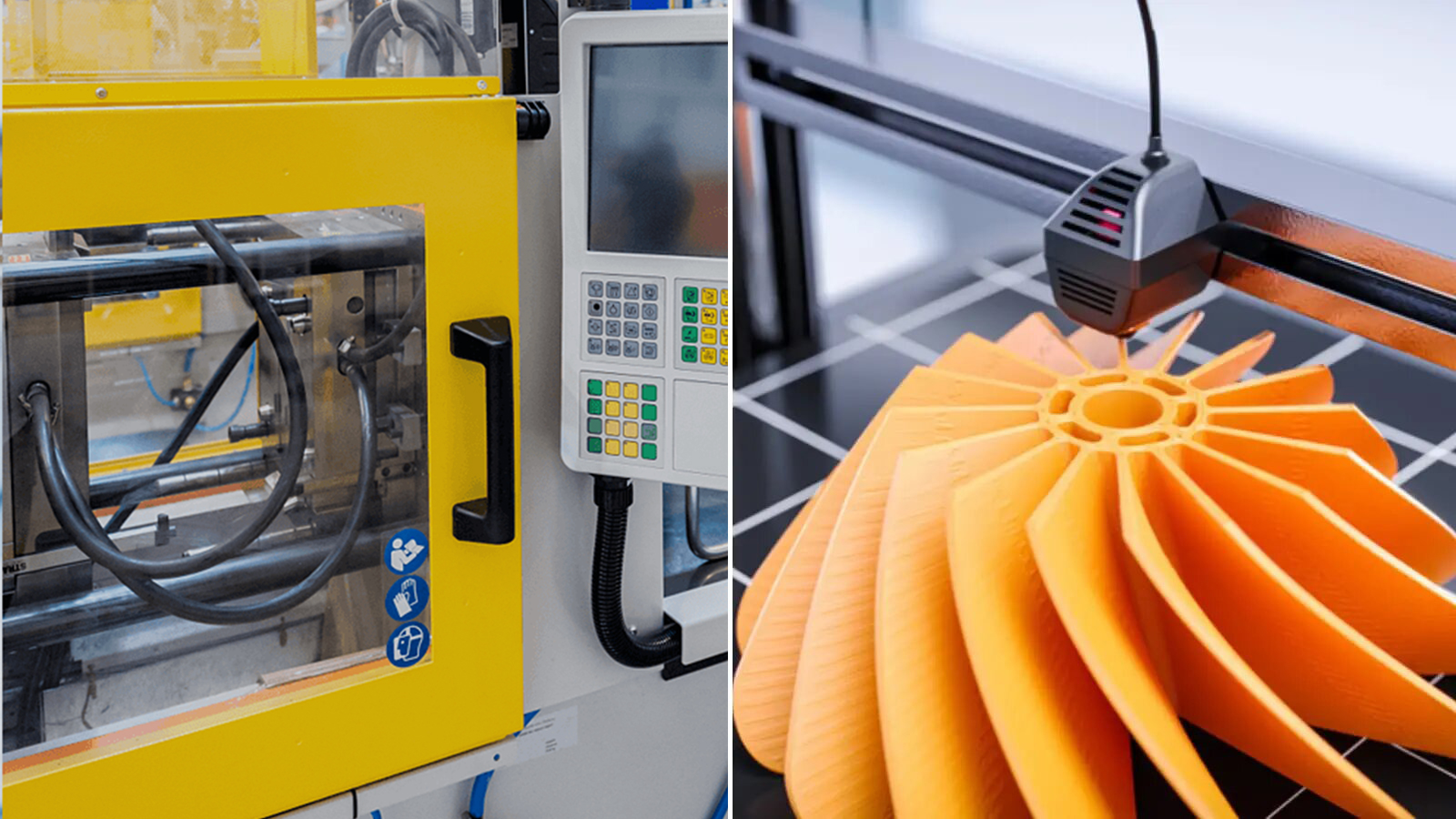
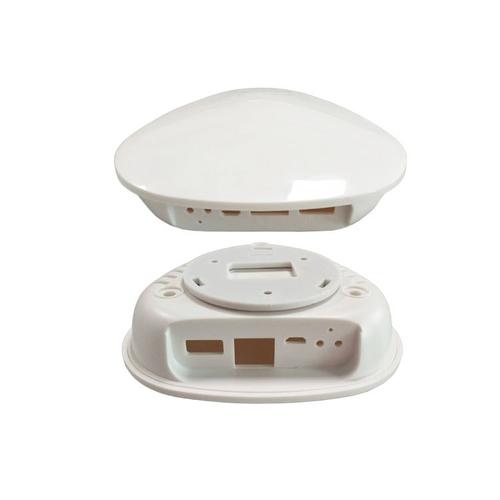
I. Plastic Part Manufacturing: Injection Molding or 3D Printing?
Production Volume Determines Direction
Design Maturity Considerations
II. Customization Process Differences
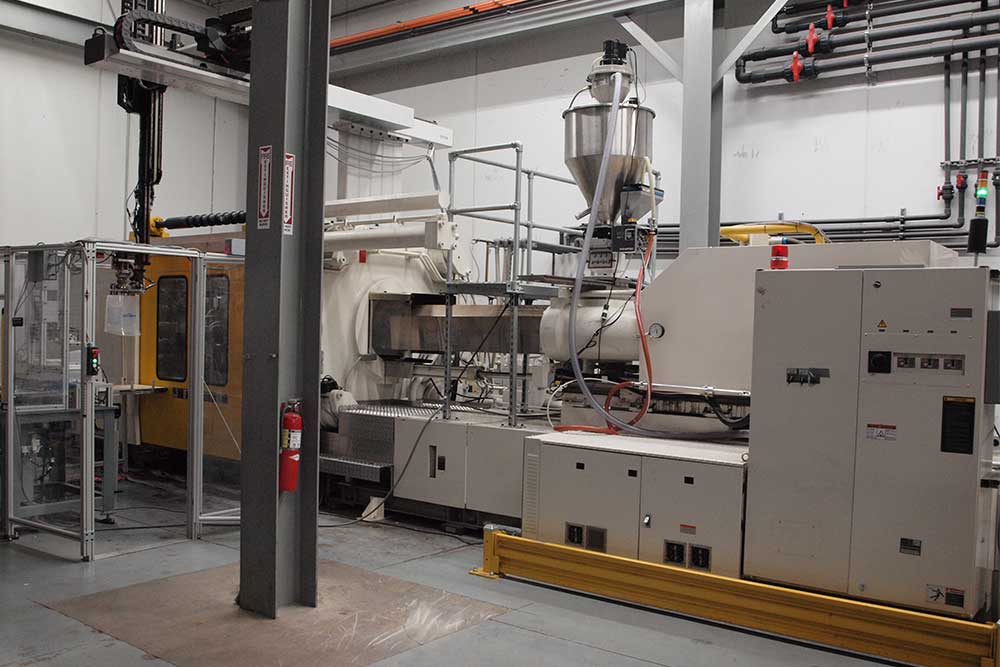
Injection Molding Customization Process
- Design & Engineering – CAD modeling and mold design
- Mold Fabrication – CNC machining of metal molds
- Tooling Validation – Test runs and adjustments
- Production – Mass manufacturing
- Quality Control – Inspection and packaging

3D Printing Customization Process
- Digital Design – 3D modeling (CAD)
- File Preparation – Slicing and parameter setting
- Printing – Layer-by-layer fabrication
- Post-Processing – Support removal and finishing
- Quality Check – Inspection and verification
III. Material Differences
Injection Molding Materials
- Thermoplastics: ABS, PP, PE, PC, PA, POM
- Thermosets: Epoxies, phenolics
- Elastomers: TPU, silicone
- Composites: Glass-filled materials
- Wide material selection
- Consistent material properties
- Higher density and strength
3D Printing Materials
- FDM Materials: PLA, ABS, PETG, TPU
- SLA/DLP Resins: Photopolymers, castable resins
- SLS Materials: Nylon, polyamides
- Specialty Materials: Carbon fiber composites, metal powders

- Rapid material changeover
- Support for functional prototypes
- Unique material combinations
IV. Finished Product Differences
Injection Molded Product Characteristics
- Homogeneous material structure
- Higher tensile strength
- Better impact resistance
- Smooth, consistent finish
- High dimensional accuracy
- Minimal post-processing needed
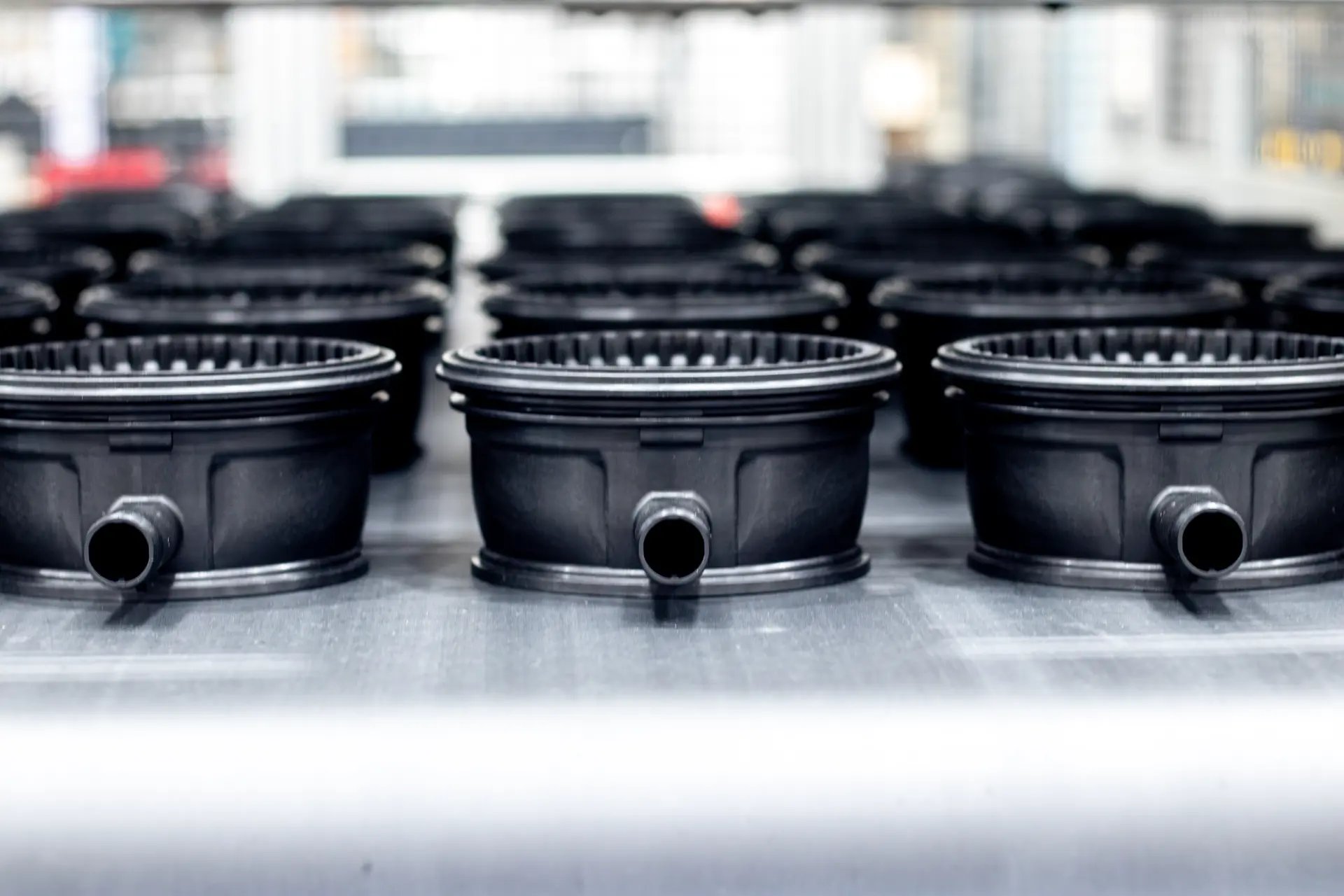

- Identical parts with tight tolerances
- Excellent repeatability
- Uniform material properties
3D Printed Product Characteristics
- Intricate geometries possible
- Internal channels and hollow structures
- Lattice and topology-optimized designs
- Anisotropic strength (layer direction dependent)
