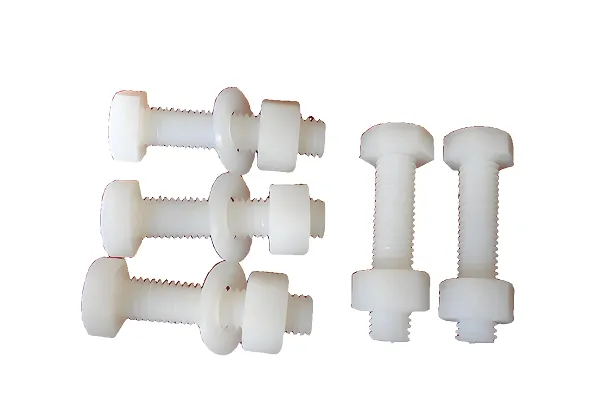
The pull rod injection molding process is a specialized manufacturing technique utilized to produce precision pull rod components. This process involves the injection of molten plastic into a mold cavity under high pressure, which then solidifies to form the desired shape. The pull rod injection molded parts are widely used in various industries due to their durability, lightweight nature, and cost-effectiveness.
1. Characteristics of Pull Rod Injection Molded Parts
The pull rod injection molded parts exhibit several distinct characteristics that make them suitable for a range of applications:
High Strength and Rigidity: The molding process ensures that the parts maintain high mechanical strength and rigidity.
Precision and Accuracy: Injection molding allows for the production of parts with tight tolerances and high precision.
Durability: The materials used in injection molding are often resistant to wear and tear, ensuring long-lasting performance.
Cost-Effectiveness: Injection molding is a highly automated process, reducing labor costs and increasing production efficiency.
2. Production Process of Pull Rod Injection Molded Parts
The production process of pull rod injection molded parts involves several key steps:
Material Preparation: Selecting the appropriate plastic resin based on the required properties such as strength, durability, and chemical resistance.
Mold Design and Manufacturing: Creating a mold with the desired shape and dimensions of the pull rod part.
Injection Molding: Injecting molten plastic into the mold cavity under controlled conditions of temperature, pressure, and time.
Cooling and Ejection: Allowing the molded part to cool and solidify before ejecting it from the mold.
Post-Processing: Trimming, assembling, and inspecting the molded parts to ensure they meet specifications.
3. Injection Molding Processing Techniques for Pull Rods
The injection molding processing techniques used for pull rods include:
High-Pressure Injection: Ensuring that the molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity at high pressure to fill all corners and crevices.
Temperature Control: Maintaining precise temperature control during the molding process to prevent material degradation and ensure optimal part quality.
Mold Ventilation: Proper ventilation of the mold to prevent air traps and ensure smooth material flow.
Cycle Time Optimization: Adjusting the cycle time to optimize production efficiency while maintaining part quality.
4. Application Areas of Pull Rod Injection Molded Parts
Pull rod injection molded parts are widely used in various industries, including:
Automotive Industry: For components such as shift levers, brake handles, and other mechanical linkages.
Electronics Industry: For parts like connectors, brackets, and enclosures.
Furniture Industry: For adjustable components like seat sliders and table legs.
Medical Devices: For handles and levers in surgical instruments and patient care equipment.
5. Materials Suitable for Pull Rod Injection Molding
A variety of materials can be used in pull rod injection molding, including:
Polypropylene (PP): Known for its good toughness, chemical resistance, and low cost.
Polyethylene (PE): Offers high flexibility and impact resistance.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): Combines strength, stiffness, and ease of processing.
Nylon (PA): Known for its wear resistance, high tensile strength, and good temperature resistance.
Characteristics of Pull Rod Injection Molded Parts Made from Different Materials (Table)
| Material | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Impact Strength (kJ/m²) | Heat Deflection Temperature (°C) | Density (g/cm³) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP | 20-35 | 15-30 | 80-100 | 0.90-0.91 |
| PE | 10-30 | 20-60 | 60-80 | 0.91-0.96 |
| ABS | 35-55 | 15-25 | 80-100 | 1.03-1.07 |
| Nylon (PA) | 50-100 | 50-150 | 150-220 | 1.12-1.15 |
Notes:
Tensile strength indicates the maximum stress a material can withstand before breaking.
Impact strength measures the material’s ability to resist sudden loads or impacts.
Heat deflection temperature is the temperature at which the material begins to deform under load.
Density reflects the material’s mass per unit volume.
Customized Pull Rod Injection Molded Parts FAQ
Q1: What is the typical lead time for customized pull rod injection molded parts?
A1: The lead time depends on the complexity of the part, material availability, and production volume. Typically, it ranges from 2-4 weeks.
Q2: Can I specify the material for my custom pull rod injection molded parts?
A2: Yes, you can choose from a variety of materials based on your specific requirements such as strength, durability, and cost considerations.
Q3: How do you ensure the quality of the pull rod injection molded parts?
A3: Quality control measures include in-process inspections, final inspections, and material testing to ensure that the parts meet the specified dimensions, tolerances, and material properties.
Q4: Can pull rod injection molded parts be used in harsh environments?
A4: Yes, depending on the material chosen, pull rod injection molded parts can be designed to withstand extreme temperatures, chemicals, and other harsh conditions.
In conclusion, customized pull rod injection molded parts offer a versatile and cost-effective solution for a wide range of applications. By understanding the materials, processes, and quality control measures involved, you can ensure that your custom parts meet your specific needs and perform reliably in their intended environments.