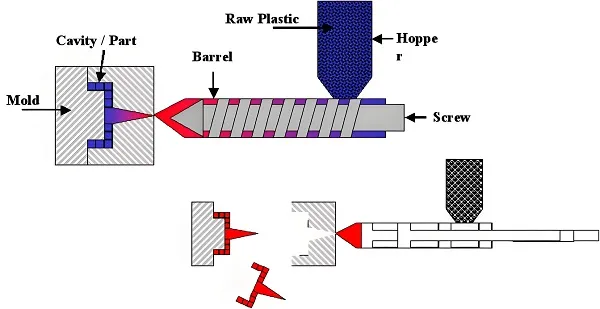
1. What is Polymer Injection Molding?
Polymer Injection Molding is a core process that transforms plastic into various products — it melts plastic pellets into a fluid state using high temperature, injects the fluid into a precision mold at high pressure, and after cooling, demolds the product to get the pre-designed shape. From small phone buttons to large car dashboards, 20%-30% of plastic products worldwide are produced through this process, and an even higher 80% of engineering plastics rely on this technology for molding.
(The first time I really looked at the plastic items around me, I realized that everyday objects like phone cases and bubble tea lids are all made using the same technology. It’s surprising to discover this “industrial power hidden in daily life.”)
2. Core Equipment and Process Secrets
(1) Three Core Systems
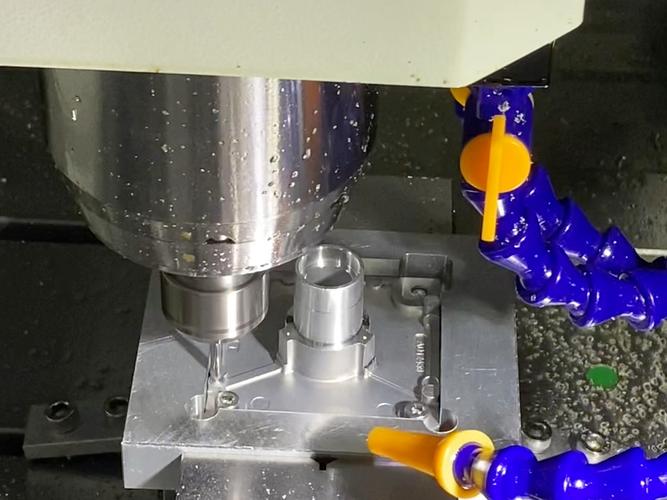
- Injection System: The “heart” of the injection molding machine, consisting of a barrel, screw, nozzle, and other components. After plastic pellets enter the barrel from the hopper, they are pushed forward by the rotating screw and heated to melt (usually at 150-300°C), and finally injected into the mold at high speed through the nozzle. The screw’s special design (length-to-diameter ratio of 10-20) ensures uniform plasticization, acting like a “precision-stirred melting furnace.”
(I once talked to a friend who works in injection molding. He said the screw’s length-to-diameter ratio isn’t chosen randomly — for example, softer PE plastic and harder PC plastic require different ratios. A slight mismatch can lead to uneven melting, resulting in bumpy surfaces on the final product. It turns out these “numerical details” are full of expertise.)
- Clamping System: The “protector” of the mold, which must provide sufficient clamping force to prevent the mold from being split by molten plastic. The common hydraulic-mechanical combined system can achieve precise movements of “fast-then-slow for mold closing, slow-fast-slow for mold opening,” protecting the mold while improving efficiency.
(I once watched the mold closing process. It snapped shut quickly at first, but slowed down right before it fully closed. My friend explained this was to avoid damaging the mold — a good-quality mold costs tens of thousands of yuan, and a crack from slamming shut would cause huge losses. This “combination of speed and slowness” is quite thoughtful.)
- Mold: The “genetic blueprint” of the product, composed of a gating system (material delivery channel), molding parts (which determine the shape), and structural parts. Precision molds can achieve an accuracy of ±0.01mm, capable of replicating fine textures and even threaded structures.
(±0.01mm is roughly one-fifth the thickness of a human hair. I once saw a factory produce plastic gears — the mold replicated the tooth patterns perfectly, and the gears rotated smoothly when installed in a small motor. That’s when I realized “mold precision” isn’t just a slogan; it truly determines how well a product works.)
(2) The Four-Step Molding “Magic”
- Preparation Stage: Dry the plastic pellets (to avoid bubbles during molding), install the mold, and preheat it;
(I once saw a worker in a small factory pouring plastic pellets into a dryer and squeezing them by hand from time to time. He said if the pellets contained moisture, the final product would have small bubbles — like “trapped air in plastic” — which would be unsellable and a waste of materials. So no matter how tedious this step is, it must be done carefully.)
