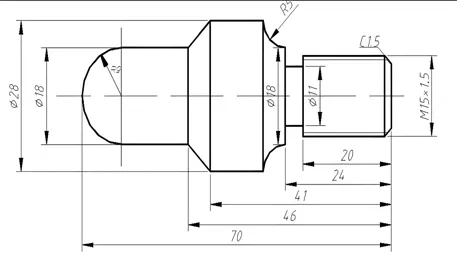
Introduction.
3D printing technology has undergone remarkable development since it was introduced in the United States in 1986. As a revolutionary manufacturing technology, 3D printing has brought unprecedented innovation to the manufacturing industry by transforming digital models into physical products by stacking materials layer by layer. Custom 3D printed parts, as one of the important applications of 3D printing technology, have gradually received extensive attention from both academia and industry for their unique performance, cost-effectiveness, wide range of applications, high quality, health and harmlessness, and high degree of customization. In this paper, we will review the research related to customized 3D printed parts in terms of product performance, cost, usage, quality, health, and customization.
Performance
Customized 3D printed parts excel in terms of performance.3D printing technology allows the use of a wide range of materials, including metals, ceramics, and plastics, which have different physical, chemical, and mechanical properties to meet the needs of different application scenarios. For example, metal 3D printing technologies such as selective laser melting (SLM), electron beam selective melting (EBSM) and laser near-net-shaping (LENS) allow for the fabrication of metal parts with high strength, high hardness and good corrosion resistance, which are widely used in aerospace, microelectronics and medical applications.
Cost
Custom 3D printed parts offer significant cost advantages over traditional manufacturing processes. First, 3D printing technology reduces raw material waste and lowers material costs by precisely controlling the amount of material used. Second, 3D printing technology streamlines the production process, reducing equipment, labor and time costs. In addition, custom 3D printed parts can be produced in small batches and personalized, avoiding the inventory pressure and capital consumption associated with mass production.
Uses
Custom 3D printed parts have a wide range of uses, covering almost all areas of manufacturing. In the aerospace field, 3D printed parts can be used to manufacture key components such as engine parts and vehicle structural parts. In the medical field, 3D printing technology can be used to create customized prosthetics, orthotics, surgical guides, and biological implants. In addition, 3D printed parts play an important role in automotive, military, jewelry, education and other fields.
Quality
The quality of customized 3D printed parts depends on a number of factors, including equipment performance, material selection, process parameters, and post-processing procedures. Advanced 3D printers excel in accuracy, stability, and speed to create 3D parts with high precision and complex shapes. Material selection is critical to the quality of the part. Different materials have different physical and chemical properties that directly affect the durability, strength and toughness of the part. The setting of process parameters, such as laser power, scanning speed, layer thickness and fill mode, directly affects the printing effect and quality of the part. Quality post-treatment processes, such as heat treatment, surface preparation and dimensional correction, can further improve part quality.
Health
Custom 3D printed parts excel in health. materials used in 3D printing technology, such as PLA (Polylactic Acid) and ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), are rigorously screened and tested to ensure that they do not contain any hazardous substances such as formaldehyde and benzene. During use, these materials do not release harmful gases or substances and have no effect on human health. In addition, 3D printing technology can also be used to manufacture medical implants and prosthetics, etc. These products need to undergo strict biocompatibility testing to ensure that they are harmless to the human body.
Customization
The biggest advantage of custom 3D printed parts is their high degree of customization. With the help of 3D printing technology, it is possible to manufacture products that are personalized to the needs and physical condition of the customer. For example, in the medical field, 3D printing technology can customize personalized prosthetics and orthotics based on a patient’s bone structure and physical condition to improve comfort and fit. In the jewelry field, 3D printing technology can create unique jewelry accessories according to customers’ design requirements and preferences. In addition, 3D printing technology can be used to manufacture customized automotive parts, aerospace components, etc.
Conclusion
In summary, custom 3D printed parts excel in terms of performance, cost, usage, quality, health and customization. With the continuous development and improvement of 3D printing technology, custom 3D printed parts will play an important role in more fields. In the future, it is foreseeable that 3D printing technology will be cross-fertilized with more disciplines to promote further development and innovation in manufacturing.