In today’s era of aesthetic economy, a product’s surface quality often determines its market competitiveness. As the preferred material in electronics, automotive parts, architectural decoration, and other fields, aluminum alloy’s surface treatment process not only affects the product’s visual appearance but also directly impacts its service life, functionality, and user experience. This article will deeply explore the characteristics, application scenarios, and selection strategies of various surface treatment processes in aluminum alloy housing CNC machining, helping readers fully understand the mysteries of this “surface engineering.”
I. Surface Treatment: More Than Just “Cosmetic Engineering”
1.1 Why Surface Treatment is Needed
After CNC machining of aluminum alloy housings, surface treatment is by no means a dispensable “cosmetic project” but has important functional significance:
- Corrosion protection: Although aluminum alloy itself has certain corrosion resistance, it can still oxidize and corrode in harsh environments. Surface treatment can form a dense protective film, significantly improving corrosion resistance.
- Wear resistance improvement: Pure aluminum is relatively soft, and surface treatment can increase surface hardness, improving wear resistance and scratch resistance.
- Appearance texture enhancement: Through different surface treatment processes, various texture effects such as matte, high-gloss, brushed, and frosted can be obtained to meet different product design requirements.
- Functionality enhancement: Certain surface treatments can also provide special functions such as conductivity, insulation, and antibacterial properties.
- Value addition: Exquisite surface treatment can significantly enhance product grade and market competitiveness.
1.2 Three Key Roles of Surface Treatment
From an engineering perspective, surface treatment mainly assumes three key roles:
- Protector: Isolates the metal substrate from the external environment, preventing corrosion and oxidation
- Beautician: Gives products unique visual effects and tactile experiences
- Function enhancer: Improves surface hardness, wear resistance, conductivity, and other properties
II. Detailed Explanation of Mainstream Surface Treatment Processes
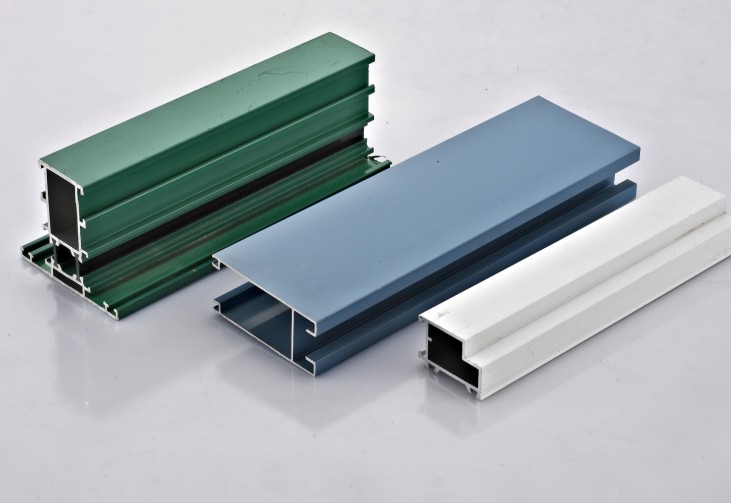
2.1 Anodizing: The Most Classic Surface Treatment Technology
Process principle: Anodizing is the process of placing aluminum alloy in an electrolyte solution and forming a dense aluminum oxide film on the metal surface through the action of an external electric current. This oxide film is usually between 5-20 microns thick and has extremely high hardness and corrosion resistance.
