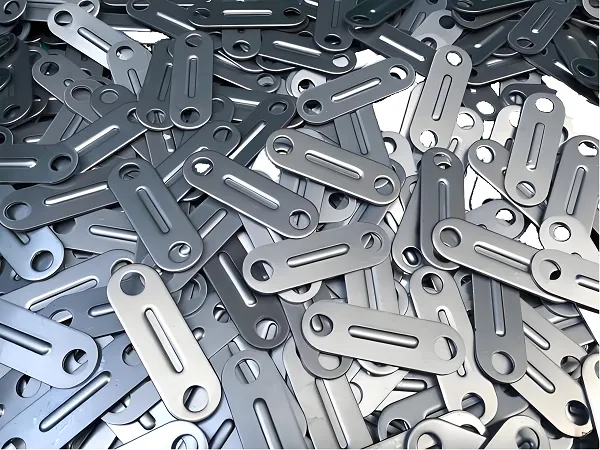
Introduction: Your Precision Manufacturing Solutions Expert
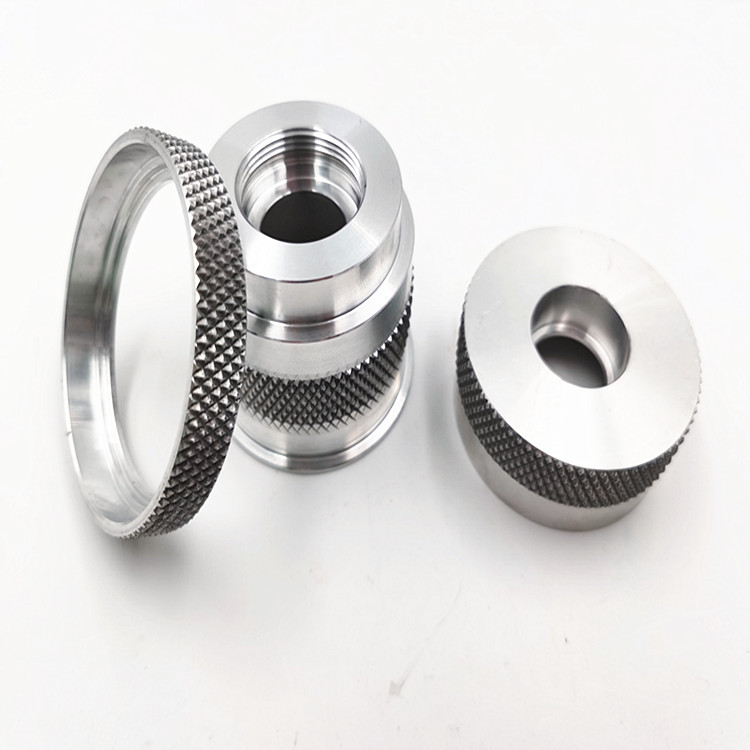

Chapter 1: Basic Understanding – Why Choose Stainless Steel CNC Turning?
