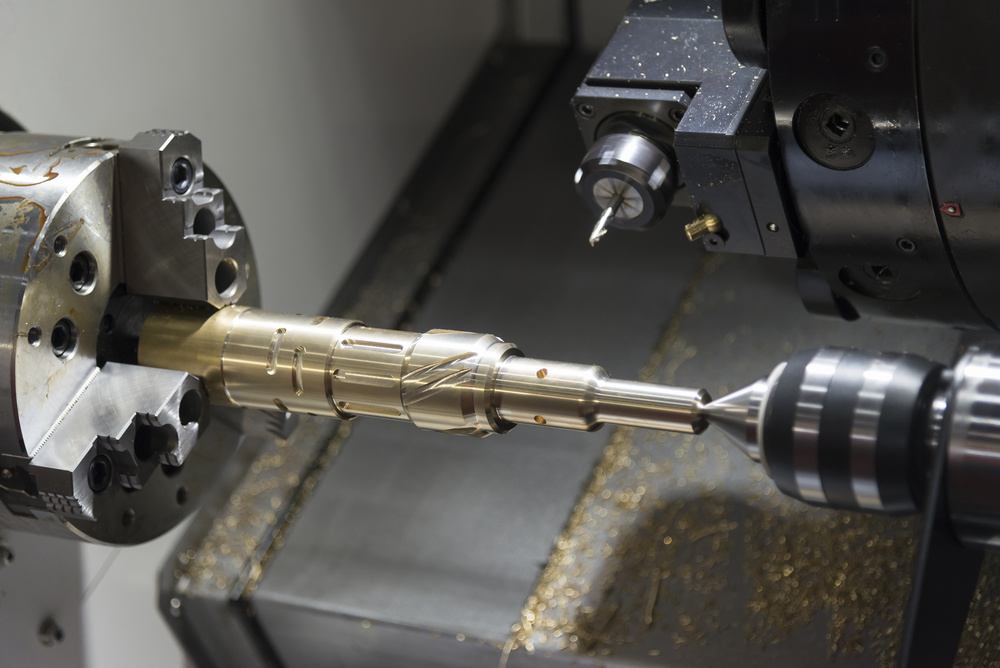
Introduction
1. Brass Material Properties
1.1 Key Characteristics
- Density: 8.4-8.7 g/cm³
- Hardness: 50-160 HB
- Tensile Strength: 250-550 MPa
- Elongation: 5-65%
- Melting Point: 885-940°C
- Electrical Conductivity: 26-40% IACS
- Thermal Conductivity: 115-150 W/m·K
- Corrosion Resistance: Excellent in most environments
- Machinability: 80-100% rating
1.2 Advantages for Machining
- Excellent Machinability: Low cutting forces, good chip control
- Corrosion Resistance: Suitable for harsh environments
- Conductivity: Ideal for electrical applications
- Aesthetic Appeal: Natural golden finish, easy to polish
2. Common Brass Alloys
2.1 Free-Cutting Brass (C36000)
- Copper: 60.0-63.0%
- Zinc: Balance
- Lead: 2.5-3.7%
- Iron: ≤0.35%
- Machinability: 100%
- Tensile Strength: 340-550 MPa
- Hardness: 70-160 HV
- Density: 8.50 g/cm³
2.2 Other Common Alloys
|
Alloy
|
Composition
|
Machinability
|
Key Applications
|
|
C26000
|
Cu 68-71%, Zn 29-32%
|
65%
|
Electrical connectors, heat exchangers
|
|
C46400
|
Cu 59-62%, Zn 35-37%, Sn 0.8-1.2%
|
70%
|
Marine hardware, valves, pump components
|
|
C23000
|
Cu 84-86%, Zn 14-16%
|
60%
|
Plumbing, heat exchangers, architectural
|
|
C35300
|
Cu 57-61%, Zn 32-36%, Pb 3.0-4.5%
|
95%
|
Bearings, threaded components, gears
|
3. CNC Machining Processes
3.1 Turning
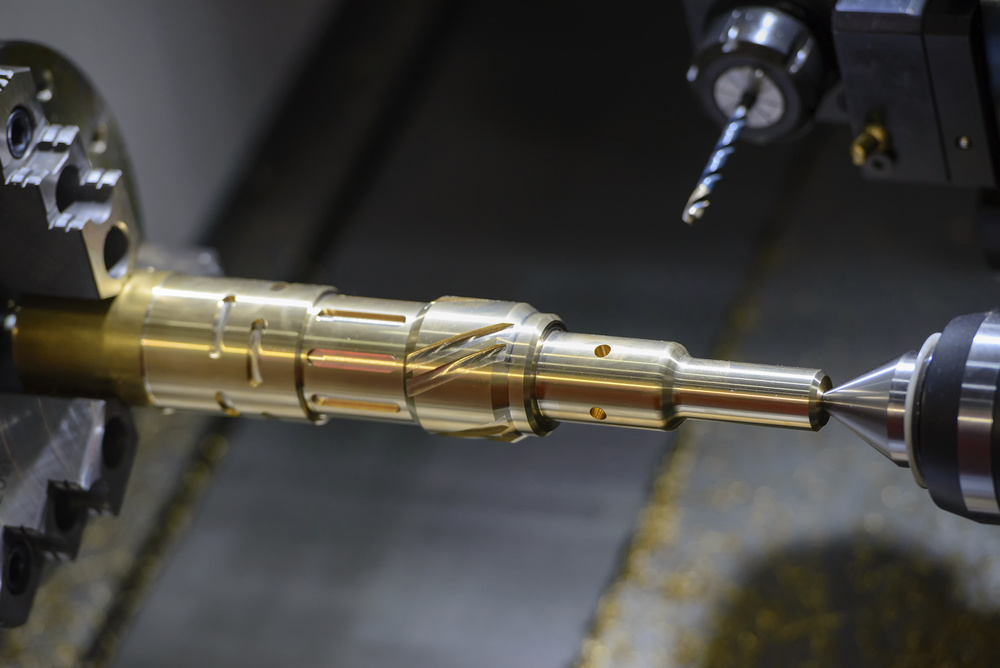

- Spindle Speed: 1500-3000 RPM
- Feed Rate: 0.1-0.3 mm/rev
- Cutting Depth: 0.5-2mm
- Tolerances: ±0.005-0.01mm
- Surface Finish: Ra 0.4-1.6μm
3.2 Milling
- Spindle Speed: 3000-6000 RPM
- Feed Rate: 200-800 mm/min
- Cutting Depth: 0.2-1mm
- Tolerances: ±0.01-0.02mm
- Surface Finish: Ra 0.4-1.6μm
3.3 Drilling and Tapping
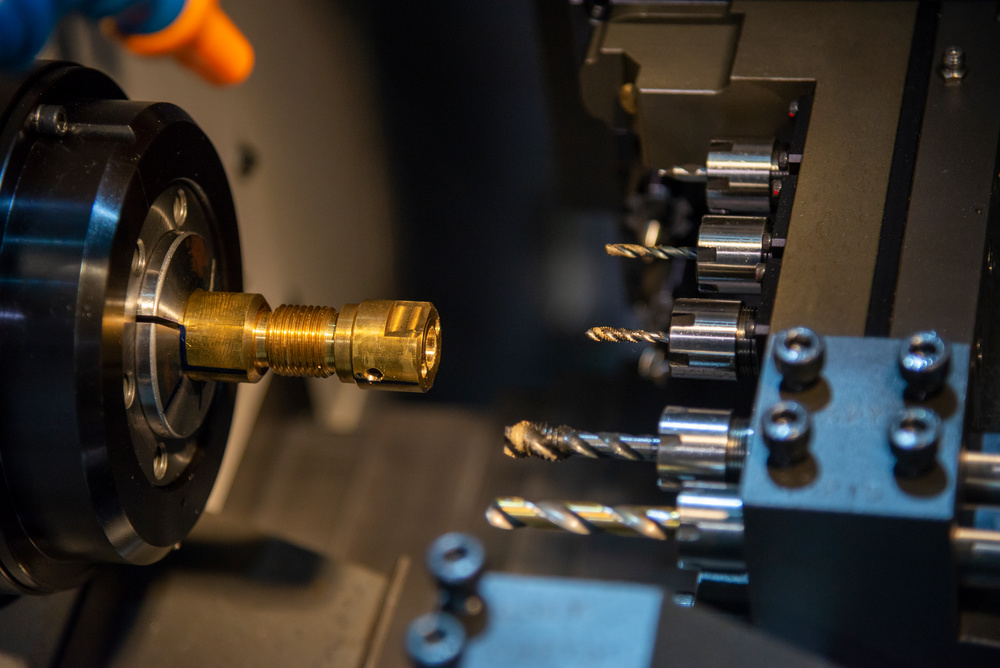

- Spindle Speed: 4000-8000 RPM
- Feed Rate: 50-200 mm/min
- Hole Diameters: 0.5-50mm
- Tolerances: ±0.01-0.03mm