Main types:
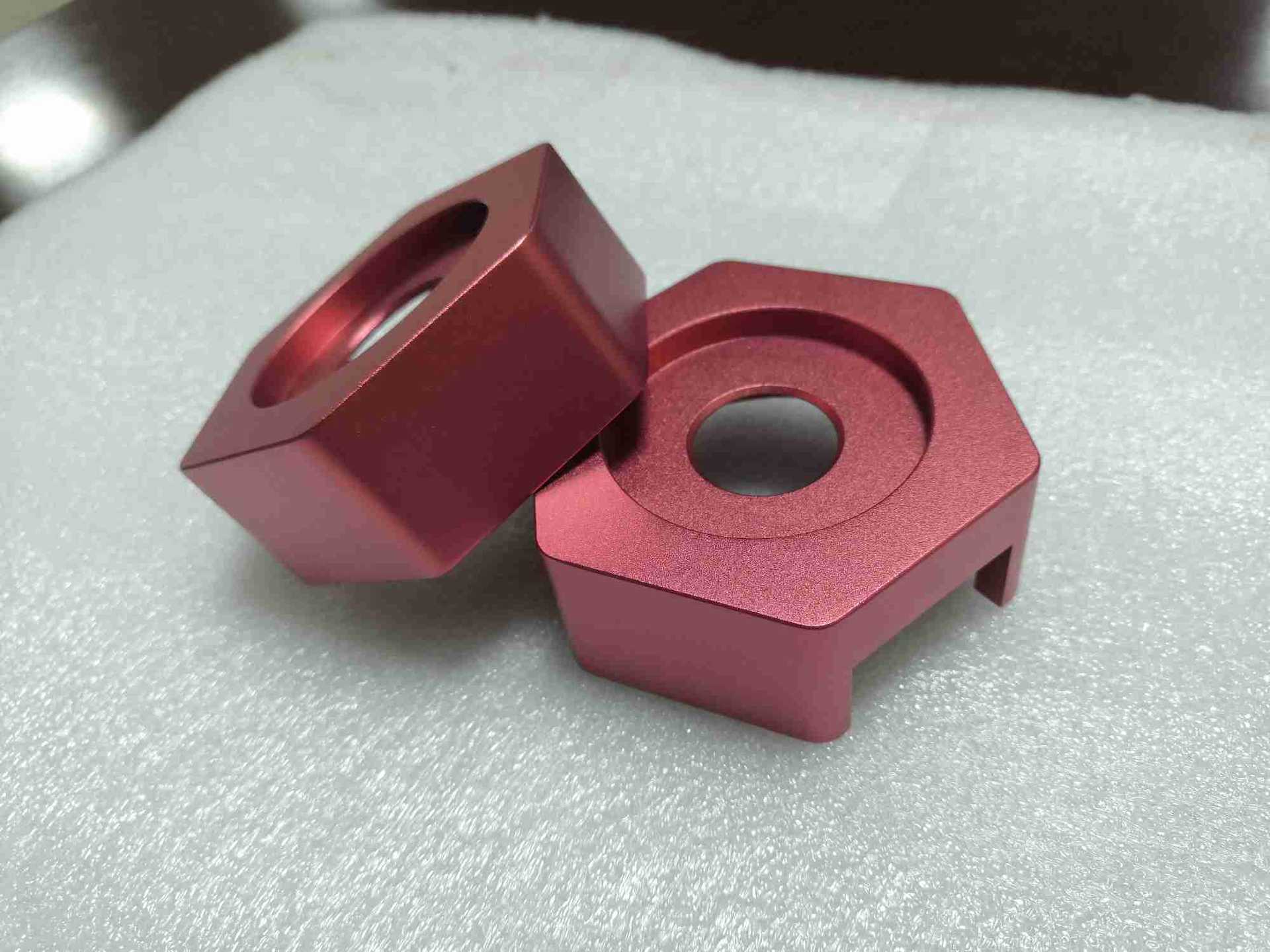
- Clear anodizing: Forms a colorless and transparent oxide film, maintaining the metal’s original luster
- Color anodizing: Obtains various colors through electrolytic coloring or dye impregnation
- Black anodizing: Special black oxidation process with good decorative effect
- Hard anodizing: Film thickness can reach 50-100 microns, with hardness comparable to hardened steel
Characteristics and advantages:
- High oxide film hardness (HV300-500), strong wear resistance
- Excellent corrosion resistance, can resist various chemical substances
- Has a microporous structure, facilitating coloring and sealing treatment
- Environmentally friendly and pollution-free, meeting modern manufacturing requirements
Application scenarios:
- Electronic product housings (mobile phones, laptops)
- Architectural decoration materials (curtain walls, doors, windows)
2.2 Sandblasting: Creating Matte Texture
Process principle: Sandblasting is the process of using compressed air to spray abrasives (such as quartz sand, alumina, glass beads, etc.) onto the metal surface at high speed, removing surface impurities and forming a uniform rough surface through the impact of the abrasives.
