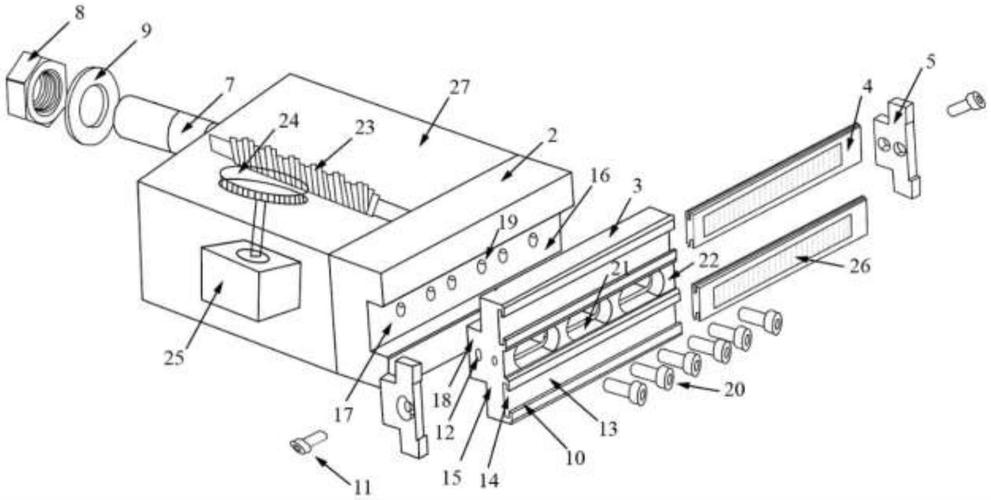
Jet bandsaws are renowned for their durability and precision in woodworking, metalworking, and industrial cutting applications. The performance of these bandsaws relies heavily on their various components, known as jet bandsaw parts. Each part plays a unique role in ensuring smooth operation, accurate cuts, and long – term reliability. From the blade that makes the cut to the motor that powers the machine, every component is vital for the overall functionality of the jet bandsaw.
1. Types of Jet Bandsaw Parts
Cutting Components
- Bandsaw Blade: The bandsaw blade is the heart of the cutting operation. Jet bandsaws use blades with different tooth configurations, pitches, and materials to handle various materials. For woodworking, blades with larger teeth and a coarser pitch are ideal for fast, rough cuts, while metalworking requires blades with smaller, finer teeth for precise, clean cuts. Bi – metal blades, which combine high – speed steel teeth with a flexible alloy steel backing, are popular for their durability and ability to cut through a wide range of materials.
- Blade Guides: Blade guides are responsible for keeping the bandsaw blade aligned and stable during cutting. They reduce blade deflection, ensuring straight and accurate cuts. Jet bandsaws typically feature roller guides or block guides. Roller guides use small wheels to support the blade, minimizing friction and allowing for smooth blade movement. Block guides, made from materials like graphite or bronze, are more durable and suitable for heavy – duty cutting applications.
Drive Components
- Motor: The motor is the power source of the jet bandsaw. It drives the band wheels, which in turn move the blade. Jet bandsaws come with different motor powers, ranging from small 1 – horsepower motors for light – duty woodworking to larger 5 – horsepower or more motors for industrial metalworking. Variable – speed motors are also available, allowing users to adjust the blade speed to match the material being cut.
- Band Wheels: Band wheels are large wheels that hold and drive the bandsaw blade. They are typically made from cast iron or steel for strength and durability. The upper wheel is often adjustable to tension the blade, while the lower wheel is connected to the motor via a belt or direct drive. Proper alignment of the band wheels is crucial to prevent blade wear and ensure smooth operation.
- Drive Belt/Pulley System: The drive belt or pulley system transmits power from the motor to the lower band wheel. Drive belts are made from rubber or polyurethane and come in different sizes and tensions to match the motor power and desired blade speed. Pulley systems allow for speed adjustment by changing the size of the pulleys, giving users flexibility in cutting different materials.
