I. Disruptive Technologies Driving Industry Transformation
1. The Cost Revolution of Flexible Forming Technology
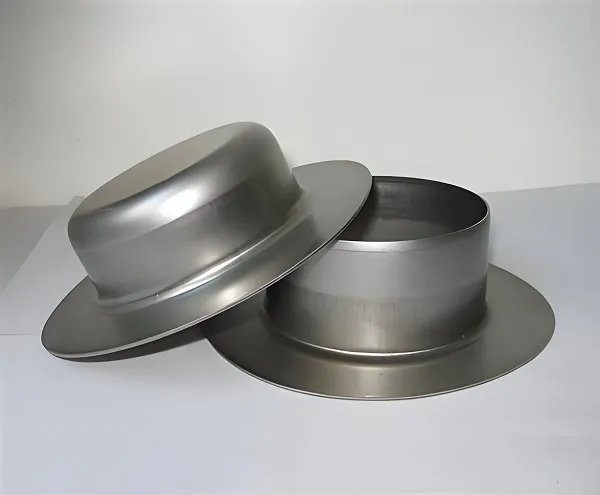
Sweden’s Quintus Flexform™ technology has achieved a breakthrough with a 90% reduction in mold costs and a 50% shortening of development cycles through ultra-high-pressure precision forming and adaptive rubber bladder technology. This technology requires only a single half-mold to form complex parts, such as aerospace special-shaped curved parts and automotive deep-drawn structural components, with one-time forming accuracy reaching ±0.1mm and surface roughness Ra≤1.6μm—far exceeding traditional stamping processes. More than 25 sets of equipment have been deployed in the Chinese market, covering new energy vehicle battery casings (20% weight reduction) and 5G base station heat dissipation components, with some models producing up to 120 parts per hour. Combined with an automatic pallet system, it enables flexible manufacturing for both small-batch rapid iteration and long-cycle high-efficiency production.
Sweden’s Quintus Flexform™ technology has achieved a breakthrough with a 90% reduction in mold costs and a 50% shortening of development cycles through ultra-high-pressure precision forming and adaptive rubber bladder technology. This technology requires only a single half-mold to form complex parts, such as aerospace special-shaped curved parts and automotive deep-drawn structural components, with one-time forming accuracy reaching ±0.1mm and surface roughness Ra≤1.6μm—far exceeding traditional stamping processes. More than 25 sets of equipment have been deployed in the Chinese market, covering new energy vehicle battery casings (20% weight reduction) and 5G base station heat dissipation components, with some models producing up to 120 parts per hour. Combined with an automatic pallet system, it enables flexible manufacturing for both small-batch rapid iteration and long-cycle high-efficiency production.

2. Full-process Penetration of Intelligent Manufacturing
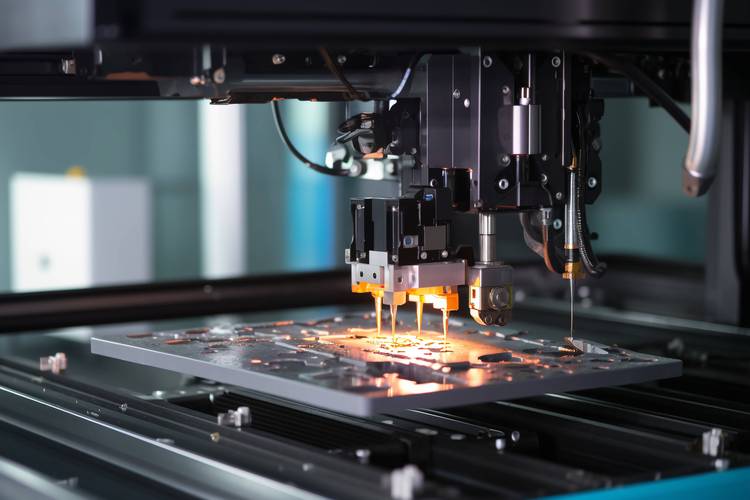
TRUMPF’s new smart factory in North America integrates laser cutting machines, CNC bending machines, and an IIoT platform to achieve real-time equipment status monitoring and adaptive process parameter adjustment, reducing equipment failure rates by over 30%. Its TruLaser 5030 Fiber laser cutting machine increases cutting speed by 40% compared to traditional equipment. Equipped with an AI visual inspection system, it can detect defects as small as 0.05mm, significantly improving the yield rate of automotive structural parts. Chinese enterprises like Suzhou Dongshan Precision have achieved full-process digitalization from order management to equipment maintenance through their self-developed “Sheet Metal Cloud Platform,” increasing production efficiency by 25% and material utilization to 85%.
