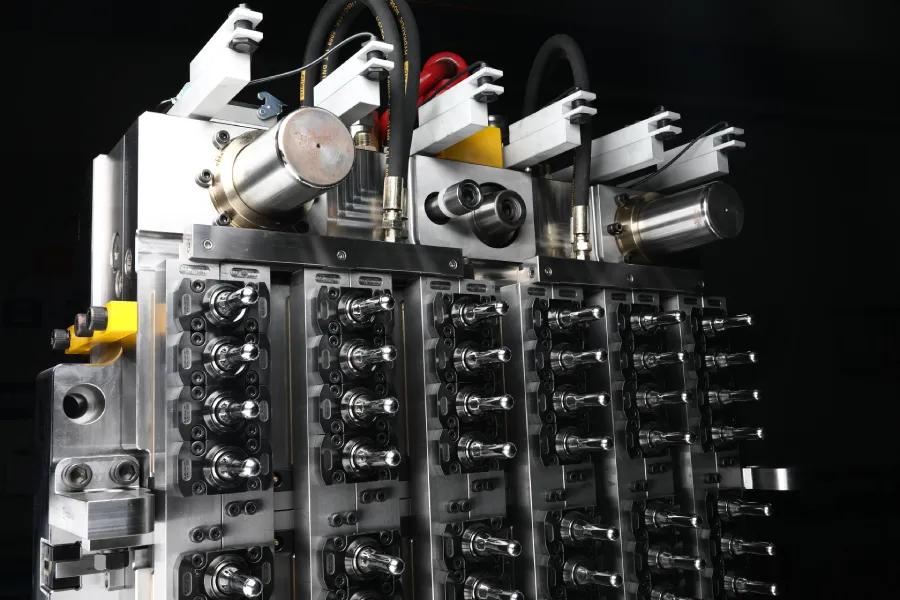
Why Prototype Stamping Dies Matter More Than You Think
The Global Market Driving Tooling Innovation
The Science Behind the Precision: How Prototype Stamping Dies Work
The Basic Functions of a Stamping Die
- Material Shaping: Transforms flat metal sheets into complex three-dimensional components
- Precision Control: Ensures consistent dimensions and tolerances across production runs
- Process Efficiency: Enables high-speed production with minimal material waste
- Cost Optimization: Reduces production costs through repeatable, automated processes
- Quality Assurance: Maintains consistent quality standards throughout manufacturing
The Physics of Metal Forming
- Consistent part dimensions with ±0.01mm tolerance
- Minimized material waste through optimized nesting
- Reduced springback through controlled deformation
- Improved surface finish through precision tooling
- 50% reduction in tool wear compared to conventional dies
- 30% increase in tool life through optimized stress distribution
- Enhanced part quality through uniform deformation
- Reduced energy consumption through efficient force application
Key Prototype Die Types and Configurations
- Simple design for basic stamping operations
- Cost-effective solution for simple part geometries
- Ideal for proof-of-concept testing and initial design validation
- Quick turnaround with 2-3 week production time
- Multiple stations for complex part production
- Sequential operations for intricate geometries
- Material utilization optimization up to 85%
- Production efficiency improvement of 400% compared to single-station dies
- Multiple operations in a single press stroke
- Superior accuracy through simultaneous operations
- Reduced handling requirements for delicate parts
- Ideal for high-precision components with tight tolerances
- Large-scale production capability for complex parts
- Modular design for easy maintenance and modification
- Automation compatibility for high-volume production
- Precision positioning with ±0.005mm accuracy
Material Science: The Tool Steel Advantage

Material Selection Criteria
- Hardness Requirements: Rockwell hardness from HRC 58-62 for optimal wear resistance
- Toughness Needs: Impact resistance for reliable performance under production conditions
- Machinability: Ease of manufacturing for complex geometries
- Heat Treatment Response: Stability during hardening and tempering processes
- Cost-Effectiveness: Balancing performance with development budget constraints
Our Tool Steel Expertise
- Premium material for high-performance prototype dies
- Rockwell Hardness: 60-62 HRC after heat treatment
- Tensile Strength: 2300 MPa (ASTM E8)
- Wear Resistance: Excellent for high-volume production
- Cost-effective solution with exceptional performance
- High-carbon, high-chromium tool steel for demanding applications
- Rockwell Hardness: 60-62 HRC
- Tensile Strength: 2200 MPa (ASTM E8)
- Superior wear resistance for abrasive materials
- Used in aerospace and medical device manufacturing
- Advanced alloy with enhanced toughness
- Rockwell Hardness: 62-64 HRC
- Tensile Strength: 2400 MPa (ASTM E8)
- Improved machinability compared to traditional tool steels
- Excellent for complex die geometries
- Traditional high-carbon tool steel for general applications
- Rockwell Hardness: 58-60 HRC
- Tensile Strength: 2000 MPa (ASTM E8)
- Good balance of hardness and toughness
- Cost-effective solution for moderate production volumes
Advanced Surface Treatments
- Surface hardness enhancement up to 1200 HV
- Improved wear resistance by 300%
- Reduced friction coefficient for smoother operation
- Operating temperature: 500°C for optimal diffusion
- Titanium nitride (TiN) coating for extreme wear resistance
- Coating thickness: 2-5 μm for optimal performance
- Coefficient of friction: 0.4 for reduced galling
- Operating temperature: 600°C continuous use
- Case depth: 0.5-2.0 mm for surface hardening
- Core hardness: 30-40 HRC for toughness
- Case hardness: 58-62 HRC for wear resistance
- Ideal for gears and sliding components
Crafting Precision Dies

The Challenges of Prototype Die Manufacturing
- Dimensional Precision: ±0.005mm tolerance for critical working surfaces
- Surface Finish: Ra 0.2μm for optimal metal flow and part quality
- Heat Treatment Control: Uniform hardness distribution within 2 HRC
- Assembly Accuracy: Parallelism and perpendicularity within 0.01mm/m
- Cost Efficiency: Balancing performance with prototype development budgets