- Potential for layer adhesion issues
- May require post-processing
- Each part can be unique
- Variable properties within single part
- On-demand production capability
V. How to Choose the Right Manufacturing Process
Decision Matrix
|
Factor
|
Injection Molding
|
3D Printing
|
|
Volume
|
High (500+)
|
Low (1-100)
|
|
Lead Time
|
Longer
|
Shorter
|
|
Cost
|
Lower at scale
|
Lower for small batches
|
|
Design Flexibility
|
Limited
|
High
|
|
Material Options
|
Extensive
|
Growing
|
|
Part Strength
|
Higher
|
Good for prototypes
|
Recommended Selection Scenarios
- Production volume exceeds 500 units
- Design is finalized and stable
- Material strength and durability are critical
- Surface finish requirements are high
- Need rapid prototyping or small batches
- Design is still evolving
- Complex geometries are required
- Customization is essential
VI. Surface Finishing
Injection Molding Surface Treatments
- SPI-A1: Mirror polish
- SPI-B1: Semi-gloss
- SPI-C1: Matte finish
- Textured surfaces: Various patterns available

- Painting and coating
- Pad printing
- Hot stamping
- Laser engraving
3D Printing Surface Treatments
- Support removal
- Sanding and polishing
- Chemical smoothing
- Priming and painting
- Vapor smoothing for SLS parts
- Acetone smoothing for ABS
- UV curing for resin parts
- Powder coating for metal parts
VII. Product Characteristics Comparison
Injection Molded Product Characteristics
- Higher tensile strength
- Better impact resistance
- Uniform material distribution
- Higher heat deflection temperature
- Tighter tolerances (±0.02mm)
- Better repeatability
- Minimal warping
- Wide range of engineering plastics
- Food-grade and medical-grade materials
- High-temperature resistant materials
3D Printed Product Characteristics
- Complex internal structures
- Overhangs without supports
- Variable density structures
- Multi-material capabilities
- Rapid design validation
- Fit and form testing
- Functional prototypes