1.1 Introduction to CNC Turning Technology
1.2 Core Advantages of Stainless Steel Materials
1.3 Synergistic Effect: The Perfect Combination of 1+1>2
- High-precision machining capability: CNC turning can achieve ±0.01mm machining accuracy, fully utilizing the material potential of stainless steel
- Complex shape manufacturing: Capable of processing complex geometric shapes that are difficult to achieve with traditional processes
- Batch consistency: Ensuring complete consistency in dimensional accuracy and performance for each batch of parts
- Design freedom: Providing engineers with greater design space to realize innovative design concepts
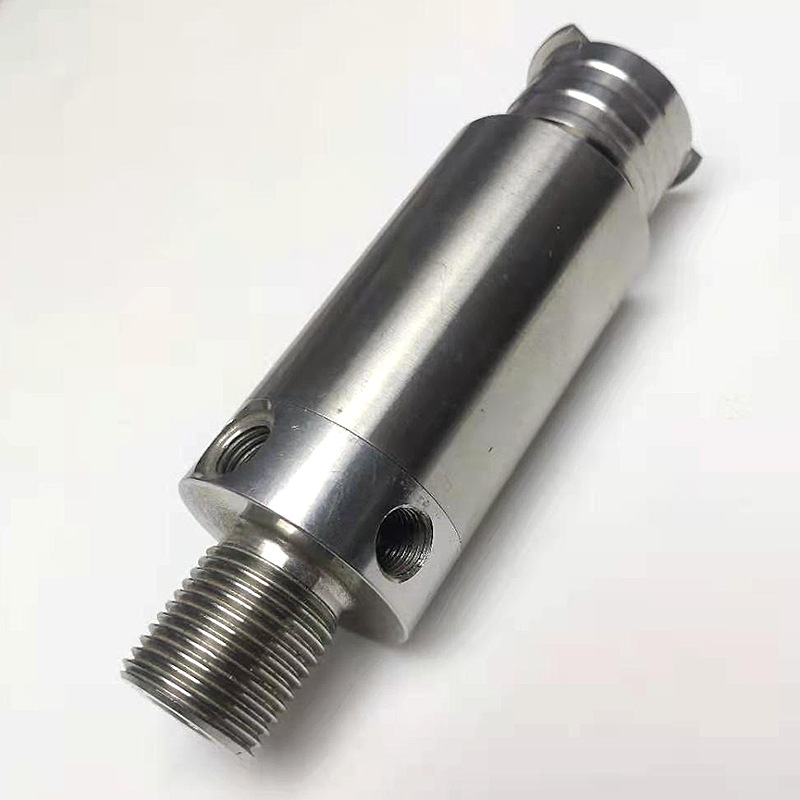

Chapter 2: Technical Core – Key Decision Points in the Customization Process
2.1 Stainless Steel Material Selection Guide
|
Grade
|
Main Composition
|
Corrosion Resistance
|
Machinability
|
Strength Level
|
Typical Applications
|
|
303
|
Cr17-19%, Ni8-10%, S≥0.15%
|
Good
|
Excellent
|
Medium
|
Precision gears, valve parts, shaft components
|
|
304
|
Cr18-20%, Ni8-10.5%
|
Excellent
|
Good
|
Medium
|
Food equipment, household appliances, architectural decoration
|
|
304L
|
Cr18-20%, Ni8-12%, C≤0.03%
|
Excellent
|
Good
|
Medium
|
Welded pipes, low-temperature vessels, petrochemical equipment
|
|
316
|
Cr16-18%, Ni10-14%, Mo2-3%
|
Excellent
|
Medium
|
Medium
|
Marine equipment, chemical vessels, medical equipment
|
|
316L
|
Cr16-18%, Ni10-14%, Mo2-3%, C≤0.03%
|
Excellent
|
Medium
|
Medium
|
Semiconductor chambers, medical implants
|
|
416
|
Cr12-14%, S0.15%
|
Fair
|
Excellent
|
High
|
Precision mechanical parts, valves, fasteners
|
|
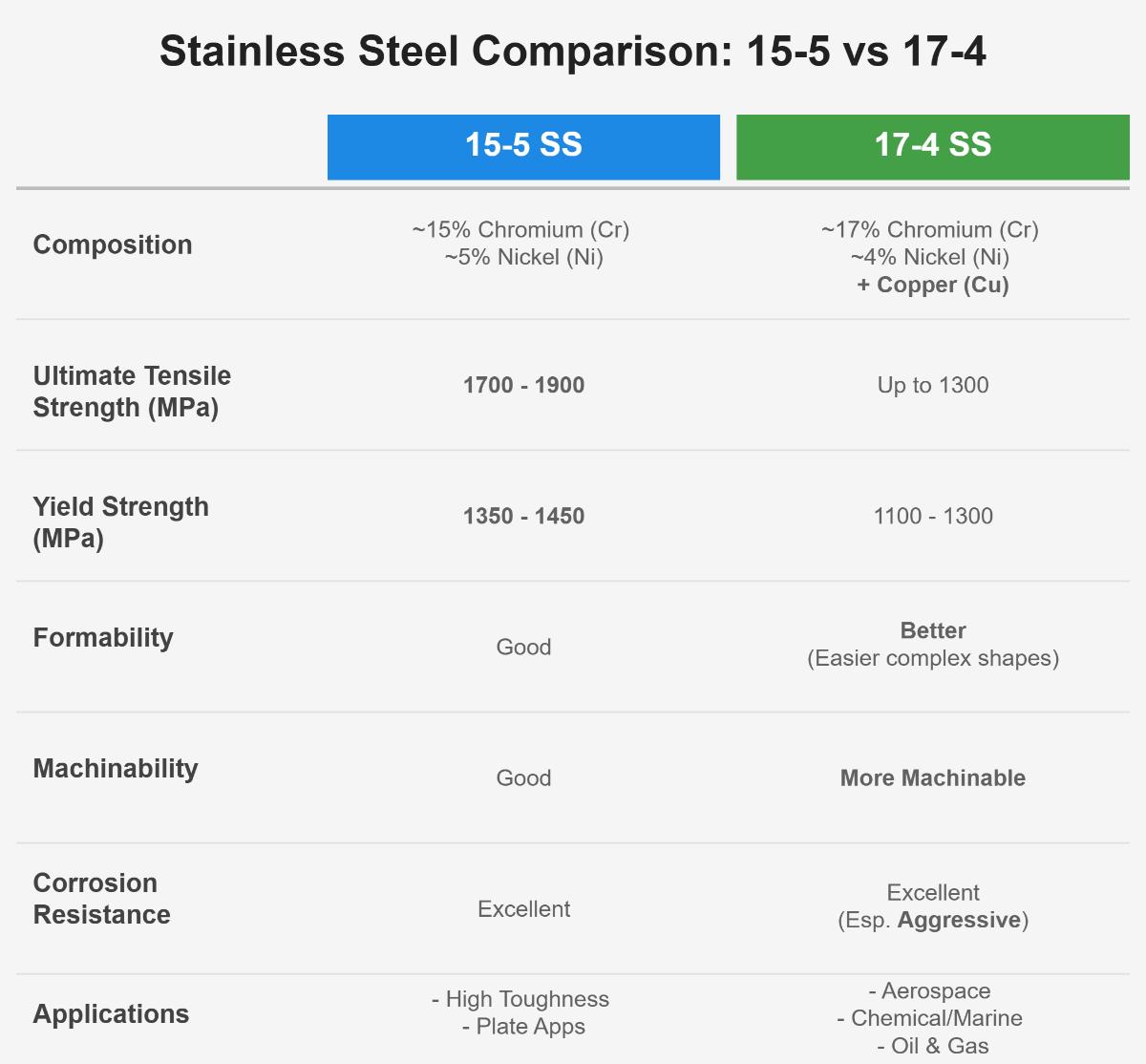
17-4PH
|
Cr15-17.5%, Ni3-5%, Cu3-5%
|
Good
|
Medium
|
Very High
|
Aerospace components, high-strength structural parts
|
- Pursuing ultimate machining efficiency: Choose 303 stainless steel, where sulfur significantly improves cutting performance
- General corrosion resistance requirements: 304 stainless steel is the most cost-effective choice
- Marine or highly corrosive environments: 316/316L stainless steel with molybdenum provides excellent chloride corrosion resistance
- Needing heat treatment strengthening: 17-4PH can achieve high strength above 1300MPa through aging treatment
- Cost-sensitive with moderate corrosion resistance: 416 stainless steel is a good choice
2.2 Key Design and Process Parameters
Tolerance and Precision Control
- Dimensional tolerance: ±0.01mm
- Roundness: 0.005mm
- Cylindricity: 0.01mm/m
- Surface roughness: Ra0.8-3.2μm
Surface Treatment Processes

|
Surface Treatment Process
|
Treatment Effect
|
Main Function
|
Applicable Scenarios
|
|
Passivation Treatment
|
Maintains original color, forms protective film
|
Improves corrosion resistance, extends service life
|
Medical devices, food equipment
|
|
Electroplating Treatment
|