TRUMPF’s new smart factory in North America integrates laser cutting machines, CNC bending machines, and an IIoT platform to achieve real-time equipment status monitoring and adaptive process parameter adjustment, reducing equipment failure rates by over 30%. Its TruLaser 5030 Fiber laser cutting machine increases cutting speed by 40% compared to traditional equipment. Equipped with an AI visual inspection system, it can detect defects as small as 0.05mm, significantly improving the yield rate of automotive structural parts. Chinese enterprises like Suzhou Dongshan Precision have achieved full-process digitalization from order management to equipment maintenance through their self-developed “Sheet Metal Cloud Platform,” increasing production efficiency by 25% and material utilization to 85%.
II. Global Layout and Regional Market Differentiation
1. Capacity Expansion in Southeast Asia and Supply Chain Reorganization
Enterprises like Chuntian Machinery have established production bases in Thailand and Malaysia, leveraging local labor cost advantages (30-40% lower than China) to build a global manufacturing network focused on electronics and automotive industries. For example, its Thai factory produces aluminum alloy battery casings for the Tesla Model Y, shortening delivery cycles to 7 days—40% faster than traditional models. Meanwhile, demand for mid-tech products in Southeast Asia has surged, with Vietnam’s sheet metal processing equipment imports increasing by 28% year-on-year in 2024, mainly for infrastructure and consumer electronics manufacturing.
Enterprises like Chuntian Machinery have established production bases in Thailand and Malaysia, leveraging local labor cost advantages (30-40% lower than China) to build a global manufacturing network focused on electronics and automotive industries. For example, its Thai factory produces aluminum alloy battery casings for the Tesla Model Y, shortening delivery cycles to 7 days—40% faster than traditional models. Meanwhile, demand for mid-tech products in Southeast Asia has surged, with Vietnam’s sheet metal processing equipment imports increasing by 28% year-on-year in 2024, mainly for infrastructure and consumer electronics manufacturing.
2. North American Manufacturing Reshoring and High-End Competition
TRUMPF’s $40 million smart factory in Connecticut focuses on high-end sectors like automotive, aerospace, and data center cabinets, adopting a “local service for local markets” strategy to address supply chain regionalization. Its TruLaser 8000 series laser cutting machines can process titanium alloy sheets up to 25mm thick, meeting the high-strength material processing needs of the aerospace industry, with product premium rates exceeding 30%. Meanwhile, North American markets have increasingly strict green manufacturing requirements: TRUMPF’s factory solar power system reduces unit energy consumption by 20%, fully complying with the EU RoHS Directive.
TRUMPF’s $40 million smart factory in Connecticut focuses on high-end sectors like automotive, aerospace, and data center cabinets, adopting a “local service for local markets” strategy to address supply chain regionalization. Its TruLaser 8000 series laser cutting machines can process titanium alloy sheets up to 25mm thick, meeting the high-strength material processing needs of the aerospace industry, with product premium rates exceeding 30%. Meanwhile, North American markets have increasingly strict green manufacturing requirements: TRUMPF’s factory solar power system reduces unit energy consumption by 20%, fully complying with the EU RoHS Directive.
III. Technological Breakthroughs and Patent Innovation in the Chinese Market
1. Patent Layout and Technological Export
China has filed 3,973 sheet metal processing patents from 2015-2024, with 708 applications in 2023 alone. Shaanxi Shimaoli Electromechanical’s “Patent No. 47584: A Sheet Metal Bending and Molding Die” achieves ±0.5° bending accuracy at any angle through arc groove design and servo motor control, already applied in high-speed rail car structural component production. Hengshui Jiayusaiou’s “auxiliary positioning device” patent solves bending deviation caused by uneven sheet metal density, improving accuracy to ±0.1mm and being included in the supply chain of BYD and other automakers.