- Spindle Speed: 500-2000 RPM
- Thread Sizes: M1 to M60
- Tolerances: 4H-6H
- Surface Finish: Ra 1.6-6.3μm
3.4 Surface Finishing

- Polishing: Ra 0.025-0.1μm (mirror finish)
- Grinding: Ra 0.2-0.8μm
- Brushing: Decorative linear finishes
- Nickel Plating: Corrosion resistance
- Chrome Plating: Hard, decorative finish
- Gold Plating: Conductivity and appearance
- Tin Plating: Solderability
4. Tool Selection and Parameters
4.1 Tool Materials
- Advantages: High wear resistance, high speeds
- Coatings: TiN, TiAlN, AlTiN
- Applications: High-volume production
- Advantages: Lower cost, good toughness
- Limitations: Lower wear resistance
- Applications: Low-volume production
4.2 Optimal Parameters
|
Operation
|
C36000
|
C26000
|
C46400
|
|
Turning
|
1500-3000
|
1200-2500
|
1000-2000
|
|
Milling
|
3000-6000
|
2500-5000
|
2000-4000
|
|
Drilling
|
4000-8000
|
3500-7000
|
3000-6000
|
- Turning: 0.1-0.3 mm/rev
- Milling (2-flute): 0.05-0.1 mm/flute
- Milling (4-flute): 0.025-0.075 mm/flute
4.3 Coolant Requirements
- Soluble Oil: 5-10% concentration
- Synthetic Coolants: Longer life, better cooling
- Semi-Synthetic: Balanced performance
- Flood cooling (most common)
- Mist cooling (reduced usage)
- Through-tool cooling (direct to cutting zone)
5. Quality Control
5.1 Tolerance Standards
|
Process
|
Standard Tolerance
|
Precision Tolerance
|
|
Turning
|
±0.01mm
|
±0.005mm
|
|
Milling
|
±0.02mm
|
±0.01mm
|
|
Drilling
|
±0.03mm
|
±0.015mm
|
- IT7-IT8: Standard precision
- IT6: High precision
- IT5: Ultra-precision
5.2 Surface Finish Requirements
|
Operation
|
Surface Finish (Ra)
|
|
Rough Turning
|
6.3-12.5μm
|
|
Finish Turning
|
0.8-1.6μm
|
|
Milling
|
0.4-1.6μm
|
|
Grinding
|
0.2-0.8μm
|
|
Polishing
|
0.025-0.1μm
|
6. Industry Applications
6.1 Key Sectors
- Components: Connectors, terminals, heat sinks
- Requirements: 26%+ IACS conductivity, ±0.01mm tolerance