Surface covered with metal layer (e.g., nickel, chromium)
|
Enhances aesthetics, improves wear resistance
|
Decorative parts, friction components
|
|
Sandblasting Treatment
|
Surface forms uniform matte effect
|
Eliminates machining marks, uniform appearance
|
Industrial components, structural parts
|
|
Brushing Treatment
|
Surface forms uniform linear texture
|
Aesthetic decoration, easy to clean
|
Panels, housings, handles
|
|
Mirror Polishing
|
Surface achieves mirror effect
|
Ultimate aesthetics, easy to clean
|
High-end decorative parts, optical components
|
Design Optimization Recommendations
- All external corners are recommended to be designed with R0.5-R1.0mm fillets
- Minimum internal corner radius not less than 0.2mm
- Minimum wall thickness not less than 0.8mm (diameter <20mm)
- Maximum wall thickness to minimum wall thickness ratio not exceeding 3:1
- Avoid sudden wall thickness changes, use gradual transitions
- Thread length not exceeding 1.5 times the thread diameter
- Design undercut at thread start and end
- 6g/6H thread tolerance fit is recommended

2.3 Machining Challenges and Solutions
Work Hardening Problem
- Reasonable cutting parameters: Use lower feed rates and appropriate cutting speeds
- Sharp tools: Use dedicated stainless steel machining tools
- Adequate cooling: Adopt high-pressure coolant system to ensure adequate cooling of the cutting area
Chip Control
- Chip breaker design: Select appropriate tool chip breakers
- Vibration cutting: Adopt micro-vibration cutting technology
- High-pressure flushing: Use high-pressure coolant for forced chip breaking
Chapter 3: Quality Control – How to Ensure Professional Reliability of Parts?
3.1 Testing Equipment and Methods

- Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM): Tests 3D dimensional accuracy of complex parts
- Optical Projector: Tests 2D contour and shape accuracy
- Micrometers, calipers: Precise measurement of conventional dimensions
- Thread gauges, ring gauges: Thread size and accuracy testing
- Surface roughness tester: Measures surface roughness Ra value
- Metallographic microscope: Observes surface microstructure
- Visual inspection system: Automated appearance defect detection
- Hardness tester: Tests material hardness (HV, HRC)
- Tensile testing machine: Tests material mechanical properties
- Spectrometer: Verifies material chemical composition
- Material chemical composition verification
- Material mechanical property testing
- Material surface quality inspection
- Material dimensional tolerance confirmation
- Complete dimensional inspection
- Geometric tolerance verification
- Surface roughness measurement
- Functional performance testing
- First article inspection report confirmation
- Regular sampling inspection system (1 piece sampled every 10-20 pieces)
- Real-time monitoring of key dimensions
