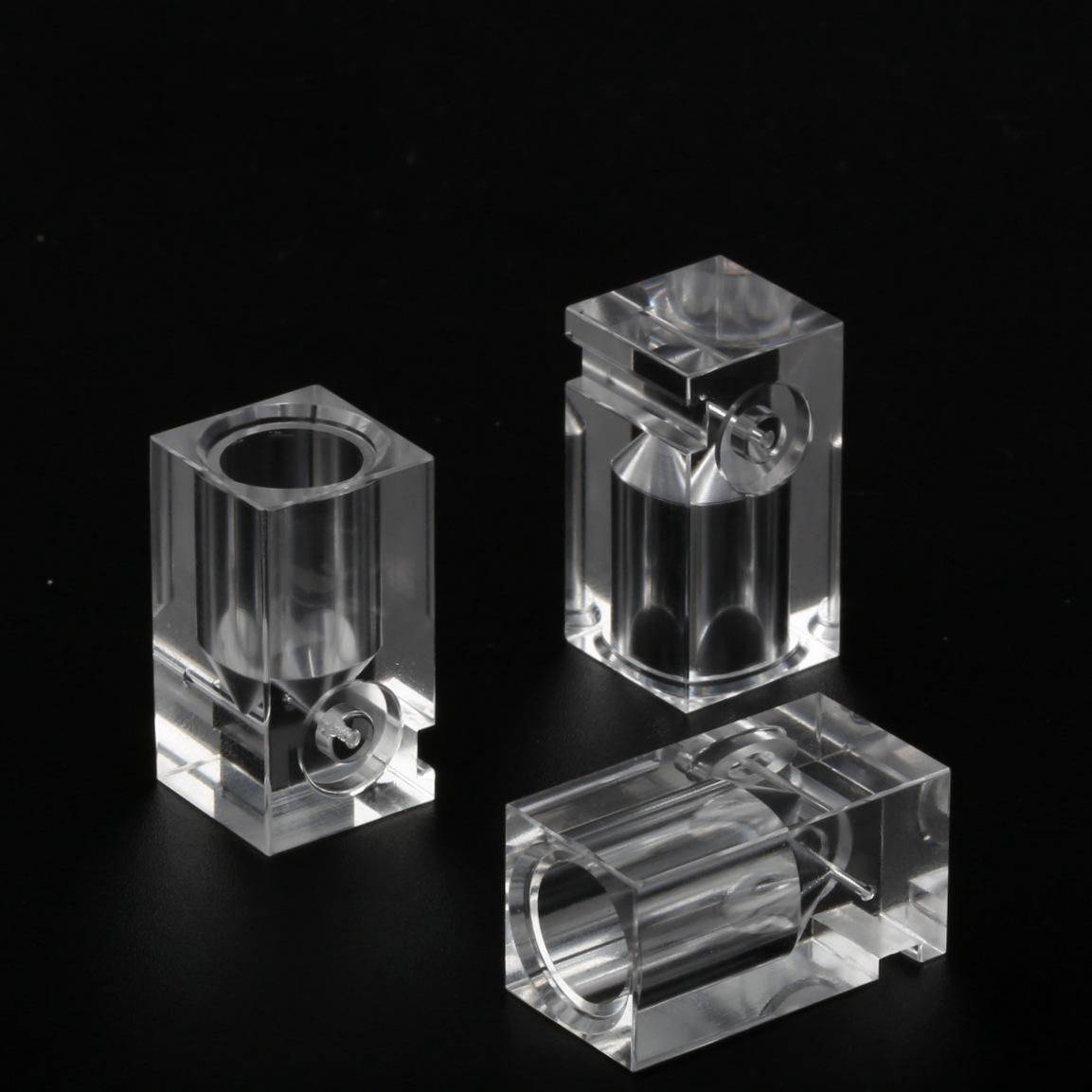
Acrylic CNC service refers to a specialized manufacturing process that uses Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines to cut, shape, engrave, or mill acrylic (also known as PMMA, or polymethyl methacrylate) into custom parts or products. Acrylic, a transparent thermoplastic with high impact resistance and optical clarity, is uniquely suited for CNC machining due to its machinability—its ability to be precisely cut without chipping or cracking when handled with proper tooling. This service transforms digital designs (from CAD software) into physical acrylic components, offering tight tolerances (often ±0.1mm) and intricate details that manual cutting cannot achieve. Acrylic CNC service is widely used for creating everything from display cases to industrial parts, valued for its efficiency, repeatability, and ability to produce both functional and decorative acrylic items.
Detailed Analysis of Acrylic CNC Service
1. Core Technologies
Acrylic CNC service relies on specialized adaptations of standard CNC technology to accommodate acrylic’s properties:
- High-Speed Spindles: CNC machines for acrylic use spindles operating at 10,000–30,000 RPM, paired with sharp, single-flute or double-flute carbide tools. These tools minimize heat buildup—critical for acrylic, which can melt or warp if overheated.
- Coolant Systems: While some acrylic machining uses air cooling to avoid surface blemishes, others employ mist coolants (a mix of water and lubricant) to reduce friction and prevent tool binding, especially during deep cuts.
