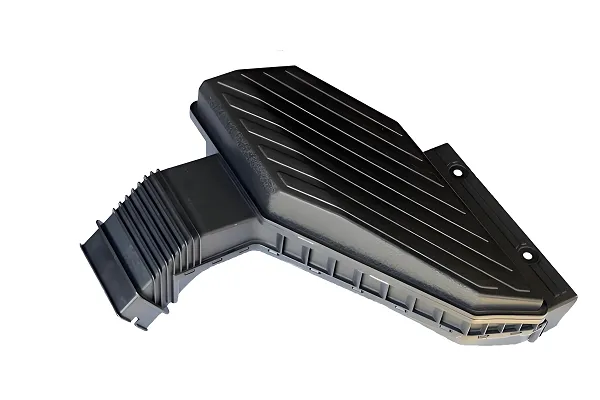
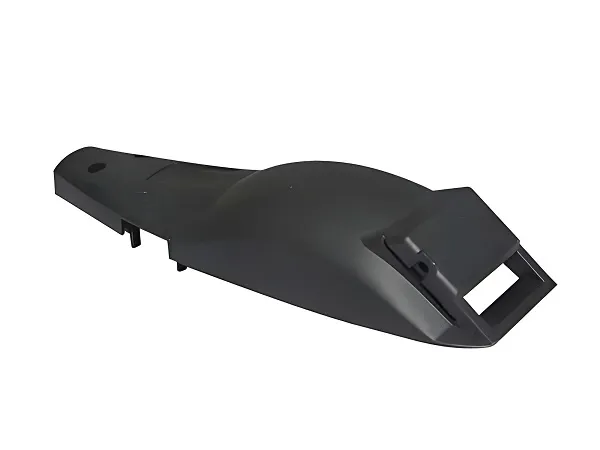
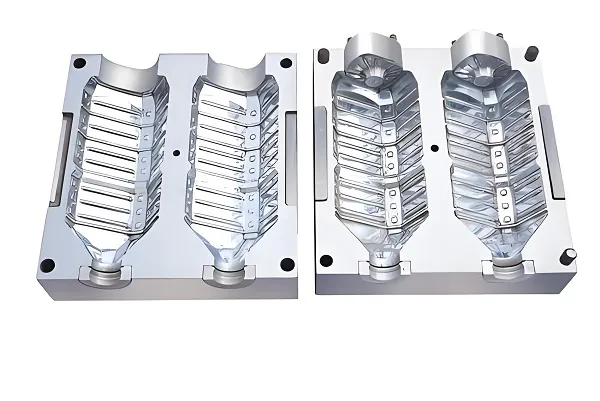
Thin-wall injection molding industrial technology plays an important role in modern manufacturing industry with its unique processing advantages, wide range of material choices, precise property parameter control and wide range of applications. With the continuous progress and innovation of technology, thin-wall injection molding technology will show its great potential and value in more fields.
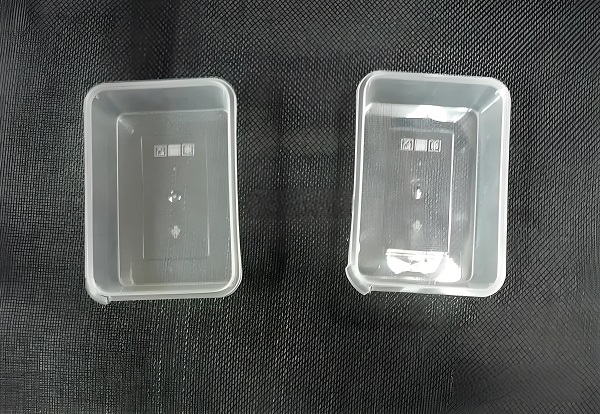

1. Processing advantages
As a special injection molding processing method, thin-wall injection molding technology has significant processing advantages, mainly reflected in the following aspects:
Light weight and small appearance and size of the product: thin-walled injection molded parts are thinner and lighter than traditional injection molded parts, occupying less space and facilitating storage and transportation.
Material and cost savings: Due to the thinner wall thickness, the amount of material used can be significantly reduced, thus lowering production costs.
Easy to integrate design and assembly: Thin-wall injection molded parts have high design flexibility, which makes it easy to integrate design and assembly with other parts, improving production efficiency and market competitiveness.
