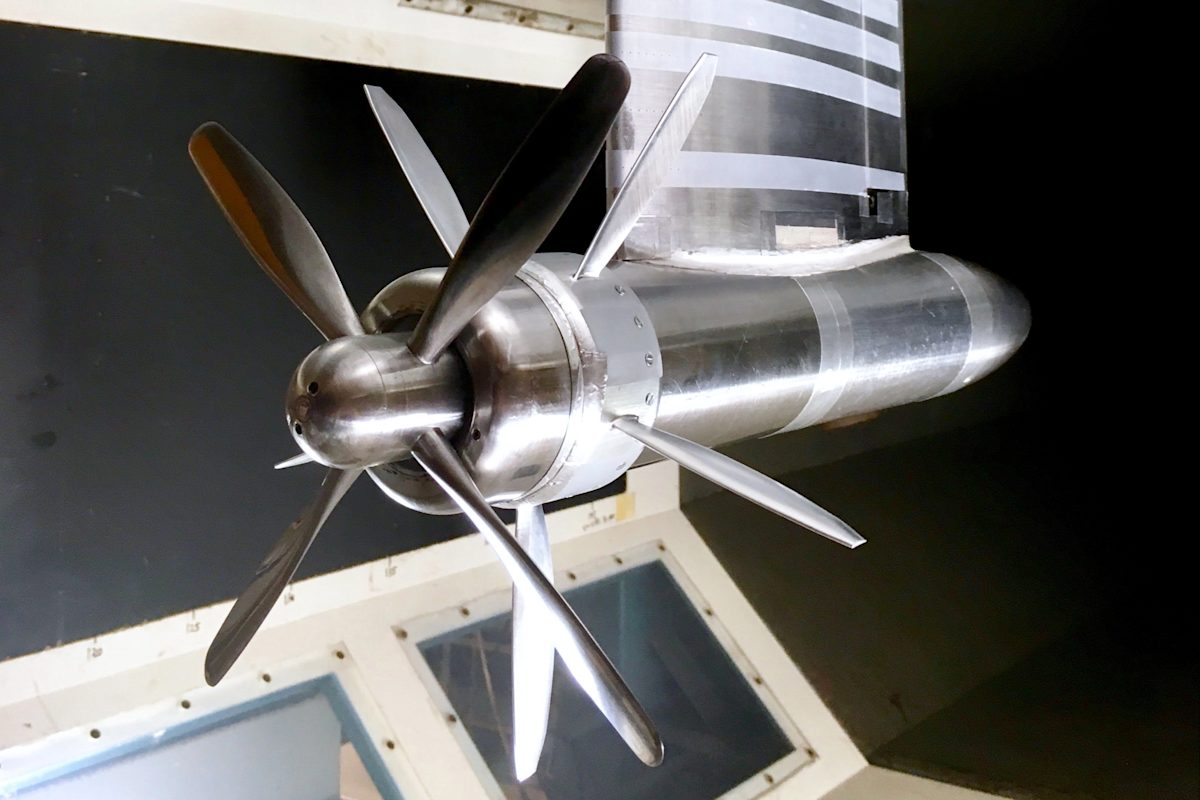
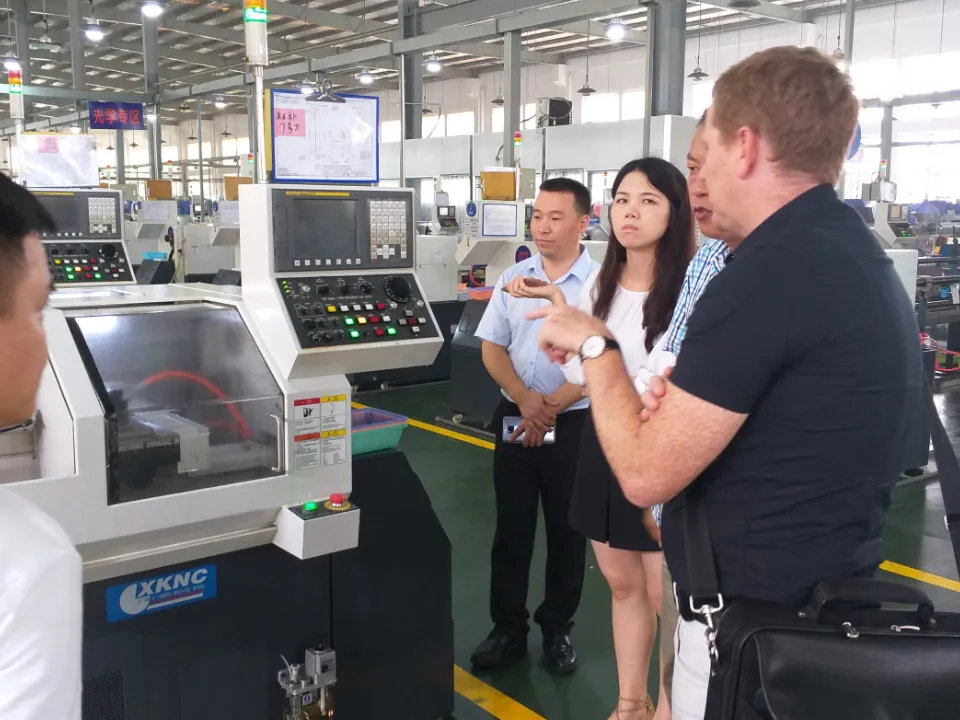
What is CNC Manufacturing? – A Complete 2026 Guide by Xiamen Goldcattle (26 Years of Precision Expertise)
In 2025, a European medical device client came to Xiamen Goldcattle with endoscope parts requiring ±0.002mm tolerance. Previous suppliers