- CAD/CAM Optimization: CAM software for acrylic prioritizes toolpaths that reduce vibration, as excessive movement can cause chipping on acrylic’s brittle edges. Programs often include “climb milling” (cutting in the direction of the tool’s rotation) to achieve smoother finishes.
- Dust Extraction: Acrylic produces fine shavings during machining, which can scratch surfaces or clog tools. Integrated vacuum systems remove debris in real time, preserving the material’s transparency.
2. Manufacturing Process
The workflow for acrylic CNC service typically follows these steps:
- Design Finalization: Clients provide 2D or 3D CAD files (e.g., .dxf, .stl) specifying dimensions, cutouts, engravings, or contours. Designers review the files to ensure they are compatible with CNC machining—for example, avoiding overly thin walls (less than 1mm) that may break during production.
- Toolpath Programming: CAM software converts the CAD design into G-code, optimizing tool selection (e.g., a 3mm single-flute bit for detailed cuts, a 10mm bit for rough shaping) and cutting speed (usually 500–1500 mm/min, depending on acrylic thickness).
- Material Setup: Acrylic sheets or blocks are secured to the CNC bed using double-sided tape, clamps, or vacuum chucks. Thinner sheets (under 3mm) often require a backing material (e.g., MDF) to prevent warping during cutting.
- Machining Execution: The CNC machine follows the programmed toolpath, performing operations like profiling (cutting the outer shape), pocketing (creating recesses), or engraving (etching designs into the surface). For 3D parts, 5-axis CNC machines may be used to achieve curved or undercut features.
- Finishing: Post-machining steps include deburring (removing sharp edges with sandpaper or a flame polisher), cleaning (using isopropyl alcohol to remove dust), and optional treatments like annealing (heating to reduce internal stress) for large parts.
3. Materials Used
Acrylic CNC service works with various types of acrylic to suit specific applications:
- Clear Acrylic: The most common type, valued for its glass-like transparency (92% light transmission). It is used for displays, lenses, or light fixtures.
- Colored Acrylic: Available in solid hues (e.g., red, blue) or translucent shades, used for signage, decorative panels, or custom enclosures.
- Cast vs. Extruded Acrylic: Cast acrylic, made by pouring liquid resin into molds, has superior machinability and uniform thickness, making it ideal for intricate parts. Extruded acrylic, formed by pushing molten plastic through a die, is cheaper but more prone to chipping, suitable for simpler cuts.
- Specialty Acrylics: Impact-modified acrylic (for durability in industrial parts) or UV-resistant acrylic (for outdoor signage) are also machined, with adjusted cutting parameters to account for their modified compositions.
4. Types of Products Produced
Acrylic CNC service excels at creating both functional and aesthetic acrylic products, such as:
- Display & Signage: Retail display cases, point-of-purchase (POP) stands, and illuminated signs with precision-cut letters or logos.
- Industrial Components: Machine guards, sight glasses, and fluid reservoirs, where acrylic’s transparency and chemical resistance are assets.
- Architectural Elements: Skylights, partition walls, and decorative panels with custom cutouts or 3D reliefs.
- Medical & Lab Equipment: Test tube racks, sample holders, and protective shields, as acrylic is easy to sanitize and shatter-resistant.
- Custom Art & Crafts: Sculptures, jewelry, and hobbyist parts, leveraging CNC’s ability to replicate intricate designs with consistency.
5. Key Applications & Industries
Acrylic CNC service serves diverse sectors:
- Retail & Advertising: Producing branded displays, product showcases, and promotional signage that highlight merchandise with clarity.
- Architecture & Interior Design: Creating custom lighting fixtures, room dividers, or furniture components (e.g., acrylic table tops) that blend functionality with modern aesthetics.
- Electronics: Fabricating enclosures for sensors, control panels, or LED screens, where acrylic’s insulation properties and transparency protect internal components while allowing visibility.
- Medical & Laboratory: Manufacturing sterile, shatterproof equipment for hospitals, clinics, and research labs, where hygiene and durability are critical.
- Events & Entertainment: Designing props, stage backdrops, or exhibition booths, as acrylic is lightweight and easy to transport compared to glass.
6. Common Scenarios & Advantages
Acrylic CNC service is ideal for scenarios such as:
- Complex Geometries: Intricate designs with fine details—e.g., lace-like engravings on acrylic awards or 3D curved surfaces for custom light diffusers—that manual cutting tools (like lasers or saws) would distort.
- Bulk Production: Creating hundreds of identical parts (e.g., acrylic brackets for electronics) with consistent dimensions, ensuring interchangeability.
- Transparency Preservation: Achieving edge finishes that remain clear (not cloudy) through precise tooling, critical for applications like display cases or optical components.
- Cost-Effective Prototyping: Rapidly iterating acrylic prototypes for product testing (e.g., new display designs) without the high costs of mold-based production.
Limitations include the risk of chipping if tools are dull or feed rates are too high, and the need for post-processing (like flame polishing) to restore clarity to cut edges. However, these challenges are manageable with proper machine calibration and tool maintenance.
In summary, acrylic CNC service combines the precision of CNC technology with acrylic’s unique properties to deliver versatile, high-quality products. Its ability to balance functionality and aesthetics makes it a go-to solution for industries ranging from retail to medical, where clarity, precision, and customization are key.