Table of Contents
- Overall Equipment Structure Design
- Spindle System Core Technology
- Feed Drive System
- Tool Magazine and Automatic Tool Changer
- Control System and Programming Technology
- Precision Control and Measurement
- Cooling and Lubrication System
- Safety Protection Design
- Maintenance and Service Technology
- Application Fields and Technical Advantages
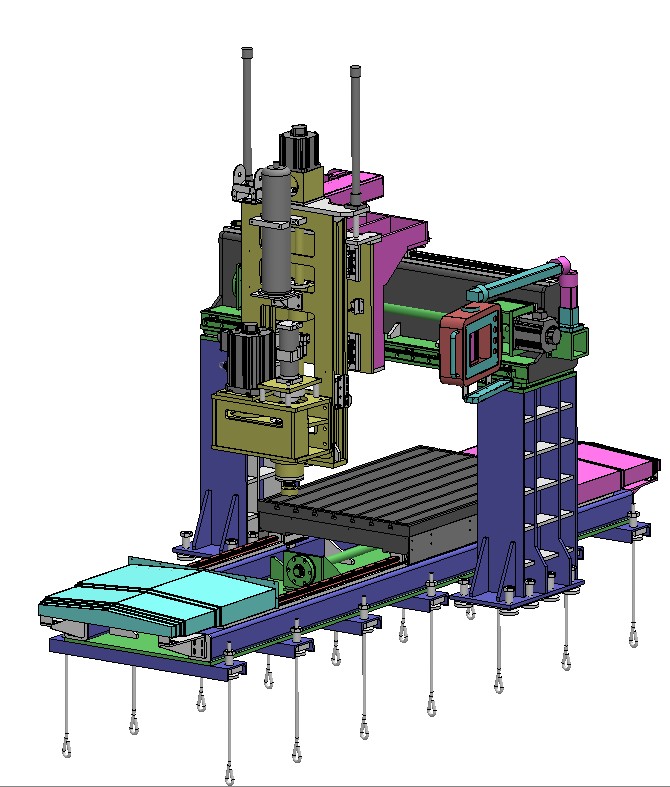
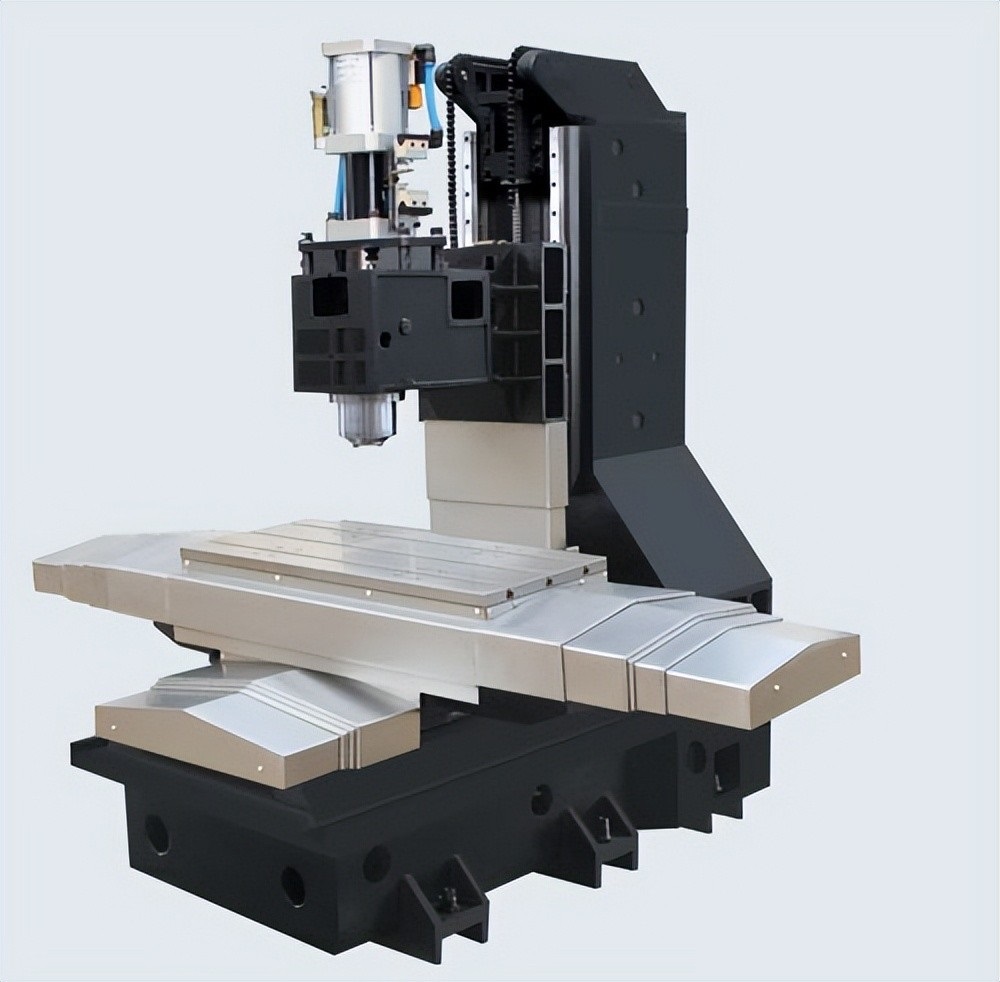
Overall Equipment Structure Design
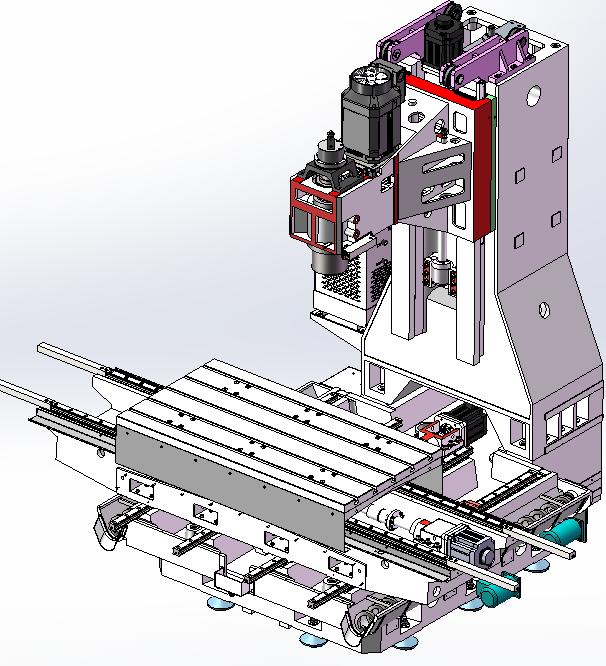
- Machine Base – Provides stable foundation support, constructed from high-strength cast iron or granite materials
- Column – Supports the spindle head, requiring excellent rigidity and vibration resistance
- Spindle Head – Houses the spindle assembly, enabling rotational movement of the spindle
- Worktable – Carries the workpiece, achieve ing X, Y, Z axis feed movements
- Tool Magazine – Stores and manages cutting tools, supporting automatic tool changing functionality
- Control System – Implements digital control of the machining process
- Rigid Design – Optimized using finite element analysis to ensure machining stability