- Injection and Pressure Holding: After molten plastic is injected into the mold, maintain pressure to ensure the mold cavity is fully filled;
(I didn’t understand why “pressure holding” was needed until my friend showed me a defective product that skipped this step — its edge was missing a small piece, like it had been nibbled. He explained that plastic shrinks when cooling; without sustained pressure, the plastic can’t fill the mold completely. It turns out this “extra moment of pressure” ensures the product is “fully formed.”)
- Cooling and Setting: Control the cooling rate through the mold’s cooling system to prevent product warping;
(I’ve seen warped plastic sheets that curved like a crescent moon. My friend said this happened because the cooling was too fast — the outer layer of plastic hardened first while the inner layer was still soft, causing deformation when shrinking. Later, they adjusted the cooling time from 10 seconds to 15 seconds, and the products became perfectly flat. Sometimes, “slowing down” is actually faster.)
- Demolding and Post-Processing: Remove the product and recycle leftover materials (recycling rate can reach over 80%);
(Nowadays, factories don’t waste leftover materials — they melt the cut plastic strips back into pellets for reuse. My friend said this saves a lot of costs and reduces waste, achieving two goals at once. However, he also noted that recycled materials can only be reused 2-3 times, as otherwise the product’s strength will decrease. It’s all about balancing “environmental protection” and “usability.”)
3. Ubiquitous Application Scenarios
(1) Pillar Industries
- Automotive Industry: Components like dashboards and headlight covers rely on injection molding for lightweighting. A complex automotive mold can cost 100,000 to 1,000,000 yuan;
(I was shocked when I first heard a single automotive mold costs hundreds of thousands of yuan. My friend smiled and said, “Look at all the buttons and textures on a car dashboard — the mold has to be like a ‘replication stamp,’ and it needs to withstand hundreds of thousands of openings and closings. The materials and craftsmanship have to be top-tier; the money is spent on ‘durability.’”)
- Medical Devices: Syringes, surgical instrument handles, and other items require medical-grade plastics (such as polycarbonate), with “zero batch variation” achieved through parameter locking;
(Medical products allow no room for error. When I visited a medical injection molding workshop, I saw dense parameters on the screen — a 1°C temperature deviation would trigger an alarm. The worker said, “If this batch of syringes is 0.1mm thicker than the last, it will be uncomfortable for doctors to use and might even pose risks.” This obsession with precision is really reassuring.)
- Optics Field: Materials like acrylic and cyclic olefin polymers are made into lenses via injection molding, which are lighter than glass and can be molded into complex curved surfaces in one piece.
(I used to think all lenses were made of glass — until I saw a plastic magnifying glass my friend made. It was half the weight of glass and could be shaped into a curve, making it comfortable to hold without digging into my hand. He said many VR headset lenses are now made via injection molding too, as it can create complex curved surfaces in one step — something glass simply can’t do. It turns out plastic can be this “high-tech.”)
(2) Daily Consumer Scenarios
From the multi-color spliced structures of children’s toys to the reinforcing rib designs on home appliance casings, injection molding technology has become the core driver of mass-produced fast-moving consumer goods, thanks to its advantage of “one-step molding of complex structures.” For example, disposable plastic cups are produced using multi-cavity molds, with a daily output of hundreds of thousands of pieces.
(I have a plastic toy car at home — the body is red and the wheels are black. It turns out they were made in one injection molding step too: the mold has separate cavities for different colors, and plastic is injected into them simultaneously to achieve the spliced effect, no gluing required later. And those disposable cups — producing hundreds of thousands a day? Manual production could never meet supermarket demand. You have to admit, its mass production capability is impressive.)
4. Technological Evolution and Practical Challenges
(1) Outstanding Advantages
- Amazing Efficiency: The molding cycle for small products is only 10-30 seconds, and an automated production line can be operated by just 2-3 people;
(Last time I watched a factory make plastic keychains, it took less than 20 seconds from when the pellets entered the machine to when the finished product came out! And only two workers were monitoring the line — the machine fed materials and demolded automatically. It’s much more “labor-saving” than I imagined, which explains how it can meet large orders from e-commerce platforms.)
- Controllable Precision: The surface smoothness of medical syringes can reach Ra ≤ 0.8μm, requiring no post-processing;
(A smoothness of Ra ≤ 0.8μm feels completely burr-free to the touch. My friend said, “If we polished them by hand, 8 out of 10 would be ruined.” Now, one-step molding achieves this, saving time and avoiding contamination — crucial for medical products.)
