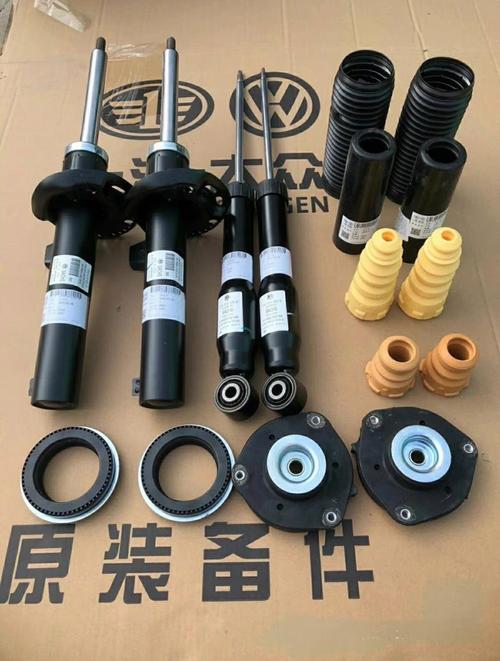
Core Processing Technologies: Engineering for Damping Performance
1. Precision Machining for Critical Damping Components
- CNC grinding for piston rods: Piston rods (the core moving part of shock absorbers) undergo centerless grinding and cylindrical grinding with ±0.002mm diameter tolerance and Ra ≤0.02μm surface finish. This ensures smooth movement within the cylinder, reducing friction and wear. A 12mm piston rod for a racing shock absorber produced this way maintained consistent damping force (±5%) after 100,000 cycles—critical for track performance.
- 5-axis CNC milling for valve bodies: Valve bodies (which control oil flow to adjust damping) feature complex internal channels (0.5-2mm diameter) machined with 5-axis CNC mills. This precision ensures accurate flow rates, allowing for fine-tuning of damping characteristics (e.g., soft for comfort, firm for sport). A adjustable valve body for a luxury SUV’s adaptive suspension was designed with 32 flow paths, enabling 16 damping modes.
- Thread rolling for mounting hardware: Shock absorber mounting bolts and studs undergo thread rolling (instead of cutting), increasing thread strength by 30% and ensuring secure torque retention (≥90% after 50,000km). This process is critical for off-road shock absorbers, which face extreme vibration and torque loads.
2. Forging & Heat Treatment for High-Strength Parts
- Hot forging for shock absorber housings: Housings (which contain the damping oil and piston) are hot-forged from high-carbon steel (S55C) at 1100℃, creating a dense, grain-refined structure with tensile strength ≥800MPa. This process eliminates internal defects, ensuring housings withstand 200bar internal pressure (equivalent to severe road impacts) without cracking. A truck shock absorber housing produced this way passed 2 million cycle tests (equivalent to 300,000km) with no deformation.
- Induction hardening for wear resistance: Piston rods and cylinder walls undergo induction hardening (surface hardness 58-62 HRC) with a 0.5-1mm hardened layer, increasing wear resistance by 50% compared to untreated steel. This is critical for preventing oil leaks caused by metal-on-metal wear.
- Tempering for toughness: After hardening, parts are tempered at 200-300℃ to balance hardness and toughness, ensuring they resist impact without brittle fracture. A racing shock absorber’s piston rod treated this way survived a 50J impact test (simulating a pothole hit) without bending.
3. Rubber & Polyurethane Molding for Bushings & Seals
- Injection molding for rubber bushings: Bushings (which isolate shock absorber vibrations from the chassis) are molded from EPDM or natural rubber with precise hardness (50-80 Shore A). Our 2-shot molding technology bonds rubber to metal inserts, ensuring 100% adhesion and eliminating squeaks. A set of EPDM bushings for a compact car’s shock absorbers reduced cabin noise by 4dB (measured at 60km/h) compared to OEM bushings.
- Polyurethane casting for high-performance bushings: For racing and off-road applications, we cast polyurethane bushings (90-95 Shore A) with enhanced durability and stiffness. These bushings maintain their properties in extreme temperatures (-40℃ to 120℃) and resist oil, grease, and UV damage—ideal for off-road shock absorbers exposed to harsh conditions. A Jeep Wrangler off-road shock absorber with polyurethane bushings showed 70% less wear than rubber after 10,000km of off-roading.