- Components: Pipe fittings, valves, pumps
- Standards: ASTM B584, NSF/ANSI 61
- Components: Fuel systems, brake parts, electrical
- Requirements: -40°C to 150°C temp range, 5000 psi pressure
- Components: Surgical instruments, connectors
- Standards: ISO 13485, FDA 21 CFR Part 820
- Components: Hardware, lighting, fixtures
- Finishes: Polished, brushed, antiqued
7. Troubleshooting Guide
7.1 Common Issues and Solutions
- Causes: Excessive speed, inadequate coolant
- Solutions: Reduce speed, improve coolant system
- Causes: Dull tools, incorrect feed rate
- Solutions: Replace tools, optimize parameters
- Causes: Thermal expansion, tool deflection
- Solutions: Temperature control, reduce cutting forces
- Causes: Incorrect tool geometry, poor coolant
- Solutions: Proper tool selection, improve evacuation
8. Process Optimization
8.1 Efficiency Improvement
- High-Speed Machining: Increase spindle speeds
- Multi-Tasking Machines: Combine operations
- Automation: Robotic loading/unloading
- Tool Management: Optimize changes and inventory
- Optimized toolpaths
- Chip thinning techniques
- Plunge milling for deep cavities
- Trochoidal milling strategies
8.2 Cost Analysis
- Material cost (stock and scrap)
- Labor cost (setup and operation)
- Tool cost (cutting tools, holders)
- Machine cost (depreciation, maintenance)
- Material optimization
- Process efficiency
- Quality control improvement
- Supplier management
9. Future Trends
9.1 Advanced Technologies
- Complex geometry in single setup
- Reduced setup time
- Improved accuracy
- IoT integration for monitoring
- AI optimization
- Digital twin simulation
9.2 Sustainable Practices
- Dry machining
- Minimum quantity lubrication
- Energy efficiency
- Scrap recycling
- REACH and RoHS compliance
- Proper waste management
- Energy conservation
Conclusion
Technical Reference Tables
Alloy Comparison