Main types:
- Glass bead sandblasting: Obtains a uniform matte surface with fine texture
- Alumina sandblasting: Stronger surface cleaning effect, suitable for removing stubborn stains
- Stainless steel shot sandblasting: Can form a compressive stress layer on the surface, improving fatigue strength
Process parameters:
- Sandblasting pressure: 2-6bar (adjusted according to material hardness)
- Sandblasting distance: 100-200mm
- Sandblasting angle: 45°-75°
- Abrasive particle size: Selected according to required roughness
Characteristics and advantages:
- Uniform surface without reflection, with unique matte texture
- Improves adhesion of subsequent coatings or oxide films
- Enhances the product’s fatigue strength
- Relatively low process cost
Application scenarios:
- Matte treatment of electronic product housings
- Surface treatment of medical devices
- Pretreatment of automotive parts
- Surface beautification of industrial equipment
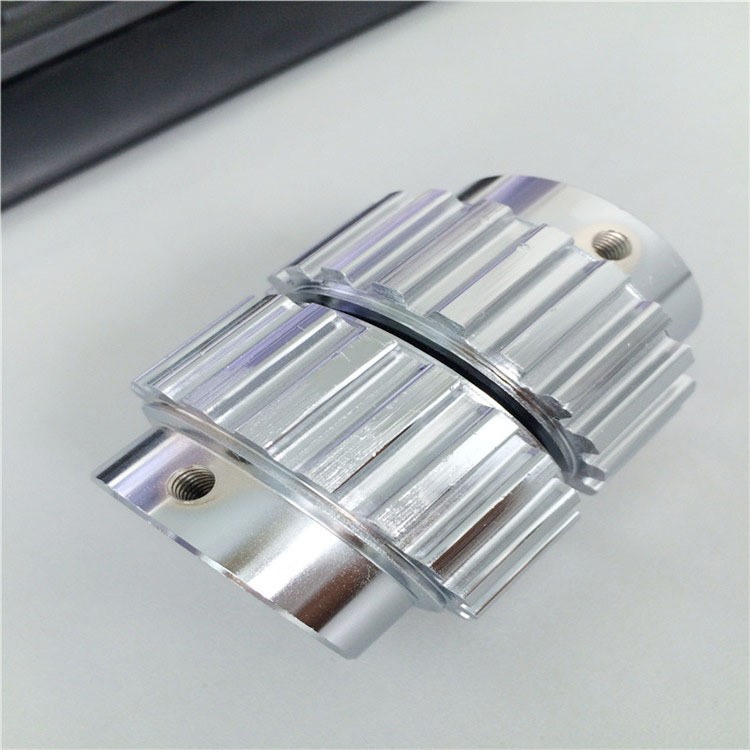
2.3 Brushing Process: Showing Metal Texture
Process principle: Brushing process is a mechanical method of repeatedly scraping fine 丝状 textures on the metal surface to form a directional metal texture surface. This process can clearly show every fine thread mark, making the metal matte surface emit fine hairline luster.
Main types:
- Straight line brushing: Forms parallel straight line textures
- Chaotic line brushing: Irregular texture direction, showing natural metal texture
- Spiral brushing: Forms concentric circular textures
Characteristics and advantages:
- Gives products a strong and elegant metal texture
- Has good anti-slip effect
- Higher wear resistance and easy to clean
- Can hide minor surface defects
Application scenarios:
- Automotive interior parts
2.4 Polishing Treatment: Pursuing Mirror Effect
Process principle: Polishing treatment is a process of reducing metal surface roughness through mechanical or chemical methods to obtain a smooth surface or mirror luster.