Adjustment and Control Components
- Tension Adjuster: The tension adjuster is used to set the correct tension on the bandsaw blade. Proper blade tension is essential for accurate cutting and preventing blade breakage. Jet bandsaws feature manual or automatic tension adjusters. Manual adjusters use a knob or lever to increase or decrease tension, while automatic adjusters maintain a constant tension as the blade heats up or wears.
- Throat Plate: The throat plate, also known as the table insert, is a removable plate located on the bandsaw table. It has a slot that the blade passes through, reducing friction and preventing workpiece material from getting caught under the blade. Throat plates are available in different materials, such as steel or phenolic, and can be replaced when worn or damaged.
- Fence: The fence is a guide that helps users make straight, parallel cuts. It attaches to the bandsaw table and can be adjusted to different distances from the blade. Jet bandsaws often come with adjustable fences that can be locked in place for precise cutting. Some fences also feature a miter gauge slot, allowing for angled cuts.
Safety Components
- Blade Guard: The blade guard covers the upper part of the bandsaw blade, protecting the user from accidental contact with the moving blade. It is usually made from metal or plastic and can be adjusted to accommodate different blade heights.
- Emergency Stop Button: The emergency stop button is a crucial safety feature that allows users to quickly stop the bandsaw in case of an emergency. Pressing the button immediately shuts off the motor, stopping the blade movement.
2. Processable Materials for Jet Bandsaw Parts
Metals
- Steel: Steel is widely used in jet bandsaw parts for its strength and durability. Band wheels, motor housings, and frame components are often made from carbon steel or alloy steel. Alloy steel, with the addition of elements like chromium and nickel, offers better corrosion resistance and mechanical properties, making it suitable for parts that are exposed to harsh environments.
- Cast Iron: Cast iron is used for components like the bandsaw table and band wheels. It provides excellent vibration damping, which helps reduce noise and improve cutting accuracy. Cast iron is also wear – resistant, ensuring long – term performance.
- Aluminum: Aluminum is used for lightweight components such as blade guides, fence brackets, and covers. It is corrosion – resistant and easy to machine, making it a cost – effective choice for non – structural parts.
Plastics and Polymers
- Nylon: Nylon is used in components like blade guide blocks and pulleys. It has low friction, high wear resistance, and good impact strength, making it ideal for parts that come into contact with moving components.
- Phenolic: Phenolic is a durable plastic used for throat plates and handle grips. It is heat – resistant and has good mechanical strength, ensuring long – term use in harsh operating conditions.
- Rubber: Rubber is used in drive belts, gaskets, and vibration – dampening pads. It provides flexibility, grip, and shock absorption, contributing to the smooth operation of the bandsaw.
3. Step – by – Step Manufacturing Process of Jet Bandsaw Parts
Design and Engineering
The manufacturing process starts with the design and engineering of jet bandsaw parts. Engineers use computer – aided design (CAD) software to create detailed 3D models of each part, ensuring they meet the required specifications for fit, function, and performance. They also conduct simulations to test the parts’ strength, durability, and performance under different operating conditions. For example, band wheels are designed to withstand the tension of the blade and the weight of the workpiece, while blades are engineered to have the right tooth geometry for efficient cutting.
Material Selection and Sourcing
Once the design is finalized, the appropriate materials are selected based on the part’s function and performance requirements. High – quality metals, plastics, and polymers are sourced from reliable suppliers to ensure consistency and quality. For example, blades are made from high – speed steel or bi – metal materials, while band wheels are cast from iron or steel.
Fabrication and Machining
- Cutting and Shaping: Metal parts are cut and shaped using various machining processes. For example, band wheels are cast from molten metal and then machined to the precise dimensions using lathes and milling machines. Blades are cut from sheet metal and then shaped into the desired length and width.
- Heat Treatment: Some metal parts, such as blades and band wheels, undergo heat treatment to improve their mechanical properties. Blades are heat – treated to harden the teeth, increasing their wear resistance and cutting performance. Band wheels may be heat – treated to reduce internal stress and improve their strength.
- Forming and Molding: Plastic parts are formed using injection molding or extrusion processes. Nylon blade guides, for example, are injection – molded into the desired shape using molds that replicate the part’s design.