struggled with rework, but we achieved 100% first-part inspection pass rate using 5-axis machining and temperature-controlled workshops—this is the true power of CNC manufacturing.
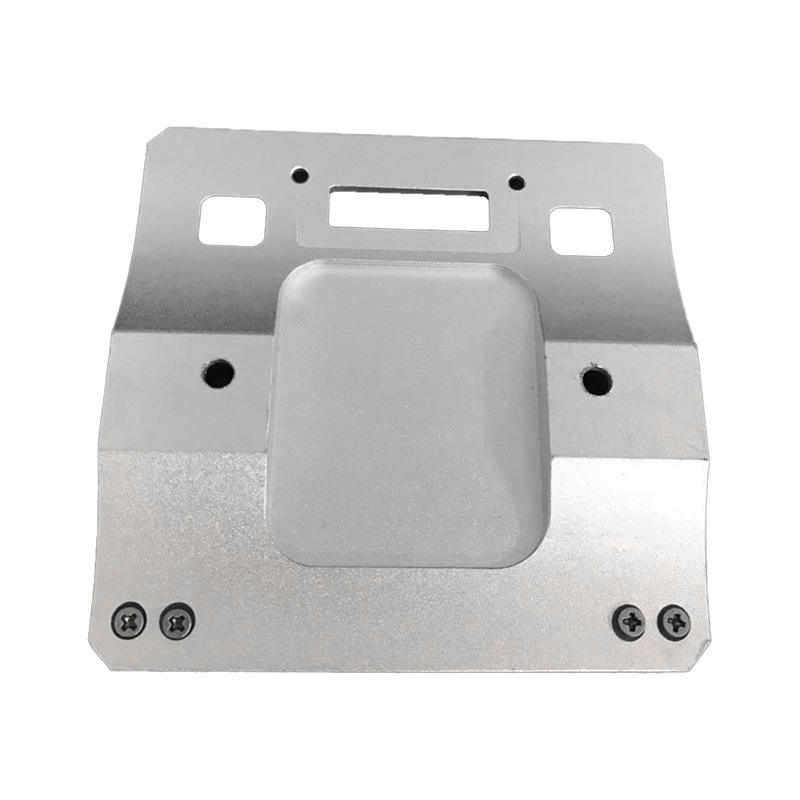

5-axis CNC machining of aluminum EV bracket with ±0.005mm tolerance
Wondering which CNC process suits your part?