Main types:
- Mechanical polishing: Using sandpaper, polishing wheels and other tools for gradual grinding, can achieve mirror effect with Ra0.025μm
- Chemical polishing: Using selective dissolution of chemical reagents to obtain a uniform glossy surface
- Electrolytic polishing: Through electrochemical dissolution, surface micro-protrusions are preferentially dissolved, especially suitable for stainless steel
Characteristics and advantages:
- Extremely high surface finish with mirror effect
- Reduces surface friction resistance
- Easy to clean and disinfect
- Enhances the high-end feel of products
Application scenarios:
- High-end electronic product housings
- Decorative metal products
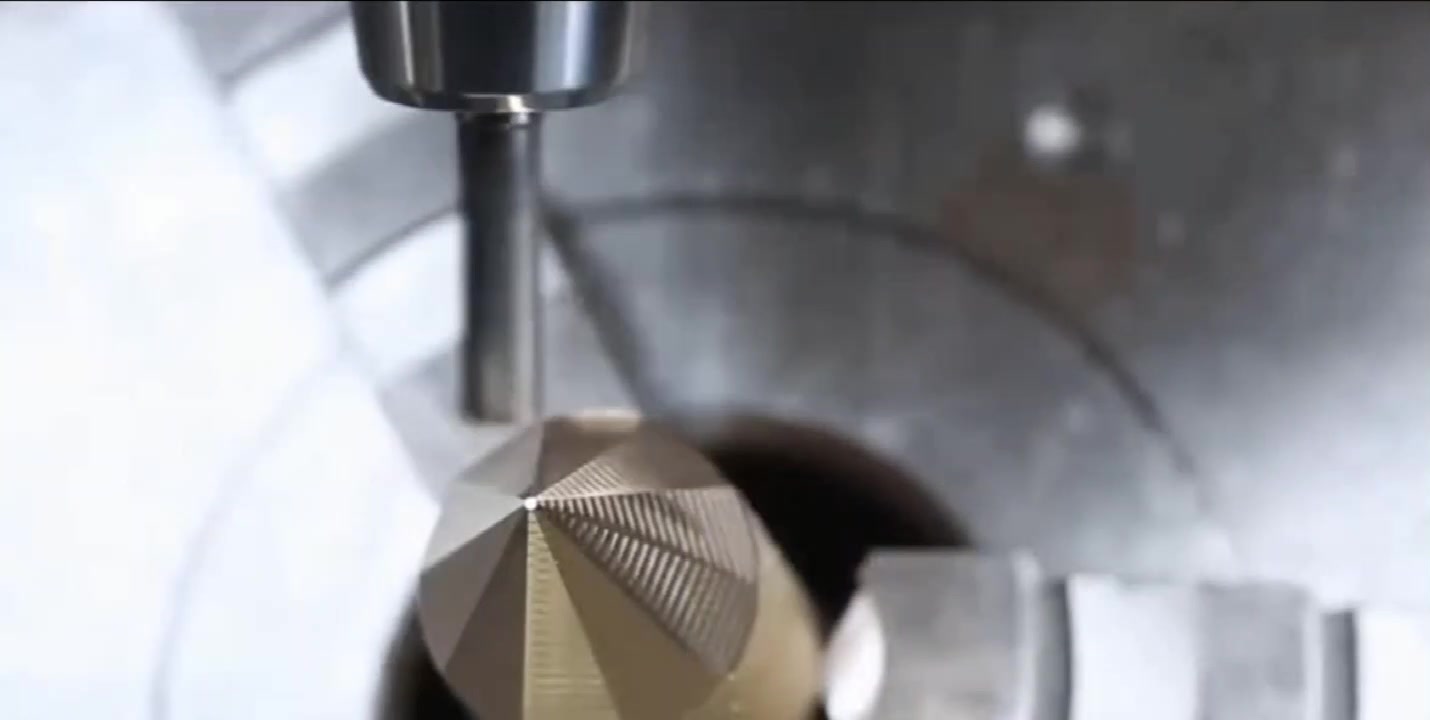
2.5 High-Gloss Milling: Embodiment of Technological Sense
Process principle: High-gloss milling uses precision engraving machines to process local high-gloss areas on the product surface. By precisely controlling the tool path and cutting parameters, high-gloss chamfers or bright grooves are formed on the metal surface.
