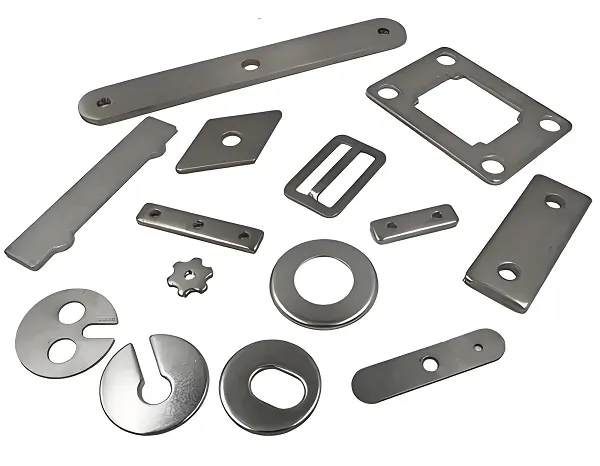
3D printing technology, a key innovation in modern manufacturing, offers unprecedented flexibility and precision in part customization. For buyers who are new to 3D printing part customization, it is crucial to understand the customization process, screening criteria, and technical processes. The following is a concise and easy-to-understand basic encyclopedic guide designed to help buyers easily grasp the core knowledge of 3D printed part customization.

Ⅰ.Basic Process of 3D Printed Part Customization
Define the need:
Determine the specific purpose, size, shape, quantity, material, delivery date, etc. of the required 3D printed parts.
If there are drawings or samples, please prepare them for the 3D printing service provider’s reference.
Choose the service provider:
Find a reputable 3D printing service provider with strong technical capabilities.
Consult the service provider’s customization capability, price, lead time, etc.
Design Confirmation:
Use CAD software to create a 3D model to ensure that all dimensions, material properties and functional requirements are met.
Communicate with the service provider to confirm design details such as tolerances, surface treatments, colors, etc.
File Preparation & Review:
Convert CAD models to STL or other formats supported by 3D printing.
The service provider reviews the files to ensure that the model is suitable for 3D printing and free of errors or defects.
Material Selection:
Select appropriate 3D printing materials, such as plastic (PLA, ABS, nylon, etc.), metal (stainless steel, titanium alloy, aluminum alloy, etc.), ceramics, etc., based on the part’s usage environment and functional requirements.
3D Printing:
The service provider carries out 3D printing according to the selected materials and process.
Monitor the printing process to ensure the print quality.
Post-processing:
Perform post-processing work such as de-supporting, grinding, polishing, etc. on the printed parts.
Conduct quality checks to ensure that the part meets the design requirements.
Packaging and Shipping:
Pack the parts to ensure that they are not damaged during transportation.
Ship the parts according to the contracted delivery date.
Ⅱ.Selection Criteria for 3D Printed Parts
Material Selection:
According to the use environment and functional requirements of the part, select the appropriate 3D printing material.
Consider the strength, toughness, heat resistance, chemical resistance, etc. of the material.
Dimensional accuracy:
Determine the appropriate range of dimensional tolerances according to the use precision requirements of the part.
3D printing technology usually has high precision, but different materials and processes will affect the final precision.
Surface quality:
Check whether the surface of the part is smooth and free of defects.
Select a post-treatment process (e.g., sanding, polishing) to improve the surface quality as needed.
Performance requirements:
Determine the required physical properties, chemical properties, etc. of the part according to its usage scenario.
If it needs to withstand certain pressure, temperature or chemical corrosion, etc., the corresponding 3D printing materials and processes need to be selected.
Cost-effectiveness:
Under the premise of meeting the functional requirements, consider the cost-effectiveness and choose cost-effective 3D printed parts.
Ⅲ.3D printing parts of the relevant technical process
Fused Deposition Molding (FDM):
Printing using thermoplastic materials (e.g. PLA, ABS).
The material is extruded through a heated nozzle and built up layer by layer to form the part.
Suitable for prototyping, education, simple structural parts, etc.
Light-curing molding (SLA/DLP):
Printing using photosensitive resin materials.
Light is projected onto the resin surface by a laser or projector to cure it.
Suitable for high-precision, complex structural parts.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS):
Printing using powdered materials such as nylon powder.
The laser selectively sinter the powder to form the part.
Suitable for parts that require higher strength and toughness.
Metal 3D printing:
Printing using metal powders or filaments.
The metal powder or filament is melted by laser or electron beam and built up layer by layer to form the part.
Suitable for aerospace, medical, automotive and other high-end manufacturing industries.
Post-treatment process:
Includes de-supporting, grinding, polishing, spraying, etc.
Improve the surface quality and performance of parts.
Summarize.
3D printed part customization offers buyers unprecedented flexibility and precision. By understanding the customization process, screening criteria, and technical processes, buyers can better communicate with 3D printing service providers to ensure that the parts are customized to meet their needs. Choosing a reputable service provider with strong technical capabilities will help improve the quality and delivery efficiency of parts and reduce production costs. We hope this guide will help buyers easily grasp the core knowledge of 3D printing part customization and contribute to the development of the manufacturing industry.