- Machining parameter stability monitoring
- Timely handling of abnormal situations
- Full-dimensional inspection
- Appearance quality inspection
- Surface treatment quality verification
- Final confirmation before packaging
3.3 Standards and Certifications
- ISO 9001: Quality management system certification
- AS9100: Aerospace quality management system
- IATF 16949: Automotive industry quality management system
- ISO 13485: Medical device quality management system
- GB/T 1220: Stainless steel bar standard
- GB/T 1221: Heat-resistant steel bar standard
- ASTM A276: Stainless steel bar and shape standard
- DIN 17440: German stainless steel standard
Chapter 4: Cooperation Process – Clear Path from Inquiry to Delivery
4.1 Standard Cooperation Process
- Provide 2D/3D drawings or samples
- Clarify material requirements and quantity
- Determine precision level and surface treatment
- Evaluate technical feasibility and cost
- Technical team reviews drawings
- Provide detailed quotation
- Confirm delivery cycle and payment terms
- Sign technical agreement
- Produce first article sample
- Conduct First Article Inspection (FAI)
- Customer confirms sample quality
- Determine final production plan
- Raw material procurement and inspection
- Mass production and process monitoring
- Product quality inspection
- Packaging and labeling
- Shipping according to agreed method
- Provide quality inspection report
- After-sales service and technical support
- Customer satisfaction survey
4.2 Key Success Factors
- Provide complete 2D/3D drawings (recommended formats: PDF, DWG, IGES, STEP)
- Clearly mark key dimensions and tolerance requirements
- Detailed description of surface treatment and packaging requirements
- Establish dedicated project communication group
- Regular production progress reporting
- Timely handling of technical issues and changes
- Sample production: 3-7 working days
- Small batch production: 5-15 working days
- Mass production: 15-30 working days
- Emergency orders: Expedited service available

Chapter 5: Industry Application Case Analysis
5.1 Medical Device Industry
- Material Selection: 316L stainless steel
- Precision Requirement: ±0.005mm
- Surface Treatment: Passivation treatment
- Quality Standard: ISO 13485 certification
- Key Challenges: Biocompatibility, cleanliness requirements
5.2 Aerospace Industry
- Material Selection: 17-4PH stainless steel
- Precision Requirement: ±0.003mm
- Surface Treatment: Natural passivation
- Quality Standard: AS9100 certification
- Key Challenges: High strength, lightweight, reliability
5.3 Food Processing Equipment
- Material Selection: 304 stainless steel
- Precision Requirement: ±0.01mm
- Surface Treatment: Electrolytic polishing
- Quality Standard: FDA certification
- Key Challenges: Hygiene standards, corrosion resistance
5.4 Electronic Communication Industry
