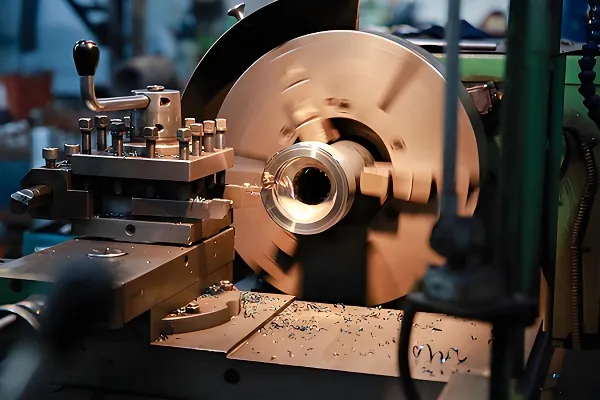
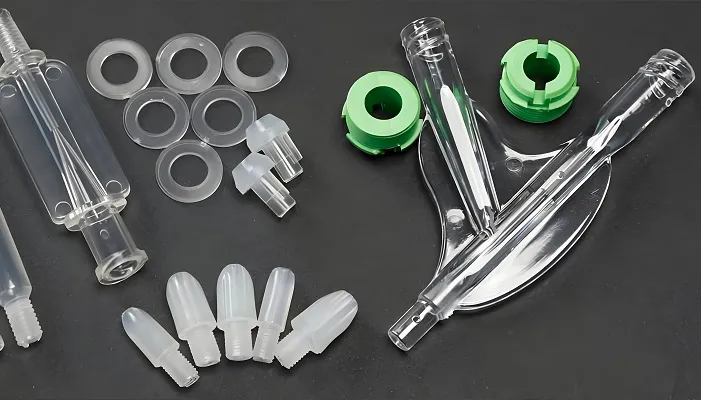
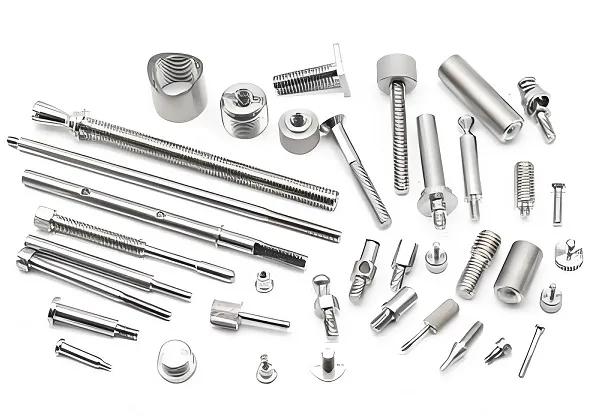
A prototype stamping die is a key tool used in the manufacturing industry to produce parts or assemblies by molding raw materials, such as sheet metal, into a desired shape through the stamping process. Prototype stamping dies are characterized by high precision, high efficiency and high durability, which are the key factors to ensure product quality and production efficiency.
1.Prototype stamping mold production process
Demand analysis: Communicate with customers to clarify the product shape, size, material, quantity and other requirements.
Design drawing: according to the demand, use CAD software to draw the 3D model and 2D drawings of the mold.
Material Purchase: Purchase suitable mold materials according to the mold design requirements.
Processing and manufacturing: Process the mold material into the required shape through milling, grinding, drilling and other processes.
Assembling and debugging: assembling the processed mold parts and debugging to ensure that the mold operates normally.
Quality Inspection: Strict quality inspection of the mold to ensure that the mold meets the design requirements.
Delivery: Deliver the qualified molds to customers and provide necessary operation and maintenance instructions.
2. Prototype stamping mold processing steps
Rough machining: Use large milling machine or machining center to carry out preliminary cutting processing on the mold material to form the general shape of the mold.
Semi-finish machining: on the basis of rough machining, using finer tools and processes, further processing of the mold, so that it is close to the final shape.
Finishing: Using high-precision machine tools and cutting tools, the mold is finely machined to ensure the accuracy and surface quality of the mold.
Heat treatment: Heat treatment is applied to the mold to improve its hardness and wear resistance.
Surface treatment: Polishing, sandblasting and other surface treatments are performed on the molds to improve their appearance quality and corrosion resistance.
3.Customized Prototype Stamping Die Service
Demand customization: Provide personalized die design solutions according to customer’s specific needs.
Rapid response: After receiving customer’s demand, we respond quickly and provide preliminary design solutions.
Full tracking: from design, processing, assembly to debugging, full tracking of the production progress and quality of the mold.
Technical support: Provide technical support for the use and maintenance of the mold to ensure the stable operation of the mold.
After-sales service: Provide maintenance and upgrading service of the molds to meet the long-term needs of customers.
4.Making prototype stamping mold material
Material: high carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, carbide, etc.
Characteristics:
High hardness: good abrasion resistance and deformation resistance.
High strength: able to withstand large stamping pressure and impact.
Good toughness: not easy to break or break in the stamping process.
Corrosion resistance: able to maintain stable performance in humid or corrosive environments.
Easy to process: good machinability, easy to cut, grind and other processing operations.
5. Prototype stamping die processable materials
Material: steel plate, aluminum plate, copper plate, stainless steel plate, etc.
Characteristics:
Good ductility: easy to form the desired shape through the stamping process.
High strength: the parts made have high strength and stiffness.
Corrosion resistance: able to maintain stable performance in wet or corrosive environments.
Easy to weld: easy to weld connections with other parts.
Aesthetics: after stamping and surface treatment of the parts have a good appearance quality.
6. Prototype stamping mold processing technology
CNC machining: Use CNC machine tools to carry out accurate cutting processing to ensure the accuracy and shape of the mold.
EDM: For complex shapes or difficult-to-machine mold parts, use EDM technology for processing.
Wire Cutting Processing: For mold parts that require precise size control, use wire cutting processing technology for processing.
Surface treatment technology: such as polishing, sandblasting, plating, etc., used to improve the surface quality and corrosion resistance of the mold.
7. Prototype stamping mold production equipment
CNC machine tools: for precise cutting processing of molds.
EDM machine tools: for complex shape processing of molds.
Wire-cut machine tools: for precise size control processing of molds.
Heat treatment equipment: such as quenching furnace, tempering furnace, etc., for mold heat treatment.
Surface treatment equipment: such as polishing machine, sand blasting machine, etc., for surface treatment of molds.
Customized Prototype Stamping Mold Service FAQ
Q1: How to determine the material of the mold?
A: The choice of material for the mold should be considered according to the shape, size, quantity of the product and the environment of use. Materials such as high carbon steel and alloy steel are commonly used for products that need to withstand greater impact and pressure; while stainless steel is suitable for products that need corrosion resistance.
Q2: How long is the processing cycle of the mold?
A: The processing cycle of a mold depends on factors such as the complexity and quantity of the product and the capacity of the production equipment. Generally speaking, simple molds have a shorter processing cycle, while complex molds may require a longer processing time.
Q3: What is the life span of the mold?
A: The life span of a mold depends on factors such as its material, processing technology, usage environment and maintenance. High-quality mold materials and fine processing techniques can significantly improve the life of the mold. Meanwhile, regular maintenance and upkeep are also important means to extend the life of the mold.
Q4: How to ensure the precision of the mold?
A: The key to ensure the accuracy of the mold lies in the precise control and inspection during the processing. Using high-precision machine tools and cutting tools for processing, and regular precision testing and calibration can ensure that the precision of the mold meets the design requirements.