- Concept visualization
- Composite materials
- Conductive filaments
- Biodegradable options
- Metal-infused materials
VIII. Processing Advantages
Injection Molding Advantages
- High production speed
- Low labor requirements
- Minimal material waste
- 24/7 operation capability
- Low per-unit cost at scale
- Long mold lifespan
- High material efficiency
- Reduced post-processing
- Consistent part quality
- Automated inspection possible
- Traceability throughout production
- Process optimization opportunities
3D Printing Advantages
- Instant design-to-part capability
- No tooling required
- Quick design iterations
- Early-stage validation
- Mass customization possible
- Personalized products
- On-demand manufacturing
- Geographical flexibility
- Complex geometries
- Topology optimization
- Lightweight structures
- Product innovation acceleration
IX. Cost-Benefit Analysis
Injection Molding Cost Structure
- Mold design: (2,000-)10,000
- Mold fabrication: (5,000-)50,000
- Equipment setup: (1,000-)5,000
- Material: (0.10-)2.00
- Labor: (0.05-)0.50
- Energy: (0.01-)0.10
- Tooling depreciation: (0.05-)0.50
- Typically around 500-1,000 units
- Lower unit costs as volume increases
- Long-term cost savings for sustained production
3D Printing Cost Structure
- 3D printer: (1,000-)100,000
- Software: (500-)5,000
- Training: (1,000-)5,000
- Material: (0.50-)50.00
- Labor: (0.50-)5.00
- Energy: (0.10-)1.00
- Post-processing: (0.50-)10.00
- No mold costs
- Lower setup costs
- Minimal material waste
- Faster time-to-market
X. Common Processing Issues and Solutions
Injection Molding Common Issues
- Causes: Uneven cooling, material selection
- Solutions: Mold temperature control, material additives, part design optimization
- Causes: Insufficient packing pressure, gate location
- Solutions: Process parameter adjustment, gate redesign, material selection
- Causes: Mold parting line issues, clamping force
- Solutions: Mold maintenance, parameter optimization, secondary trimming