- Thermal Symmetric Design – Reduces the impact of temperature changes on precision
- Modular Design – Facilitates maintenance and functional expansion
- Ergonomic Design – Optimized operator interface and maintenance access
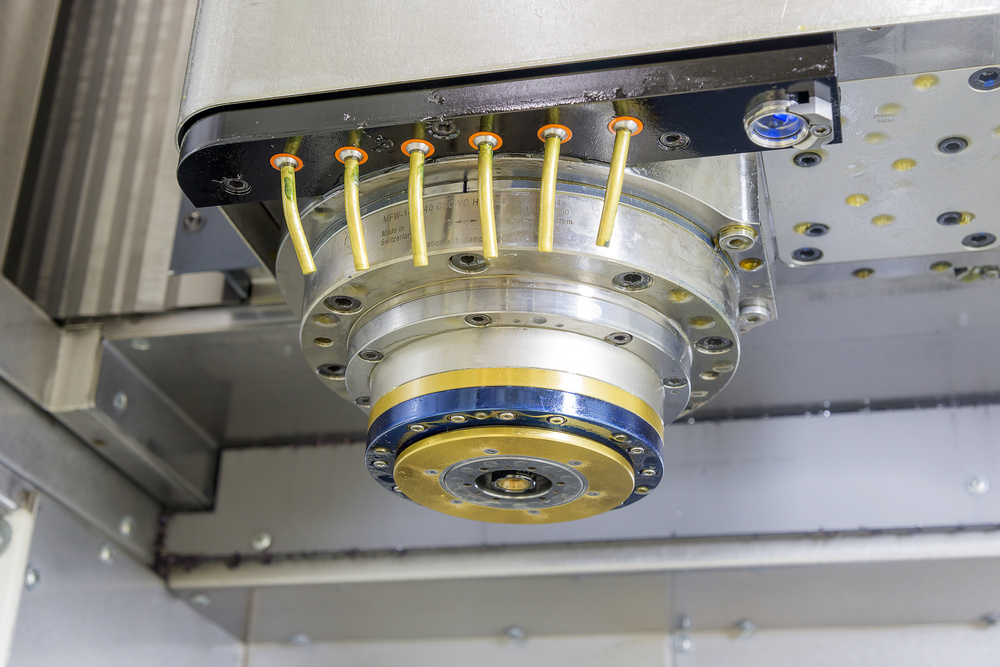
Spindle System Core Technology

|
Parameter Item
|
Technical Specification
|
Technical Features
|
|
Spindle Speed
|
8000-15000 RPM
|
Variable frequency control, constant power output
|
|
Spindle Taper
|
BT40/BT50
|
High-precision taper 配合
|
|
Spindle Motor Power
|
7.5-22 kW
|
Direct servo motor drive
|
|
Axial/Radial Runout
|
≤0.003mm
|
High-precision bearing support
|
- High-Precision Bearings – Utilizing ceramic bearings or precision angular contact ball bearings
- Oil Mist Lubrication – Ensuring proper lubrication and cooling of bearings at high speeds
- Spindle Temperature Control – Active temperature control system maintains stable spindle temperature
- Dynamic Balancing Technology – Reduces vibration during high-speed rotation
- Belt Drive – Suitable for medium-low speed spindles, cost-effective
- Direct Drive – Motor directly drives the spindle, high transmission precision
