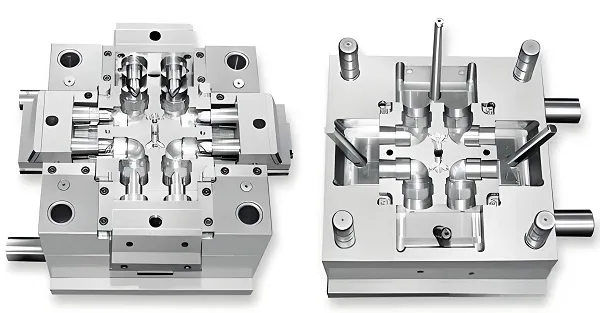
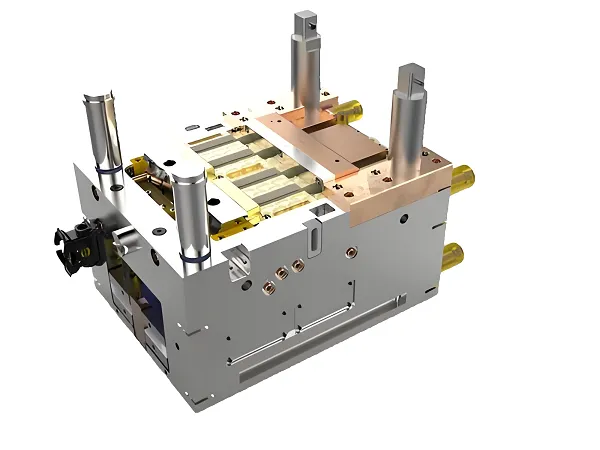
Thermoplastic molding is an important molding process that plays a key role especially in the field of mechanical customization. The core of this process lies in the use of the heat-softening properties of thermoplastics, which are molded into the desired shape in a mold by gas, liquid or mechanical pressure.
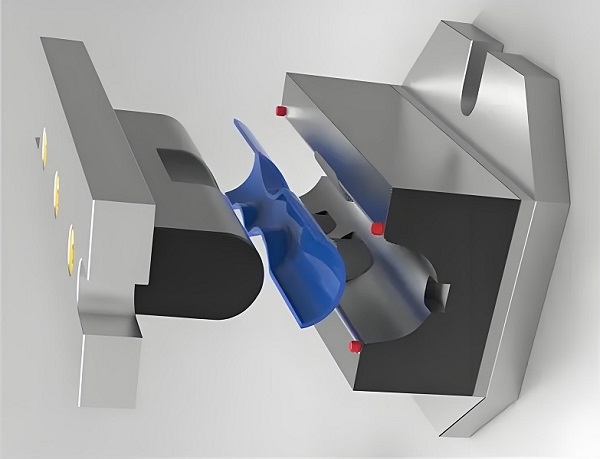
1. Process Principle
Thermoplastic molding begins with cutting the thermoplastic sheet into blanks of a certain size and shape, which are then heated to a softening temperature, i.e., a high elastic-plastic state. In this state, the plastic is easy to deform but not yet melted, so you can apply appropriate pressure (such as vacuum, compressed air or mechanical pressure) to bend and extend the blank, and ultimately shaped into the desired shape of the product.
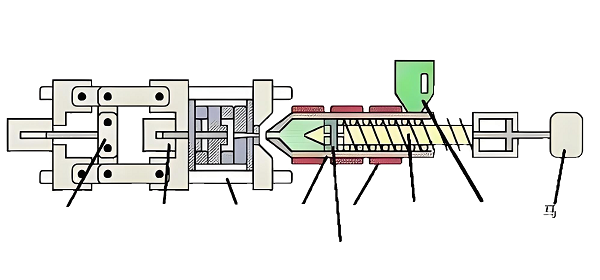
2. Process flow
Raw material preparation: choose the appropriate thermoplastic sheet, and cut into blanks to meet the requirements of the mold size.
Heating and softening: Heat the blank to its softening temperature, so that it enters the high elasticity and plasticity state.
Pressure molding: After heating and softening, the blank is quickly placed in the mold and gas, liquid or mechanical pressure is applied to deform it and make it fit the shape of the mold.
Cooling and shaping: maintain the pressure for a certain period of time, so that the blank is cooled and solidified in the mold to form a stable shape.
Demolding and post-processing: After the product has cooled to room temperature, it is removed from the mold and subjected to the necessary post-processing, such as trimming the edges, punching holes, and so on.
Technical Characteristics
High molding accuracy: Through precise mold design and pressure control, high precision products can be produced.
High production efficiency: The thermoplastic molding process is relatively simple, with high production efficiency, suitable for mass production.
High material utilization: less material loss in the molding process, which helps to improve material utilization.