Enhanced product performance: For products of the same size, thin-walled parts can provide more space and accommodate more functional components, thus greatly enhancing product performance.
High production efficiency: Thin-wall injection molding technology achieves rapid manufacturing through high-speed injection and rapid cooling, which improves production efficiency.
Good product appearance: Thin-wall injection molding technology can realize the smooth and delicate surface of the product and improve the appearance quality of the product.
2. Processable materials
Thin-wall injection molding technology can process a wide range of materials, mainly including but not limited to the following:
Polyolefin materials: such as polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), etc. These materials have good fluidity and molding properties, suitable for thin-wall injection molding.
Polyester materials: such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which have good transparency and mechanical properties.
Polystyrene (PS): with good transparency and rigidity, suitable for making thin-walled packaging containers, etc.
Nylon (PA), Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene Copolymer (ABS), Polycarbonate (PC), etc.: These materials are also widely used in the field of thin-wall injection molding and have their own unique performance advantages.
3. Property Parameters
The property parameters of thin-wall injection molding technology involve a number of aspects, including but not limited to the following:
Barrel temperature: Depending on the material used, the barrel temperature needs to be adjusted accordingly. For example, the barrel temperature for PP is usually between 160 and 300°C, while the barrel temperature for PE is slightly lower.
Mold temperature: Mold temperature has an important effect on the cooling rate and molding quality of the product. Thin wall injection molding usually requires a lower mold temperature to achieve rapid cooling, but also to avoid too low a temperature to cause increased internal stresses in the product.
Injection Pressure: Thin wall injection molding requires a high injection pressure to ensure that the melt can fill the mold cavity. However, too much injection pressure can lead to product distortion or mold damage.
Holding Pressure: Holding pressure has a significant impact on the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of the product. Thin wall injection molding usually requires a long holding pressure to ensure that the product is sufficiently cooled and cured.
Injection Speed: Thin wall injection molding usually uses high injection speeds to reduce the residence time of the melt in the mold and to avoid overheating and degradation. However, high injection speeds can also lead to surface defects.
4. Technology Application Areas
Thin wall injection molding technology has a wide range of applications in many fields, mainly including:
Food packaging: Thin-wall injection molded products are lightweight, strong and durable, and can meet the requirements of food packaging for freshness, sealing and safety. Common applications include boxes, containers, bottles and other packaging materials.
Electronic products: As electronic products focus on the appearance of design and size requirements, the thin-wall injection molding products of lightweight and thin features make it an ideal choice for the shell of electronic products. Common applications include cell phone cases, tablet cases, TV cases, etc.
Automotive manufacturing: The automotive industry has put forward higher requirements for product lightweight and cost control. Thin-wall injection molding technology can meet these requirements, and is used in automotive manufacturing to make instrument panels, lights, body structure parts and other components.
Medical devices: Thin-wall injection molding technology is also used in the field of medical devices, such as the manufacture of syringes, infusion sets and other medical supplies. These products need to have good sealing and biocompatibility.
Thin Wall Injection Molding FAQ
1. What is thin wall injection molding?
A. Thin wall injection molding is a plastic processing technology in which molten plastic is injected into a mold cavity under high pressure and cooled to obtain a plastic product of the desired shape. It is characterized by the ability to produce plastic products with a wall thickness of 0.5mm or less, and has the advantages of lightweight, thin-wall and miniaturization. The definition of thin-wall injection molding is usually related to the ratio of flow length to thickness (L/T), the thickness of the plastic part and the projected area.
2. What are the advantages of thin-wall injection molding?
A. The advantages of thin-wall injection molding mainly include:
Lightweighting: Reduce product weight, transportation costs and energy consumption.
Thin-wall: Reduce the amount of material used, reduce production costs.
Miniaturization: meet consumer demand for product portability.
High efficiency: short molding cycle, improve production efficiency.
3. What are the material requirements for thin-wall injection molding?
A: Thin wall injection molding has high requirements for materials, usually need to choose plastics with large flow length, high impact strength, high heat distortion temperature, high thermal stability, low directionality and good dimensional stability. Commonly used raw materials for thin-wall injection molding include polycarbonate (PC), acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), PC/ABS blends, and PA6.