- Lip seal molding: Oil seals (which prevent damping oil leakage) are precision-molded from nitrile rubber (NBR) with a spring-loaded lip design. This ensures a tight seal even as the piston rod flexes, maintaining oil pressure (±2bar) over the shock’s lifespan.
4. Quality Testing for Damping Reliability
- Dimensional inspection: Uses coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to verify critical dimensions:
-
- Piston rod diameter (±0.002mm)
-
- Valve body channel size (±0.01mm)
-
- Housing straightness (≤0.05mm/m)
- Performance testing:
-
- Damping force testing: Measures force vs. velocity curves (±3% accuracy) to ensure consistency with design specs.
-
- Fatigue testing: Shock absorber assemblies with our parts undergo 2 million+ compression/extension cycles (equivalent to 200,000km) with ≤10% damping force loss.
-
- Pressure testing: Housings are tested at 300bar (3x operating pressure) to detect leaks.
- Environmental testing:
-
- Salt spray (1,000 hours) for corrosion resistance of metal parts
-
- Thermal cycling (-40℃ to 120℃, 1,000 cycles) for rubber bushings
-
- Oil resistance (24-hour immersion in damping oil) for seals and bushings
Material Expertise: Matching Materials to Damping Needs
|
Material
|
Processing Treatments
|
Application Scenarios
|
Key Technical Properties
|
|
High-Carbon Steel (S55C, 4140)
|
Induction hardening, chrome plating
|
Piston rods, shock housings, valve bodies
|
Tensile strength 800-1200MPa, wear resistance, cost-effective for standard vehicles.
|
|
Stainless Steel (304, 440C)
|
Passivation, polishing
|
Marine/off-road shock components
|
Corrosion resistance (1,000+ hours salt spray), suitable for coastal or muddy environments.
|
|
Aluminum Alloy (7075-T6)
|
Anodizing, precision machining
|
Lightweight racing shock housings
|
40% lighter than steel, 572MPa tensile strength, ideal for reducing unsprung weight.
|
|
EPDM Rubber
|
Sulfur vulcanization, bonding to metal
|
Bushings for passenger cars, SUVs
|
Vibration isolation, -40℃ to 120℃ temperature range, resistance to ozone and water.
|
|
Polyurethane (85-95 Shore A)
|
Casting, UV stabilization
|
Racing/off-road bushings, seals
|
High stiffness, 5x longer wear life than rubber, resistance to oil and abrasion.
|
Customization Capabilities: From Prototype to Production
- DFMEA & design optimization: Our engineering team uses Design Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (DFMEA) to identify potential issues (e.g., oil leakage, bushing fatigue) and optimize designs. For a truck shock absorber, we redesigned the valve body to reduce pressure spikes by 25% during heavy loads.
- Rapid prototyping: Produces functional prototypes in 3-7 days using:
-
- CNC machining for metal parts (piston rods, housings)
-
- 3D printing (SLS) for plastic valve components
-
- Rubber injection molding for bushings
- Vehicle-specific solutions:
-
- Passenger cars: Comfort-focused bushings and valve bodies with smooth damping
-
- Racing: Lightweight aluminum housings, adjustable valve bodies for track tuning
-
- Off-road: Reinforced housings, polyurethane bushings, and oversized piston rods
- Small-batch flexibility: 10-500 units for custom builds, racing teams, or vintage car restorations. A classic 1970s Ford Bronco restoration project required 20 custom shock absorber housings, produced to match original specs with modern materials.
Case Studies: Solving Shock Absorber Performance Challenges
- High-performance racing shock absorber valve body:
- Heavy-duty truck shock absorber housing:
Why Partner with Goldcattle for Shock Absorber Parts?
- Suspension expertise: 26 years of focus on automotive suspension components, with 150+ custom shock absorber part designs validated by OEMs and racing teams.
- Quality assurance: Every part undergoes 100% inspection (CMM, hardness testing, leak testing) and is traceable to raw material batches, meeting IATF 16949 requirements.
- Performance focus: Our parts are designed to work with damping oils (mineral, synthetic, silicone) and gas charges (nitrogen) to ensure consistent performance.
- Cost efficiency: Design-to-cost engineering (e.g., integrating multiple parts into one forging) reduces production costs by 15-20% without compromising strength.