China has filed 3,973 sheet metal processing patents from 2015-2024, with 708 applications in 2023 alone. Shaanxi Shimaoli Electromechanical’s “Patent No. 47584: A Sheet Metal Bending and Molding Die” achieves ±0.5° bending accuracy at any angle through arc groove design and servo motor control, already applied in high-speed rail car structural component production. Hengshui Jiayusaiou’s “auxiliary positioning device” patent solves bending deviation caused by uneven sheet metal density, improving accuracy to ±0.1mm and being included in the supply chain of BYD and other automakers.
2. Globalization Practices of Local Enterprises
Swiss Bystronic’s Tianjin factory has achieved full localization of laser cutting machine manufacturing through local R&D, reducing costs by 25% compared to imported equipment, and reverse-integrated Chinese suppliers into its global supply chain. For example, its high-strength aluminum alloy sheets developed with Hebei Iron & Steel, with a tensile strength of 600MPa, have been successfully used in Airbus A350 fuselage components. Chinese enterprises’ competitiveness in international markets has significantly improved, with sheet metal processing equipment export volumes increasing by 18% year-on-year in 2024, including a 35% market share for CNC bending machines in Southeast Asia.
Swiss Bystronic’s Tianjin factory has achieved full localization of laser cutting machine manufacturing through local R&D, reducing costs by 25% compared to imported equipment, and reverse-integrated Chinese suppliers into its global supply chain. For example, its high-strength aluminum alloy sheets developed with Hebei Iron & Steel, with a tensile strength of 600MPa, have been successfully used in Airbus A350 fuselage components. Chinese enterprises’ competitiveness in international markets has significantly improved, with sheet metal processing equipment export volumes increasing by 18% year-on-year in 2024, including a 35% market share for CNC bending machines in Southeast Asia.
IV. Industry Trends and Sustainable Development Paths
1. Deep Integration of Intelligence and AI
AI algorithms and IoT technologies are reshaping production processes: Quintus plans to integrate Flexform™ technology with AI adaptive pressure adjustment for remote maintenance and process optimization, expected to reduce equipment downtime by 30%. TRUMPF’s smart factory predicts mold life with 90% accuracy through real-time data monitoring, reducing maintenance costs by 20%. Chinese enterprises like Wuxi Jufeng CNC have developed an “intelligent bending system” that uses machine learning to optimize bending paths, reducing programming time for complex parts from 4 hours to 30 minutes.
AI algorithms and IoT technologies are reshaping production processes: Quintus plans to integrate Flexform™ technology with AI adaptive pressure adjustment for remote maintenance and process optimization, expected to reduce equipment downtime by 30%. TRUMPF’s smart factory predicts mold life with 90% accuracy through real-time data monitoring, reducing maintenance costs by 20%. Chinese enterprises like Wuxi Jufeng CNC have developed an “intelligent bending system” that uses machine learning to optimize bending paths, reducing programming time for complex parts from 4 hours to 30 minutes.
2. Lightweighting and Material Innovation
Applications of high-strength aluminum alloys, titanium alloys, and composite materials continue to expand: new energy vehicle battery casings use integrated forming technology to achieve 20% weight reduction while maintaining strength, with material utilization increasing from 65% to 85%. The integration of 3D printing and sheet metal processing (e.g., hybrid manufacturing) shows potential in complex structural components—for example, GE Aviation’s engine brackets produced by this technology are 40% lighter with a 3x longer fatigue life.
Applications of high-strength aluminum alloys, titanium alloys, and composite materials continue to expand: new energy vehicle battery casings use integrated forming technology to achieve 20% weight reduction while maintaining strength, with material utilization increasing from 65% to 85%. The integration of 3D printing and sheet metal processing (e.g., hybrid manufacturing) shows potential in complex structural components—for example, GE Aviation’s engine brackets produced by this technology are 40% lighter with a 3x longer fatigue life.