Advanced Manufacturing Processes
1. Precision CNC Machining
- Simultaneous 5-axis movement for complex geometries
- Positioning accuracy: ±0.002mm
- Spindle speed: 15,000-24,000 RPM for high-speed machining
- Tool change time: 0.8 seconds for maximum productivity
- Cutting speed: 100-300 m/min for tool steel
- Feed rate: 5-15 m/min for optimal surface finish
- Tool diameter: 0.1-20 mm for intricate details
- Coolant temperature control: ±1°C for thermal stability
2. EDM Technology

- Cutting accuracy: ±0.001mm for precision parts
- Surface finish: Ra 0.2μm after fine cutting
- Wire diameter: 0.1-0.3 mm for narrow slots
- Cutting speed: 100-300 mm²/min for productivity
- Electrode wear ratio: 0.1% for precise cavity reproduction
- Surface finish: Ra 0.1μm after polishing
- Jump motion control: 1-100 μm for deep cavity machining
- Power supply: 0.1-50 A for material removal rate control
3. Heat Treatment Excellence
- Heating rate: 5-20°C/min for uniform temperature distribution
- Quenching pressure: 6-8 bar for optimal cooling
- Temperature uniformity: ±5°C throughout the workload
- Distortion control: Less than 0.05mm per 100mm length
- Multiple tempering cycles for stress relief
- Temperature control: ±2°C for consistent results
- Holding time: 1-4 hours based on section thickness
- Cooling rate: Controlled to minimize residual stresses
- Measurement accuracy: ±0.001mm
- Probe diameter: 0.5-2.0 mm for detailed measurements
- Scanning speed: 500 points/second for efficient inspection
- Reporting capability: Full GD&T compliance documentation
- Measurement range: Ra 0.01-10 μm
- Sampling length: 0.25-8 mm for different surface textures
- Measurement accuracy: ±5% of reading
- Traceability: ISO 17025 accredited calibration
Our Customization Process: From Concept to Reality
Step 1: Design Consultation
- Part Geometry: Complexity, dimensions, and tolerance requirements
- Material Specifications: Type, thickness, and mechanical properties
- Production Volume: Prototype quantities and future production needs
- Cycle Time Requirements: Production speed and efficiency targets
- Budget Considerations: Development costs and return on investment
Step 2: Engineering Design
- CAD Modeling: Parametric design with full associativity
- Finite Element Analysis: Stress and deformation simulation
- Die Flow Simulation: Material flow and springback prediction
- Tooling Cost Analysis: Optimization for cost-effectiveness
- Manufacturing Process Planning: Production sequence development
Step 3: Prototyping and Validation
- Design Review: Cross-functional team evaluation of tooling concepts
- Prototype Machining: Rapid production of test components
- Forming Trials: Material testing under production conditions
- Dimensional Inspection: Verification of part quality and accuracy
- Design Optimization: Refinement based on testing results
Step 4: Production and Delivery
- Precision Manufacturing: State-of-the-art machining and EDM equipment
- In-Process Inspection: Quality checks at every manufacturing stage
- Assembly and Fitting: Meticulous assembly with precision adjustments
- Final Testing: Complete functionality verification before shipment
- Documentation: Comprehensive technical documentation and maintenance guides
Quality Standards: Certifications You Can Trust
International Quality Certifications
- Quality management system certification
- Process approach with risk-based thinking
- Continuous improvement methodology
- Customer satisfaction monitoring
- Automotive quality management system
- Advanced product quality planning (APQP)
- Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA)
- Measurement system analysis (MSA)
- Environmental management system
- Sustainable manufacturing practices
- Waste reduction and energy efficiency
- Environmental performance monitoring
Tooling and Performance Standards
- Working surface flatness: 0.005mm/m
- Parallelism between die halves: 0.01mm/m
- Perpendicularity of guide pillars: 0.005mm/m
- Positioning accuracy of working components: ±0.003mm
- Tool steel hardness: 58-62 HRC
- Surface roughness: Ra 0.2μm
- Impact toughness: 15-20 J/cm²
- Wear resistance: 500,000+ cycles for prototype use
- CE marking for European market compliance
- OSHA safety standards for North America
- ISO 12100 machinery safety requirements
- Risk assessment documentation
OEM-Specific Requirements
- General Motors: GMW14044 (tooling requirements), GMW16385 (quality standards)
