Answer
Extended Response
I. Working Principle and Scope of CNC Routers
(1) Core Principle
(2) Application Scenarios
II. Classified Materials and Characteristics
(1) Metals
(2) Wood and Composites
(3) Plastics and Rubber
(4) Stone and Glass

| Material | Cutting Difficulty | Suitable Tools | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Low | Carbide end mill | Electronic casings, heat sinks |
| Brass | Medium | Diamond-coated tool | Decorations, hardware |
| Low-carbon steel | High | CBN tool | Mold inserts, small structures |
| Material | Cutting Features | Tool Selection | Surface Quality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid wood | Possible grain cracking | Spiral-edge mill | Grain-aligned cut Ra≤6.3μm |
| Plywood | Interlayer delamination | Double-edge mill | Sanding required |
| Carbon fiber | Hazardous dust, fiber breakage | Diamond saw blade | Edge deburring needed |
| Material | Thermal Deformation Risk | Tool Requirements | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABS | Medium | Sharp single-edge mill | Models, toys |
| Acrylic | High | Diamond-coated tool | Transparent panels, crafts |
| Silicone | Extremely high | Cryogenic cutting (LN₂) | Seals, medical molds |
| Material | Mohs Hardness | Tool Selection | Cutting Thickness Limit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marble | 3–4 | Diamond saw blade | ≤30mm |
| Granite | 6–7 | Resin-bonded grinding wheel | ≤20mm |
| Glass | 6.5–7 | Laser-assisted cutting | ≤10mm |
| Material | Spindle Speed (rpm) | Feed Rate (mm/min) | Cut Depth (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | 18,000–24,000 | 1,000–3,000 | 1–3 |
| Wood | 12,000–18,000 | 3,000–8,000 | 5–10 |
| Acrylic | 15,000–20,000 | 500–1,500 | 0.5–2 |
| Carbon fiber | 10,000–15,000 | 300–800 | 0.3–1 |
| Material Type | Recommended Spindle Power (kW) | Suitable Tool Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Soft materials (wood, foam) | 2.2–3.7 | 3.175–12.7 |
| Metals (aluminum, copper) | 4.5–7.5 | 6–16 |
| Hard materials (stone, glass) | 7.5–11 | 6–20 |

In the dynamic manufacturing landscapes of the United States and Europe, the demand for efficient, high – quality CNC machining services is soaring. Xiamen Goldcattle emerges as a leading provider,…

CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling technology, as one of the key technologies in modern manufacturing, plays an irreplaceable role in prototyping, mold development, parts production and other fields with its…
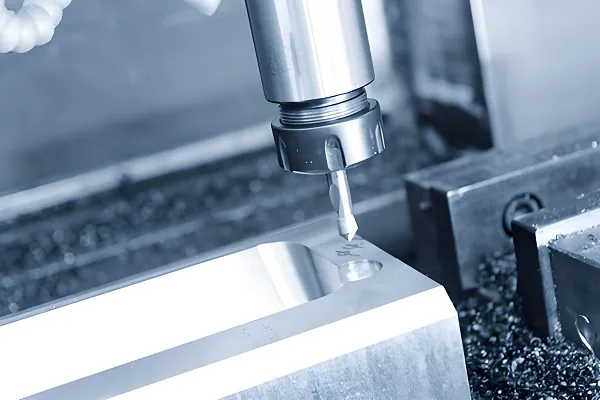

Precision milling and drilling is a machining method controlled by a high-precision computerized control system, which combines the two processes of milling and drilling, allowing for a variety of machining tasks to…

Customized railing hardware refers to the process of tailoring the hardware required for railings according to customer needs and specific application scenarios. This includes design, material selection, manufacturing and surface…
Introduction: Unlocking Core Technology for Unconventional Part Manufacturing When you encounter a shaft part with misaligned axes on your design drawing, do you feel challenged? This type of “eccentric” part…

In the vast field of customized machining, CNC machined parts undoubtedly occupy an extremely critical position. With the continuous development of the modern manufacturing industry, customers for mechanical parts of the growing…