Wide range of application: It can be applied to a wide range of thermoplastics and complex shapes.
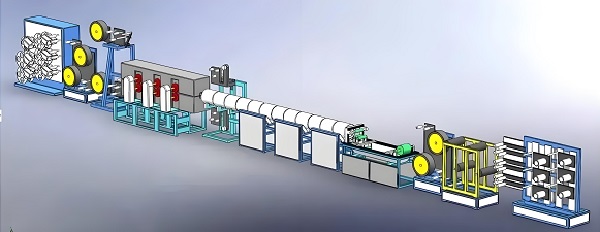
3.Thermoplastic molding customization process
Demand communication: Firstly, we have in-depth communication with customers to understand their specific needs, including the shape, size, material, quantity and usage scenarios of the products. Through detailed demand analysis, ensure that both parties have a clear understanding of the customization requirements.
Design and development: According to the customer’s needs, we carry out mold design and product development. This stage requires the use of CAD (Computer Aided Design) and other software for 3D modeling and simulation of the molding process to ensure the rationality and feasibility of the design. At the same time, it is also necessary to consider the thermal properties of the material, molding process parameters and other factors in order to optimize the product design.
Mold Manufacturing: According to the design drawings, special thermoplastic molding molds are manufactured. The precision and durability of the molds have an important impact on the quality of the final product, so advanced processing equipment and techniques are needed to ensure the quality of the molds.
Material Preparation: Select thermoplastic material that meets customer’s requirements and carry out necessary pre-treatment, such as drying and cutting. Ensure that the material has good fluidity and molding properties during the molding process.
Molding production: Put the prepared material into the mold, heat it to soften it, and then apply appropriate pressure to make it deform and fit the shape of the mold. During the molding process, process parameters such as temperature, pressure and time need to be strictly controlled to ensure product quality and consistency.
Quality Inspection: Strict quality inspection is carried out on the molded products, including appearance inspection, size measurement and performance test. Ensure that the products meet customer requirements and relevant standards.
Delivery and after-sales service: Deliver qualified products to customers and provide necessary after-sales service. Including product use guidance, maintenance and follow-up technical support.
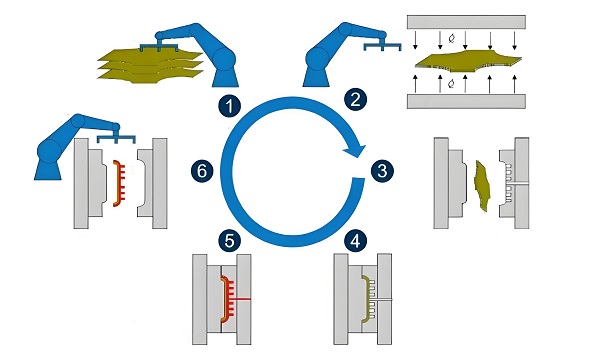
4.Technical features
Highly customized: Thermoplastic molding customized service can be personalized design and production according to the specific needs of customers to meet the special needs of different fields.
High precision: Through accurate mold design and advanced production process, high precision thermoplastic molding products can be produced.
High efficiency: The thermoplastic molding process is relatively simple and highly productive, suitable for mass customized production.
Versatility: Thermoplastic molding materials are rich in variety, and different materials can be selected for production according to customers’ needs to meet diversified market demands.
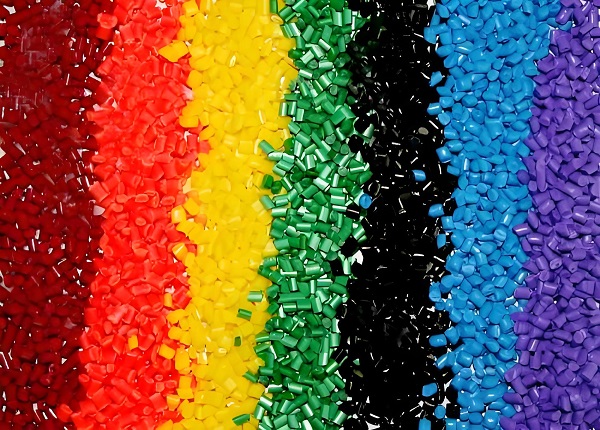

5.Application materials
Thermoplastic molding is widely applicable to a wide range of thermoplastics, including but not limited to polystyrene (PS), plexiglass (PMMA), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and so on. These materials exhibit good plasticity and ductility when heated, and can be molded to meet the needs of complex shapes and structures.
6. Application Areas
Thermoplastic molding process has a wide range of applications in the field of mechanical customization, such as automotive parts, electronic product shells, daily necessities, packaging containers and so on. In addition, with the advancement of technology and process improvement, thermoplastic molding in aerospace, medical equipment and other high-end applications are also expanding.