3D Printing Common Issues
- Causes: Temperature settings, material quality
- Solutions: Print temperature adjustment, material drying, print speed optimization
- Causes: Bed adhesion, cooling rates
- Solutions: Heated bed, adhesion promoters, enclosure use
- Causes: Overhang angles, part orientation
- Solutions: Support generation optimization, part reorientation, soluble supports
XI. Xiamen Goldcattle Custom Injection Molding Services
Core Service Offerings
- High-precision plastic components
- Tight tolerance control (±0.005mm)
- Complex geometry manufacturing
- Multi-cavity mold design
- Product design and engineering
- Mold design and fabrication
- Injection molding production
- Assembly and finishing
- International certifications (SGS, RoHS, CE)
- Advanced inspection equipment
- Strict quality control processes
- Reliable supply chain management
Technical Advantages
- 100+ processing machines
- Multi-axis CNC machining centers
- Automated production lines
- Robotic handling systems
- Wide range of engineering plastics
- Custom material formulation
- Color matching capabilities
- Material testing and validation
- Automotive components
- Electronic enclosures
- Medical devices
- Consumer products
XII. How to Choose the Right Manufacturing Solution for You
- What is your production volume? – Small batches favor 3D printing, large volumes favor injection molding
- How stable is your design? – Evolving designs benefit from 3D printing flexibility
- What are your material requirements? – Specialized materials may dictate the process
- What is your timeline? – Urgent projects often use 3D printing for speed
XIII. Call to Action: Contact Us for Professional Advice
- Free manufacturing consultation
- Cost estimation and analysis
- Design for manufacturability review
- Production timeline planning
- Product type and application
- Expected production quantity
- Material requirements
- Delivery time requirements