Technical characteristics:
- Achieved using high-precision CNC equipment
- Tool speed up to 20000-40000rpm
- Surface roughness up to Ra0.01-0.02μm
- Can form sharp high-gloss lines on metal surfaces
Characteristics and advantages:
- Creates a strong sense of technology and fashion
- Sharp lines with extremely high precision
- Can be perfectly combined with other surface treatment processes
- Enhances the visual layering of products
Application scenarios:
- High-gloss chamfers on mobile phone metal frames
III. The Wisdom of Process Selection: How to Find the Most Suitable Solution
3.1 Consider Product Usage and Environment
Outdoor products:
- Priority selection of processes with good weather resistance
- Recommended: Fluorocarbon spraying, hard anodizing
- Avoid: Ordinary polishing, unsealed anodizing
Electronic products:
- Focus on appearance texture and feel
- Recommended: Anodizing, sandblasting, brushing
- Consider: Conductivity, heat dissipation requirements
Medical devices:
- Emphasize cleanliness and corrosion resistance
- Recommended: Electrolytic polishing, passivation treatment
- Comply with: Medical-grade surface treatment standards
3.2 Balance Cost and Effect
Cost ranking from low to high:
- Standard surface treatment (deburring, cleaning)
- Sandblasting treatment
- Chemical polishing
- Anodizing
- Mechanical polishing
- High-gloss milling
- PVD coating
Cost-effectiveness considerations:
- Mass production: Priority selection of mature and stable processes
- High-end products: Multiple process combinations can be considered
- Functional parts: Focus on performance rather than appearance
- Appearance parts: Appropriately increase surface treatment budget
3.3 The Art of Process Combination
Modern product design increasingly adopts combinations of multiple surface treatment processes:
Classic combination schemes:
- Sandblasting + Anodizing: Matte texture + color effect
- Brushing + High-gloss milling: Metal texture + technological lines
- Polishing + Electroplating: Mirror effect + metal luster
- Anodizing + Laser engraving: Color base + fine patterns
Design principles:
- Clear hierarchy, highlighting design focus
- Color coordination, avoiding excessive complexity
- Process complementarity, leveraging respective advantages
- Cost control, considering production feasibility
IV. Practical Case Analysis: From Requirements to Solutions
4.1 Case 1: Tablet Computer Housing
Product requirements:
- Appearance: Matte texture, high-end atmosphere
- Performance: Wear-resistant, drop-resistant, comfortable feel
- Function: Good heat dissipation
Solution: Sandblasting + Anodizing
- Sandblasting: Using 0.1-0.3mm alumina abrasive to obtain uniform matte surface
- Anodizing: 15-20μm oxide film to improve wear resistance and corrosion resistance
- Effect: Comfortable feel, low-key luxury appearance
4.2 Case 2: High-end Mobile Phone Middle Frame
Product requirements:
- Appearance: Strong sense of technology, sharp lines
- Performance: High hardness, scratch-resistant
- Process: Multiple effect combinations
- Positioning: Flagship product
Solution: CNC machining + High-gloss milling + Anodizing
- CNC machining: High-precision forming
- High-gloss milling: Frame high-gloss chamfering
- Anodizing: Black oxide film to enhance texture
- Effect: Coexistence of technological sense and luxury
4.3 Case 3: Industrial Equipment Panel
Product requirements:
- Appearance: Simple and practical, not easily soiled
- Performance: Chemical corrosion resistance
- Function: Good identification
- Environment: Industrial workshop environment
Solution: Brushing + Screen printing
- Brushing treatment: Straight line brushing, easy to clean
- Screen printing: Clear identification and scales
- Effect: Practical and beautiful, easy to maintain
V. Development Trends of Surface Treatment Technology
5.1 Rise of Environmental Protection Processes
With increasing environmental requirements, green surface treatment technologies have become the development direction:
- Chromium-free passivation: Replacing traditional chromate treatment
- Low-temperature processes: Reducing energy consumption and environmental impact
- Water-based coatings: Reducing organic solvent usage
- Recycling: Circulation and reuse of process waste liquids
5.2 Intelligence and Automation
- Online detection: Real-time monitoring of surface treatment quality
- Automatic control: Precise control of process parameters
- Robot applications: Automated polishing, brushing, etc.
- AI optimization: Intelligent selection of optimal process parameters
5.3 Functional Surface Treatment
Future surface treatment will pay more attention to functionality:
- Self-cleaning surfaces: Superhydrophobic, oleophobic coatings
- Antibacterial surfaces: Special treatments that inhibit bacterial growth
- Smart surfaces: Coatings that can respond to environmental changes
- Conductive coatings: Meeting the needs of the 5G era
VI. Conclusion: The Art and Science of Surface Treatment
Surface treatment of aluminum alloy housing CNC machining is both a technology and an art. It requires us to find the best balance between technical feasibility, cost control, and design requirements.
Choosing the right surface treatment process can not only enhance the product’s appearance texture but also improve its functionality and service life. From classic anodizing to modern high-gloss milling, from practical sandblasting to exquisite brushing, each process has its unique charm and application scenarios.
In today’s constantly developing manufacturing industry, surface treatment technology is also continuously innovating. The emergence of environmental protection processes, intelligent control, functional coatings and other new technologies provides more possibilities for product design. As designers and manufacturers, we need to continuously learn and explore, applying the latest surface treatment technologies to products to create more competitive products.
Remember, excellent surface treatment is not just “cosmetic engineering,” but also an important manifestation of product quality and brand value. In this era where both appearance and strength are valued, mastering the “secrets” of surface treatment can help you stand out in the fierce market competition.