Upload your drawing for free DFM feedback → Contact us now
Q1: What exactly is CNC Manufacturing?
At its core, CNC Manufacturing (Computer Numerical Control Manufacturing) is a process where computer programs control machine tools to shape raw materials (metal, plastic, composites) into precise, functional parts. Unlike manual machining—where a craftsman guides tools by hand—CNC uses preprogrammed code (G-codes, M-codes) to automate cuts, drills, and mills with consistent accuracy.
It’s not just “machining with a computer”; it’s a system that turns digital designs into physical parts at scale. For example, a CNC mill can take a 3D model of an aluminum EV bracket and produce 1,000 identical units in a day—each with a tolerance of ±0.005mm (1/20 the width of a human hair).
Goldcattle Success Story
“At Xiamen Goldcattle, we produced over 10,000 motor shaft brackets for a new energy vehicle client, maintaining consistent ±0.005mm tolerance on every piece. This precision ensures smooth motor operation and long service life.”
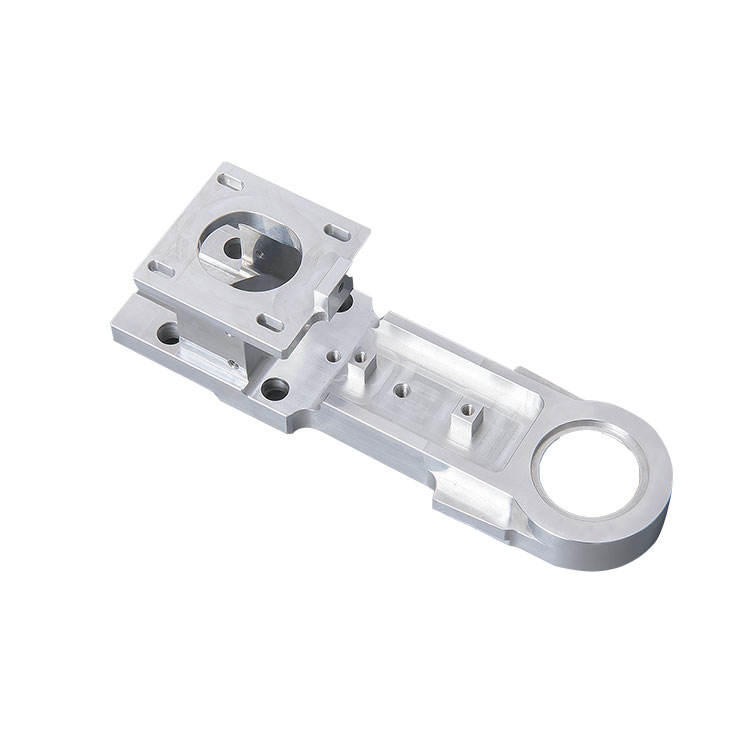

CNC machined aluminum component with complex geometries
Industry context: CNC Manufacturing accounts for 75% of global precision part production (Source: 2025 Global Manufacturing Report), powering everything from cars to medical devices.
“I used to manually machine 50 steel shafts a day—by the end, my hands were tired, and 5-10% were off-spec. With CNC, I run 500 shafts a day, and only 1 or 2 need rework. It’s not about replacing skill—it’s about letting skill focus on design, not repetition.”
— Xiamen Goldcattle Senior Machinist
Q2: How does CNC Manufacturing actually work?