|
Alloy
|
Machinability
|
Tensile Strength
|
Hardness
|
Key Applications
|
|
C36000
|
100%
|
340-550 MPa
|
70-160 HV
|
Fasteners, connectors
|
|
C26000
|
65%
|
300-420 MPa
|
60-100 HB
|
Electrical, heat exchangers
|
|
C46400
|
70%
|
380-480 MPa
|
90-120 HB
|
Marine, valves
|
|
C23000
|
60%
|
320-400 MPa
|
70-100 HB
|
Plumbing, architectural
|
Machining Parameters
|
Operation
|
Speed Range
|
Feed Range
|
Depth of Cut
|
|
Turning
|
1500-3000 RPM
|
0.1-0.3 mm/rev
|
0.5-2mm
|
|
Milling
|
3000-6000 RPM
|
200-800 mm/min
|
0.2-1mm
|
|
Drilling
|
4000-8000 RPM
|
50-200 mm/min
|
0.1-0.5mm
|
|
Tapping
|
500-2000 RPM
|
Pitch × RPM
|
Progressive
|
Surface Finish Standards
|
Process
|
Ra Range
|
Application
|
|
Roughing
|
6.3-12.5μm
|
Functional surfaces
|
|
Finishing
|
0.8-1.6μm
|
General purpose
|
|
Precision
|
0.4-0.8μm
|
Critical components
|
|
Mirror
|
0.025-0.1μm
|
Decorative parts
|
Disclaimer
- All information, opinions, and data contained in this article are for the purpose of information transmission only and do not constitute any advice on investment, transactions, law, medical care, or other matters.
- The content of the article is compiled based on public information or created based on the author’s personal understanding. Although every effort is made to ensure accuracy, it does not guarantee the completeness, accuracy, and timeliness of the information, nor does it bear any responsibility for any losses caused by the use of the content of this article.
- If the article involves third-party opinions, pictures, data, and other content, the copyright belongs to the original author. In case of infringement, please contact us for deletion.
- Readers should make independent decisions based on their actual situation and combined with professional opinions. The user shall bear all consequences arising from the use of the content of this article.