Assembly and Finishing
- Assembly: The fabricated parts are assembled into complete jet bandsaw components. For example, the motor is connected to the drive system, the blade is mounted on the band wheels, and the guides and fences are attached to the table. Each assembly step is carefully monitored to ensure proper fit and function.
- Finishing: Metal parts are finished to improve their appearance, corrosion resistance, and performance. This may include painting, powder coating, or plating. For example, band wheels are often painted or powder – coated to prevent rust, while blades are coated with a lubricant to reduce friction during cutting.
Quality Inspection and Testing
After assembly, each jet bandsaw part undergoes rigorous quality inspection and testing. Inspectors check the parts’ dimensions, surface finish, and mechanical properties using precision measuring tools and testing equipment. For example, blades are tested for straightness, tooth sharpness, and tension strength, while band wheels are checked for runout and balance. Any defective parts are rejected or repaired before they are assembled into the final product.
4. Customizing Jet Bandsaw Parts
Sharing Requirements
To get custom jet bandsaw parts, customers need to share their specific requirements with the manufacturer. This includes details such as the model of the jet bandsaw, the type of cutting application, the material to be cut, and any special features or modifications needed. For example, a customer who needs to cut thick metal plates may require a custom – made blade with a specific tooth pitch and material. Providing drawings or samples of the required part can help the manufacturer understand the exact specifications.
Engineer Consultation
The manufacturer’s engineering team reviews the customer’s requirements and provides expert advice on the best materials, designs, and manufacturing processes for the custom parts. They may suggest modifications to the part’s design to improve its performance or reduce costs. For example, if a customer needs a longer blade for a specific application, the engineer may recommend a different material or tooth configuration to ensure the blade can withstand the increased tension.
Prototype Development
For complex custom parts, a prototype is developed to test the design and functionality. The prototype is made using the same materials and manufacturing processes as the final part, allowing the customer to evaluate its performance. Any issues or improvements identified during testing are addressed, and the design is modified accordingly. For example, a prototype blade may be tested for cutting speed and accuracy, and adjustments are made to the tooth geometry if necessary.
Production and Delivery
Once the prototype is approved, mass production of the custom jet bandsaw parts begins. The manufacturing process is closely monitored to ensure consistency and quality. After production, the parts are inspected again to ensure they meet the customer’s specifications. They are then packaged and delivered to the customer, along with any necessary installation instructions or technical support.
5. Application Fields of Jet Bandsaw Parts
Woodworking
In woodworking, jet bandsaw parts are used for cutting a variety of wood materials, including hardwoods, softwoods, and plywood. Blades with larger teeth and a coarser pitch are used for rough cutting, while finer – toothed blades are used for detailed work like scroll sawing and curve cutting. The adjustable fence and throat plate allow for precise cutting of different shapes and sizes, making jet bandsaws essential tools in woodworking shops.
Metalworking
Jet bandsaw parts are widely used in metalworking for cutting ferrous and non – ferrous metals, such as steel, aluminum, and copper. Bi – metal blades are commonly used for metal cutting, as they can withstand the high temperatures and pressures generated during the cutting process. The variable – speed motor allows users to adjust the blade speed to match the metal’s thickness and hardness, ensuring clean, accurate cuts.
Industrial Manufacturing
In industrial manufacturing, jet bandsaws are used for cutting large – scale materials, such as pipes, bars, and sheets. Heavy – duty parts, like large band wheels and powerful motors, allow for efficient cutting of thick and tough materials. Jet bandsaw parts are also used in the production of automotive parts, aerospace components, and other industrial products, where precision and reliability are crucial.
Hobby and DIY
Jet bandsaws are popular among hobbyists and DIY enthusiasts for a variety of projects, from woodworking crafts to metalworking repairs. The portable and easy – to – use design of some jet bandsaws, along with their affordable replacement parts, makes them accessible to home users. Hobbyists can use jet bandsaws to cut wood for furniture, metal for jewelry making, and other materials for various creative projects.