The process has 5 core steps—each building on the last to turn a digital idea into a physical part:
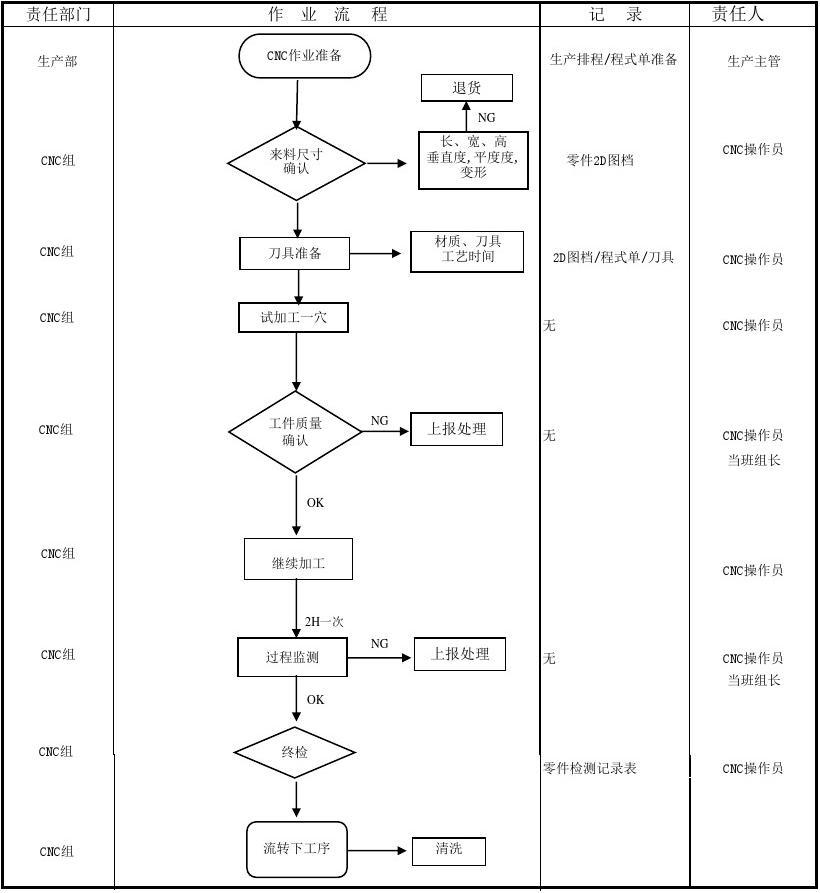
5-step CNC manufacturing process from design to delivery
Design (CAD)
Create 3D model using CAD software. Defines dimensions, holes, curves, and tolerances.
Example: Titanium implant with 2mm stem
Programming (CAM)
Convert CAD to machine code with CAM software. Generates G-codes and M-codes.
Machine Setup
Prepare machine with tooling, material, and fixture. Calibrate zero point.
Production
Machine executes code automatically. Tools move along preprogrammed paths.
Quality Control
Inspect parts with calipers, micrometers, or CMMs. Critical parts use X-ray testing.
Goldcattle Lesson Learned
“We once skipped simulation and crashed a tool into a fixture, losing half a day of production. Now we run complete simulations before every program goes live—this strict verification process ensures every machining operation is flawless.”
Pro Tip:
The best CNC shops “fail fast”—we run 1-2 test parts first. If a test part is off, we tweak the program before running the full batch.
Q3: What makes CNC Manufacturing better than manual machining?
The advantages are transformative—especially for precision, efficiency, and consistency. Here’s how they stack up:
| Factor | CNC Manufacturing | Manual Machining |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | ±0.001–0.005mm (micron-level) | ±0.1–0.3mm (craftsman skill) |
| Efficiency | 3–5x faster (500 parts/day vs. 100) | Slow—fatigue reduces speed |
| Consistency | 99.9% part uniformity | 85–90% uniformity |
| Complexity | 5-axis shapes (turbine blades) | 2–3-axis simple parts |
| Downtime | 24/7 operation | Stops for tool changes |
Real-World Impact
A client once needed 1,000 plastic sensor housings. Manual machining would have taken 5 days; CNC did it in 1 day—with zero defects.