3. Green Manufacturing and Circular Economy
Sheet metal processing enterprises widely adopt recycled metals, energy-efficient equipment, and closed-loop production systems: TRUMPF’s factory solar power system meets 30% of energy demand, with unit energy consumption 20% lower than the industry average. Quintus’ Flexform™ technology indirectly reduces steel waste by minimizing mold consumption, cutting carbon emissions by 12 tons per 100,000 parts produced. The “Green Manufacturing Zone” at the China International Metal Forming Exhibition showcases energy-efficient laser cutting machines (30% lower energy consumption) and recyclable material applications, driving the industry’s low-carbon transition.
Sheet metal processing enterprises widely adopt recycled metals, energy-efficient equipment, and closed-loop production systems: TRUMPF’s factory solar power system meets 30% of energy demand, with unit energy consumption 20% lower than the industry average. Quintus’ Flexform™ technology indirectly reduces steel waste by minimizing mold consumption, cutting carbon emissions by 12 tons per 100,000 parts produced. The “Green Manufacturing Zone” at the China International Metal Forming Exhibition showcases energy-efficient laser cutting machines (30% lower energy consumption) and recyclable material applications, driving the industry’s low-carbon transition.
V. Challenges and Future Outlook
1. Technical Barriers and Talent Shortages
Core technologies for high-end equipment remain monopolized by European and American companies, such as TRUMPF’s laser cutting machine optical systems and Quintus’ ultra-high-pressure sealing technology. Chinese enterprises need to strengthen basic research and industry-university-research cooperation. Meanwhile, intelligent production has surged demand for composite talent, with a 30% gap in engineers skilled in “machinery + software + data analysis.”
Core technologies for high-end equipment remain monopolized by European and American companies, such as TRUMPF’s laser cutting machine optical systems and Quintus’ ultra-high-pressure sealing technology. Chinese enterprises need to strengthen basic research and industry-university-research cooperation. Meanwhile, intelligent production has surged demand for composite talent, with a 30% gap in engineers skilled in “machinery + software + data analysis.”
2. International Trade and Policy Risks
Technical standards in European and American markets (e.g., EU CE certification) and green barriers (e.g., carbon tariffs) increase export costs, while rising local capacity in emerging Southeast Asian markets intensifies competition. Chinese enterprises must respond through localized production (e.g., setting up factories in Mexico to serve North America) and technical compliance (e.g., obtaining UL certification).
Technical standards in European and American markets (e.g., EU CE certification) and green barriers (e.g., carbon tariffs) increase export costs, while rising local capacity in emerging Southeast Asian markets intensifies competition. Chinese enterprises must respond through localized production (e.g., setting up factories in Mexico to serve North America) and technical compliance (e.g., obtaining UL certification).
3. Future Competition Focus
Competition will center on three dimensions: ① technical integration capabilities, such as “laser cutting + bending + welding” integrated solutions; ② service model innovation, such as shifting from equipment sales to “processing services + data subscriptions”; ③ sustainable development practices, such as carbon footprint management and circular economy models. The global sheet metal processing market is expected to exceed $500 billion by 2030, with intelligence, lightweighting, and greening becoming key markers of corporate competitiveness.
Competition will center on three dimensions: ① technical integration capabilities, such as “laser cutting + bending + welding” integrated solutions; ② service model innovation, such as shifting from equipment sales to “processing services + data subscriptions”; ③ sustainable development practices, such as carbon footprint management and circular economy models. The global sheet metal processing market is expected to exceed $500 billion by 2030, with intelligence, lightweighting, and greening becoming key markers of corporate competitiveness.
Conclusion
The sheet metal processing industry in 2025 is undergoing profound transformation from technological breakthroughs to global layout. Flexible forming technologies are restructuring cost structures, smart factories are redefining manufacturing paradigms, Chinese enterprises are rising through patent innovation and supply chain integration, and sustainable development has become a global competitive prerequisite. In the future, winners will be those who deeply integrate technological innovation, regional strategies, and green practices—a challenge and a historic opportunity to reshape industry landscape.