6. Manufacturing Challenges of Jet Bandsaw Parts
Ensuring Blade Performance and Durability
One of the main challenges in manufacturing jet bandsaw blades is ensuring their performance and durability. Blades need to be sharp enough to cut through various materials efficiently, while also being strong enough to withstand the tension and stress of the cutting process. Achieving the right balance between hardness and flexibility is crucial, as a blade that is too hard may be brittle and prone to breaking, while a blade that is too soft may wear quickly. Manufacturers address this by using high – quality materials and precise heat – treatment processes.
Maintaining Precision in Band Wheel Alignment
Band wheels must be precisely aligned to ensure the blade runs smoothly and evenly, preventing premature wear and ensuring accurate cuts. Even a small misalignment can cause the blade to track improperly, leading to uneven cutting, blade breakage, and increased noise and vibration. Manufacturers use advanced machining techniques and precision measuring tools to ensure the band wheels are aligned within tight tolerances.
Producing Reliable Drive Components
The drive components, such as motors, belts, and pulleys, must be reliable and efficient to ensure the bandsaw operates smoothly. Motors need to provide consistent power, while belts and pulleys must transmit power without slipping or wearing prematurely. Manufacturers select high – quality components and conduct rigorous testing to ensure the drive system can withstand the demands of continuous operation.
7. Expert Manufacturing Tips for Jet Bandsaw Parts
Optimizing Blade Tooth Geometry
The tooth geometry of the blade, including the tooth pitch, angle, and shape, has a significant impact on cutting performance. Manufacturers optimize the tooth geometry based on the material to be cut. For example, blades for cutting wood have larger, more aggressive teeth, while blades for metal have smaller, finer teeth with a higher rake angle to reduce cutting forces.
Using Advanced Machining Techniques
Advanced machining techniques, such as CNC machining, are used to ensure the precision and consistency of jet bandsaw parts. CNC lathes and milling machines can produce parts with tight tolerances, ensuring they fit together properly and function as intended. This is especially important for components like band wheels and blade guides, where precision is critical for performance.
Implementing Quality Control Measures
Strict quality control measures are implemented throughout the manufacturing process to ensure the quality of jet bandsaw parts. This includes inspecting raw materials, monitoring the fabrication and machining processes, and testing finished parts. Statistical process control (SPC) is often used to identify and correct any variations in the manufacturing process, ensuring consistent quality.
8. Common Questions About Jet Bandsaw Parts
Q: How often should I replace the bandsaw blade?
A: The frequency of blade replacement depends on the type of material being cut, the cutting speed, and the amount of use. Generally, a blade should be replaced when it starts to produce rough cuts, becomes dull, or shows signs of wear, such as broken teeth or cracks. For heavy – duty use, blades may need to be replaced every few weeks, while for light use, they can last several months.
Q: Can I use a wood – cutting blade to cut metal?
A: No, it is not recommended to use a wood – cutting blade to cut metal. Wood – cutting blades have larger, coarser teeth that are not designed to handle the hardness and density of metal. Using a wood – cutting blade for metal cutting can result in poor – quality cuts, blade damage, and even safety hazards. It is important to use a blade specifically designed for metal cutting, such as a bi – metal blade.
Q: How do I adjust the tension on my jet bandsaw blade?
A: To adjust the tension on a jet bandsaw blade, locate the tension adjuster, which is usually located on the upper band wheel assembly. Turn the adjuster clockwise to increase tension or counterclockwise to decrease tension. The correct tension depends on the blade’s width and material. A general rule of thumb is to tension the blade until it makes a clear “ping” sound when plucked, similar to a guitar string. Refer to the bandsaw’s user manual for specific tension recommendations.
9. Get Your Jet Bandsaw Parts Today
If you need high – quality jet bandsaw parts to keep your bandsaw running smoothly and efficiently, look no further. We offer a wide range of genuine jet bandsaw parts, including blades, blade guides, motors, band wheels, and more. Our parts are manufactured to the highest standards, ensuring they fit perfectly and perform reliably. Whether you need a replacement blade for woodworking or a custom – made part for industrial use, our team of experts is here to help. Contact us today to place your order or to learn more about our products and services!