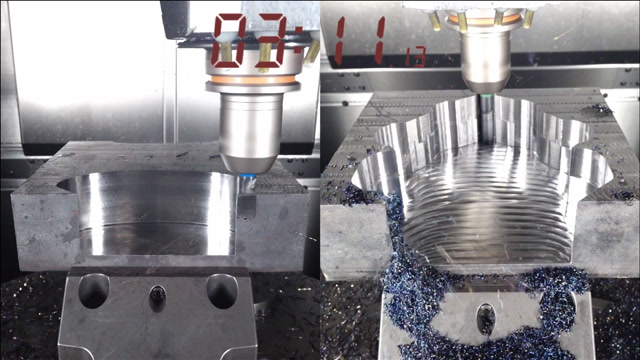
CNC vs manual machining surface finish comparison (Ra 0.8μm vs Ra 3.2μm)
“Manual machining is an art, but CNC is a tool that elevates the art. I still use my knowledge of materials to tweak CNC parameters—like slowing feed rates for titanium—but the machine handles the repetitive, error-prone work.”
— Xiamen Goldcattle Machinist
Q4: What materials can be used in CNC Manufacturing?
Nearly any rigid material that holds shape during cutting works—CNC’s flexibility is one of its biggest strengths.

Aluminum (6061/7075)
Lightweight, easy to cut, affordable
EV battery trays, smartphone frames
Use high speeds (3000–5000r/min)
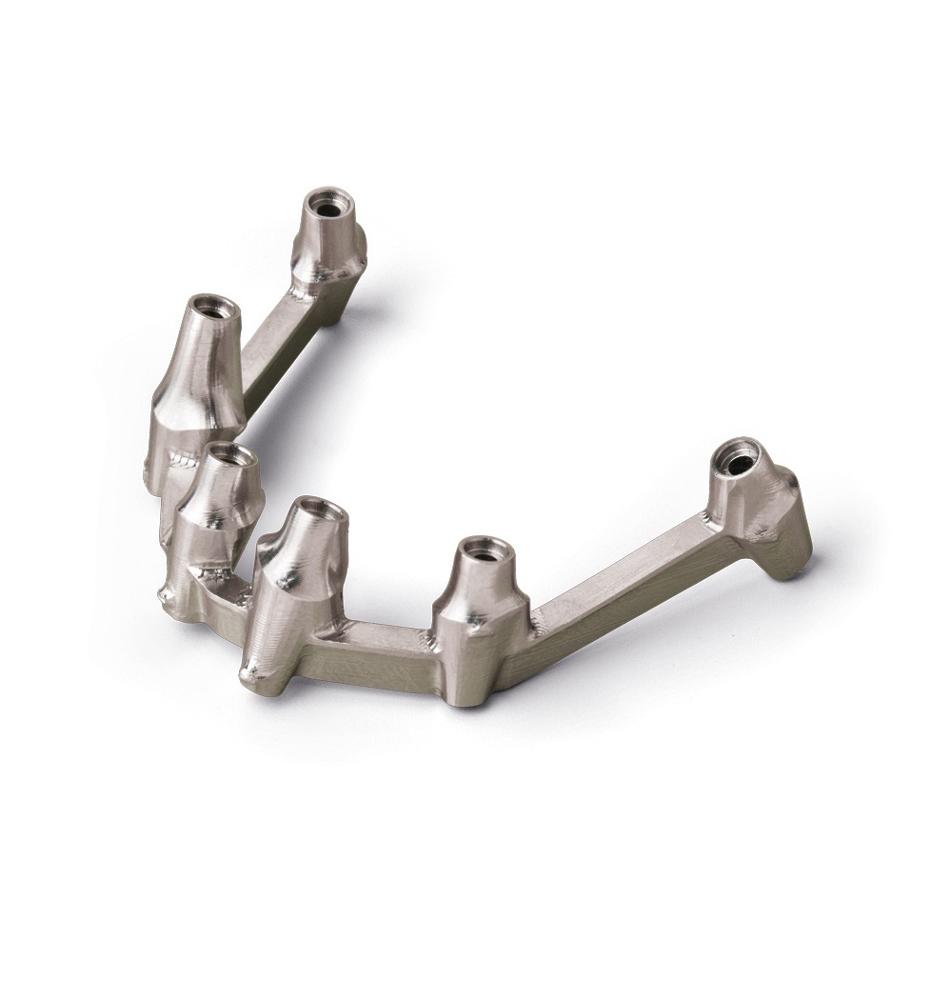

Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V)
Biocompatible, high strength-to-weight
Medical implants, aerospace parts
Slow speeds + high coolant pressure
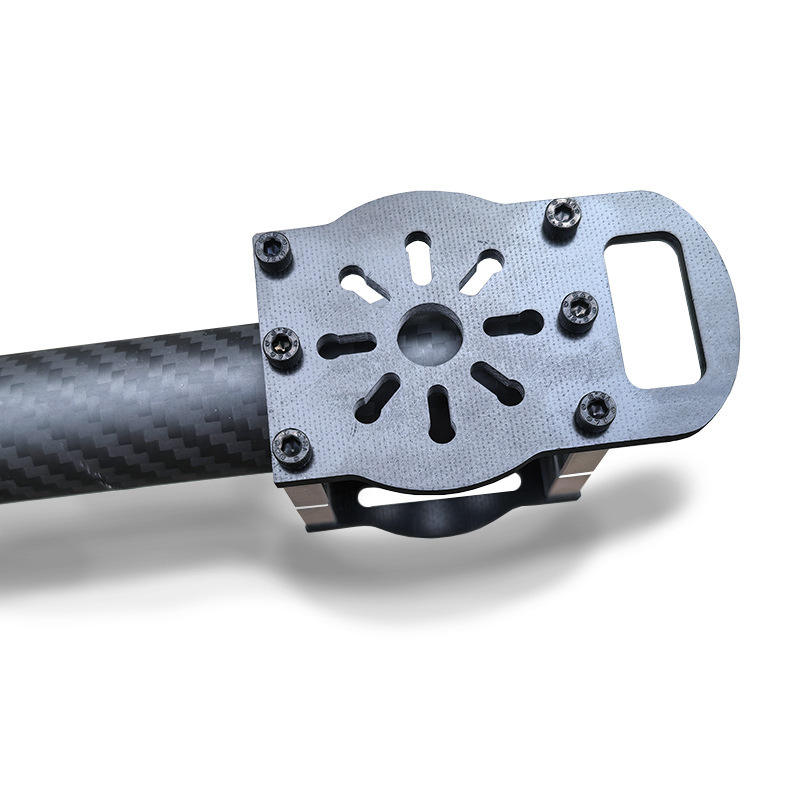

Carbon Fiber
Lightweight, ultra-strong
Aerospace panels, drone frames
Use diamond-coated tools

Plastics (PEEK/ABS)
Low cost, chemical-resistant
Medical housings, electronics cases
Use compressed air, not liquid coolant
Goldcattle Lesson Learned
“I once tried machining carbon fiber with a standard carbide tool—the fibers frayed and the part was ruined. Switching to diamond-coated tools solved the problem. Always match the tool to the material!”
Q5: Is CNC Manufacturing only for large factories?
No—this is one of the biggest myths! CNC works for businesses of all sizes:
Small Shops/Hobbyists
Tabletop CNC mills ($5,000–$15,000) fit in garages. A one-person shop makes custom bike parts with a compact CNC router.
Mid-Size Factories
3–5 CNC machines handle batches of 100–10,000 parts (custom automotive brackets).
Large Plants
50+ CNC machines (cloud-connected) run 24/7 for mass production (100,000 EV door hinges/month).