- Material Selection: 303 stainless steel
- Precision Requirement: ±0.008mm
- Surface Treatment: Nickel plating
- Quality Standard: RoHS compliance
- Key Challenges: Miniaturization, high precision, large quantities
Chapter 6: Cost Control and Optimization Strategies
6.1 Cost Composition Analysis
- Raw material price fluctuations
- Material utilization rate
- Scrap disposal cost
- Equipment depreciation
- Tool consumption
- Labor cost
- Energy consumption
- Testing equipment investment
- Testing labor cost
- Rework and scrap cost
- Project management cost
- Quality system maintenance
- After-sales service cost
6.2 Cost Optimization Strategies
- Reasonable selection of material grades
- Optimization of part structure design
- Selection of appropriate tolerance levels
- Simplification of surface treatment requirements
- Optimization of cutting parameters
- Improvement of tool life
- Reduction of processing steps
- Improvement of production efficiency
- Reasonable arrangement of production batches
- Optimization of procurement strategy
- Improvement of equipment utilization
- Reduction of changeover costs
Chapter 7: Future Development Trends and Technological Innovation
7.1 Technology Development Trends
- AI-driven process parameter optimization
- Application of digital twin technology
- Adaptive control machining systems
- Predictive maintenance technology
- Nanoscale machining accuracy
- Ultra-precision testing technology
- Multi-axis linkage machining
- Composite machining technology
- Environmentally friendly cutting fluids
- Energy-saving machining processes
- Waste recycling and utilization
- Clean production technology
7.2 Application Field Expansion
- New energy vehicle components
- Photovoltaic equipment precision parts
- Energy storage equipment structural parts
- Hydrogen energy equipment key components
- Industrial robot precision parts
- 3C equipment structural parts
- Precision instrument components
- Smart equipment core components
Conclusion: Choose Professional Partners to Create a Precision Manufacturing Future
- 15 years of professional experience: Focused on stainless steel precision machining for 15 years
- 80+ advanced equipment: Possessing imported CNC lathes, machining centers, and other equipment
- ISO 9001 certification: Complete quality management system
- 24-hour rapid response: Professional technical team at your service anytime
- One-stop solution: Full-process service from design optimization to final delivery
- Upload drawings for quotation: Send your 2D/3D drawings to our technical email
- Technical consultation hotline: Call our technical hotline for professional technical advice
- Factory visit: Welcome to make an appointment to visit our production workshop and testing center
- Sample production: Rapid sample production to verify product quality and technical solutions