- Flexible Material Compatibility: It works with almost all thermoplastics and some thermosetting plastics.
(My friend has made soft silicone gaskets and hard nylon gears. I asked, “These are so different — do you need to change the machine?” He said only the temperature, pressure, and mold need adjustment, no machine replacement required. This “one-machine-multiple-uses” flexibility has saved him a lot of money on equipment.)
(2) Unsolved Challenges
- High Upfront Investment: A precision mold takes 1-6 months from design to testing, with costs often reaching tens of thousands of yuan;
(A friend of mine who does cultural and creative products wanted to make a batch of custom plastic ornaments. When he found out the mold would cost 50,000 yuan and take 3 months, he had to give up — small-batch customization simply can’t bear this cost. This is probably a “pain point” for many small businesses.)
- Low Flexibility: Once a mold is finalized, it’s hard to modify, making it unsuitable for small-batch customized products;
(Once my friend took a small order where the customer wanted an extra small hole in a plastic box. But the mold couldn’t be modified, so he had to make a new one — resulting in a big loss. He said, “If molds were like building blocks, where you could just replace a small part to make changes, we wouldn’t be so stuck.”)
- High Energy Consumption: Large injection molding machines require multiple supporting devices, with higher unit energy consumption than extrusion processes.
(My friend’s factory has extremely high electricity bills in summer — the injection molding machines use power for heating, and the chillers for cooling also consume electricity. He said, “We spend several thousand yuan more on electricity each month than the extrusion factory next door.” More energy-efficient equipment would save a lot on costs.)
(3) Innovative Breakthroughs
- Intelligentization: AI monitoring systems adjust temperature and pressure in real time, reducing defect rates by over 30%;
(My friend installed an AI system last year. Before, workers had to stare at screens to adjust parameters, which left their eyes sore after a day and still resulted in frequent defects. Now, the AI monitors in real time — automatically lowering the temperature if it’s too high, and increasing pressure if it’s too low. Defects have dropped by 30%, and workers are much more relaxed. Technology really solves “long-standing troubles.”)
- Greenification: Servo-motor injection molding machines save 30%-50% energy, and the application of biodegradable plastics is expanding;
(After switching to servo-motor machines, my friend said his monthly electricity bill was cut nearly in half! He also started using biodegradable plastics to make takeout boxes, which have received good feedback from customers. “It not only complies with environmental policies but also attracts customers who care about sustainability,” he said — a real “win-win.”)
- Acceleration: Aluminum alloy rapid prototyping molds cost only 1/3 of steel molds, and the production cycle is shortened by 50%;
(It used to take 2 months to make a sample mold, but now with aluminum alloy, it takes just 1 month — and costs much less. My friend said, “If a customer wants to modify the design, we don’t have to worry about wasting money anymore. Rapid trial and error helps us secure orders.” These “fast molds” have really helped small businesses.)
5. Personal Insights: The Future Path of Injection Molding Technology
- Technological Balance is Key: The conflict between mold costs and production flexibility can be resolved through “modular molds” — separating universal structures from customized parts. This reduces the threshold for small-batch production while retaining precision advantages;
(I think the “modular mold” idea is excellent. For example, when making plastic boxes, you can keep the universal box body mold and just replace a “small module” to add holes or textures — no need to make a whole new mold. This would lower costs for small-batch customization and reduce material waste. If popularized, it would definitely help many small businesses like my friend’s.)
- Material Innovation Defines Direction: Current biodegradable plastics have the drawback of insufficient heat resistance. If nanocomposite technology can be used to improve their performance, they are expected to be widely used in packaging and medical fields as replacements for traditional plastics;
(Biodegradable plastics are great, but they can’t hold hot soup or rice — which makes many customers reluctant to use them. If nanotechnology could make them heat-resistant, say able to withstand 100°C, then takeout boxes and disposable spoons could all be made of biodegradable materials. That would truly solve the “environmental but not durable” problem.)
- Ecological Collaboration Drives Development: Small and medium-sized enterprises can jointly build a “mold sharing platform,” enabling the reuse of idle molds through cloud-based scheduling to reduce resource waste. This aligns with environmental trends and allows more innovative enterprises to benefit from technological dividends.
(Many small businesses have molds that sit idle after being used a few times. If these molds were placed on a sharing platform, other enterprises in need could use them — for example, Enterprise A’s cup mold could be used by Enterprise B to make similar cups, no new mold needed. This not only avoids waste but also saves Enterprise B money. This “teamwork” approach would make the industry more efficient and eco-friendly — well worth trying.)