Cost Myth Buster
For small batches (10–50 parts), CNC is often cheaper than manual machining. Why? You write the program once, then run parts quickly—no need to pay a craftsman for hours of handwork.
Example
A startup needed 20 custom stainless steel brackets. Manual machining would have cost $20/part; CNC cost $8/part—even with program setup time.
Q6: Which industries rely most on CNC Manufacturing?
CNC is the backbone of industries where precision and consistency are non-negotiable. Here are the top 4:
Fun Fact: A single commercial airplane uses 10,000+ CNC-machined parts—from the smallest fastener to the largest wing bracket.
Q7: Will CNC Manufacturing replace human workers?
No—CNC changes what workers do, not if they work. Here’s how roles evolve:
Before CNC
80% manual tool guidance
20% problem-solving
With CNC
20% loading/unloading
80% higher-value tasks
Example
Our shop had 5 manual machinists 10 years ago. Now we have 3 CNC operators who also program machines—and we produce 10x more parts. No one was laid off; we retrained the team.
“CNC needs human judgment. Last month, a machine’s sensor failed—if I hadn’t noticed the tool was dull, it would have ruined 50 parts. Machines follow code, but humans fix problems code can’t predict.”
— Xiamen Goldcattle CNC Operator
Q8: What’s the future of CNC Manufacturing?
The next 5 years will bring 4 big shifts—all making CNC faster, smarter, and more sustainable:
Industry 4.0 Integration
CNC machines connected to the cloud for remote monitoring. Check shop status from your phone—get alerts instantly if a machine breaks.
AI-Powered Optimization
AI auto-adjusts cutting parameters based on real-time data. Detects tool wear and slows machine before failure.
5-Axis + Advanced Tools
More shops adopt 5-axis CNC (30% of market) for complex parts. Testing “hybrid” machines combining CNC with 3D printing.
Sustainability
Recycle more scrap (95% aluminum chips) and use eco-friendly coolants. Solar-powered machines reduce carbon footprints.
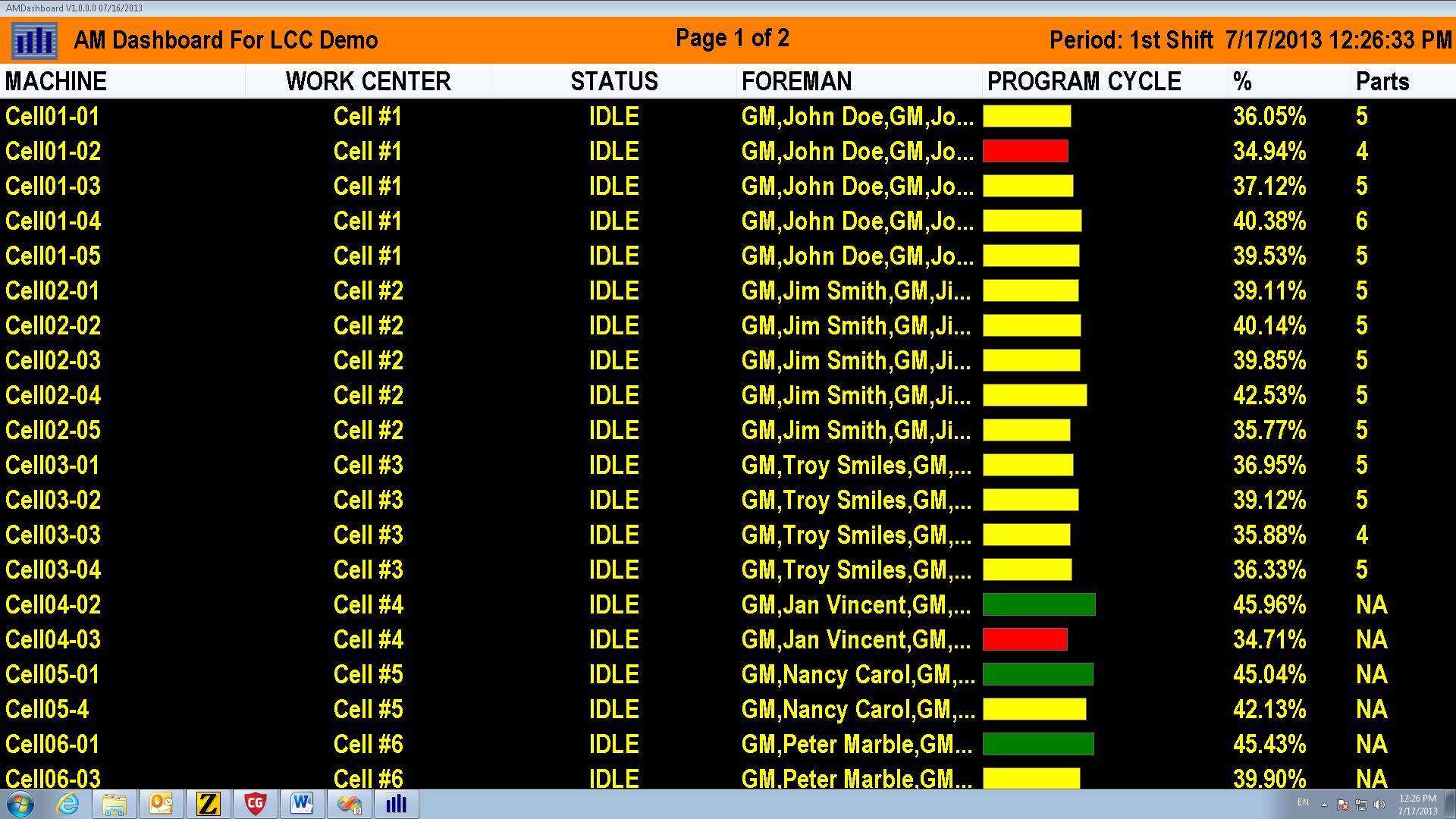
Industry 4.0 CNC machine monitoring dashboard for remote management