- Ford: WSS-M99P1111-A (tooling materials), WSS-M33J19-A2 (manufacturing processes)
- Toyota: TSM 0508G (quality management), TSM 0509G (supplier requirements)
- Volkswagen: VW 50180 (tooling specifications), VW 50190 (performance standards)
Technical Advantages: Why Choose Xiamen GoldCattle
Performance Comparison
|
Performance Metric
|
Industry Standard
|
Our Capability
|
Improvement
|
|
Dimensional Accuracy
|
±0.01mm
|
±0.005mm
|
50% better
|
|
Surface Finish
|
Ra 0.8μm
|
Ra 0.2μm
|
75% smoother
|
|
Tool Life
|
100,000 cycles
|
500,000+ cycles
|
400% longer
|
|
Production Lead Time
|
6-8 weeks
|
3-4 weeks
|
50% faster
|
|
Cost Efficiency
|
100%
|
85%
|
15% lower
|
Design and Engineering Expertise
- Tooling Design: Senior engineers with 15+ years of stamping die experience
- Materials Science: Metallurgists specializing in tool steel selection and heat treatment
- Manufacturing Engineering: Experts in precision machining and EDM technology
- Quality Assurance: Specialists in metrology and process control
Custom Solutions for Every Need
- Automotive Industry: Body panels, structural components, and powertrain parts
- Aerospace Applications: Precision components with tight tolerances
- Electronics Manufacturing: Small, intricate parts with complex geometries
- Medical Devices: Biocompatible materials and sterile manufacturing
- Consumer Products: High-volume production with consistent quality
Case Study: Automotive Component Prototype Die

- Produce complex structural components with ±0.01mm tolerance
- Handle high-strength steel (1500 MPa tensile strength)
- Reduce development time by 40% compared to conventional methods
- Provide cost savings of 25% in the prototype phase
- Ensure seamless transition to production tooling
Our Solution
Results
Advanced Applications: Beyond Traditional Stamping
High-Strength Steel Forming
- Material Capability: Handling up to 2000 MPa tensile strength materials
- Springback Control: Advanced die design for minimal shape distortion
- Forming Precision: Complex geometries with consistent quality
- Production Readiness: Direct transition to production tooling
- Variable Blank Holder Force: Computer-controlled for optimal material flow
- Draw Bead Technology: Precision control of material movement
- Heated Tooling: For improved formability of advanced materials
- In-Die Monitoring: Real-time process control and quality assurance
Micro-Precision Stamping
- Feature Size: Down to 0.1mm with ±0.005mm tolerance
- Material Thickness: 0.05-0.5mm for delicate components
- Surface Finish: Ra 0.1μm for critical surfaces
- Production Volume: From prototype to high-volume production
- Ultra-Precision Machining: Sub-micron accuracy for working components
- Specialized Coatings: Reduced friction for thin material forming
- In-Die Sensing: Real-time quality monitoring
- Cleanroom Compatibility: For medical and electronics applications
Sustainable Manufacturing
- Material Efficiency: 85%+ material utilization through optimized nesting
- Energy Savings: 30% reduction in energy consumption
- Waste Reduction: Minimal scrap generation through precision design
- Recyclability: Tooling materials designed for end-of-life recycling
Technical Challenges and Solutions
Material Formability Issues
- Challenge: Springback and shape distortion during forming
- Solution: Advanced die design with overbending and restrike operations
- Benefit: Consistent part geometry with minimal rework
- Challenge: Material wrinkling and tearing during forming
- Solution: Precision blank holder force control and draw bead technology
- Benefit: High-quality parts with minimal scrap
Manufacturing Process Optimization
- Challenge: Maintaining precision across multiple features
- Solution: 5-axis machining and EDM technology
- Benefit: Complex geometries with consistent accuracy
- Challenge: Ensuring consistent hardness throughout the tool
- Solution: Vacuum heat treatment with precise temperature control
- Benefit: Uniform performance and extended tool life
Maintenance and Longevity
- Regular inspection schedules based on production volume
- Lubrication optimization for specific materials
- Wear monitoring and replacement planning
- Performance tracking and continuous improvement
- Training Services: Operator and maintenance training
- Technical Support: 24/7 assistance for critical issues
- Spare Parts Program: Quick delivery of replacement components
- Performance Audits: Regular assessment and optimization