Goldcattle Future Plans
“We have already started testing AI parameter optimization and cloud monitoring systems, with full implementation expected by the end of 2026. This will help us further improve production efficiency and product quality, providing better service to our customers.”
Prediction: By 2030, 50% of CNC shops will use AI to optimize production—cutting energy use by 20% and tool waste by 30%.
Common CNC Manufacturing Myths & Realities
Have you encountered these common misconceptions about CNC manufacturing? Let’s set the record straight:
Myth: CNC is too expensive for small businesses
Reality: Tabletop CNC machines start at $5,000, and for small batches, CNC is often cheaper than manual machining due to faster production times.
Myth: CNC can only make simple parts
Reality: 5-axis CNC machines create incredibly complex shapes like turbine blades and medical implants with micron-level precision.
Myth: CNC will replace all machinists
Reality: CNC changes roles, not eliminates them. Machinists focus on programming, troubleshooting, and quality control—higher-value tasks.
Myth: CNC is only for mass production
Reality: CNC excels at both prototype (1 part) and mass production (100,000 parts) with the same precision and consistency.
FAQs About CNC Manufacturing
Ready to turn your design into precision parts?
Contact Xiamen Goldcattle today for a no-obligation quote and expert DFM review. With 26 years of precision expertise, we’re ready to help you bring your ideas to life with the highest quality CNC manufacturing.
Get Your Free Precision Manufacturing Quote
- • Free DFM feedback on your design
- • Detailed cost breakdown
- • Lead time estimate
- • Material recommendations
- • Quality assurance plan
- • 24-hour response guarantee
For 26 years, Xiamen Goldcattle has specialized in high-precision CNC manufacturing, from ordinary aluminum parts to aerospace titanium alloys. We treat every machining operation as a commitment to quality. Whether you need 1 prototype or 100,000 production parts, we deliver consistent precision and quality.