- Motorized Spindle – Motor rotor integrated with spindle, speeds up to 40000 RPM
Feed Drive System
- Servo Motor – Provides power output, utilizing AC servo motors
- Ball Screw – Converts rotational motion to linear motion
- Guideway System – Ensures motion precision and stability
- Position Detection – Real-time position feedback
- High-Precision Ball Screws – Pitch error compensation, positioning accuracy up to ±0.005mm
- Linear Guideways – Low friction coefficient, smooth motion
- Servo Control System – Achieves precise control of position, speed, and torque
- Dynamic Error Compensation – Real-time compensation of motion errors
|
Axis
|
Rapid Traverse Speed
|
Feed Rate
|
Positioning Accuracy
|
|
X-axis
|
30-48 m/min
|
1-24 m/min
|
±0.003mm
|
|
Y-axis
|
30-48 m/min
|
1-24 m/min
|
±0.003mm
|
|
Z-axis
|
24-36 m/min
|
1-18 m/min
|
±0.003mm
|
Tool Magazine and Automatic Tool Changer
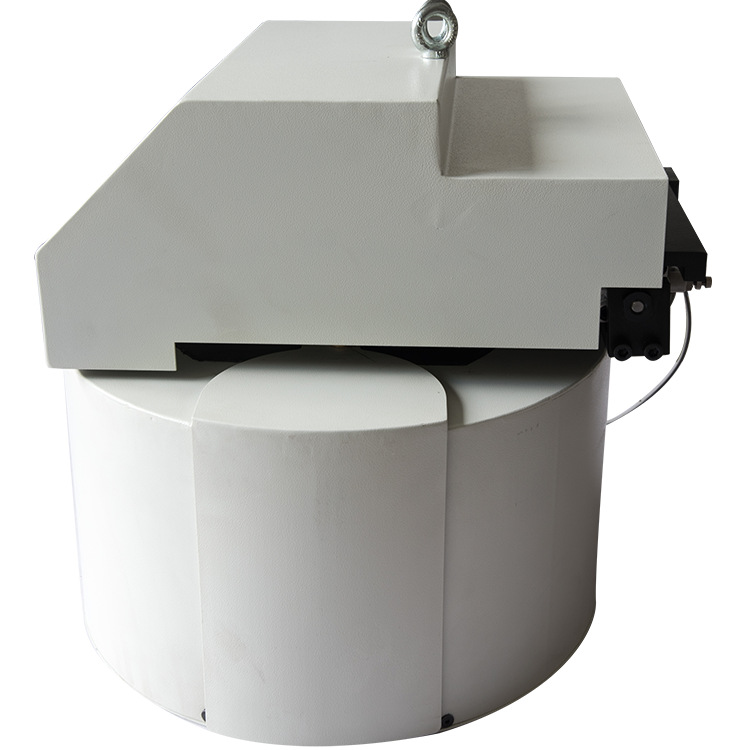

1. Turret-Type Tool Magazine
- Capacity: 16-24 tools
- Tool Change Time: 8-12 seconds
- Structural Features: Simple structure, cost-effective
- Application: Small to medium batch production
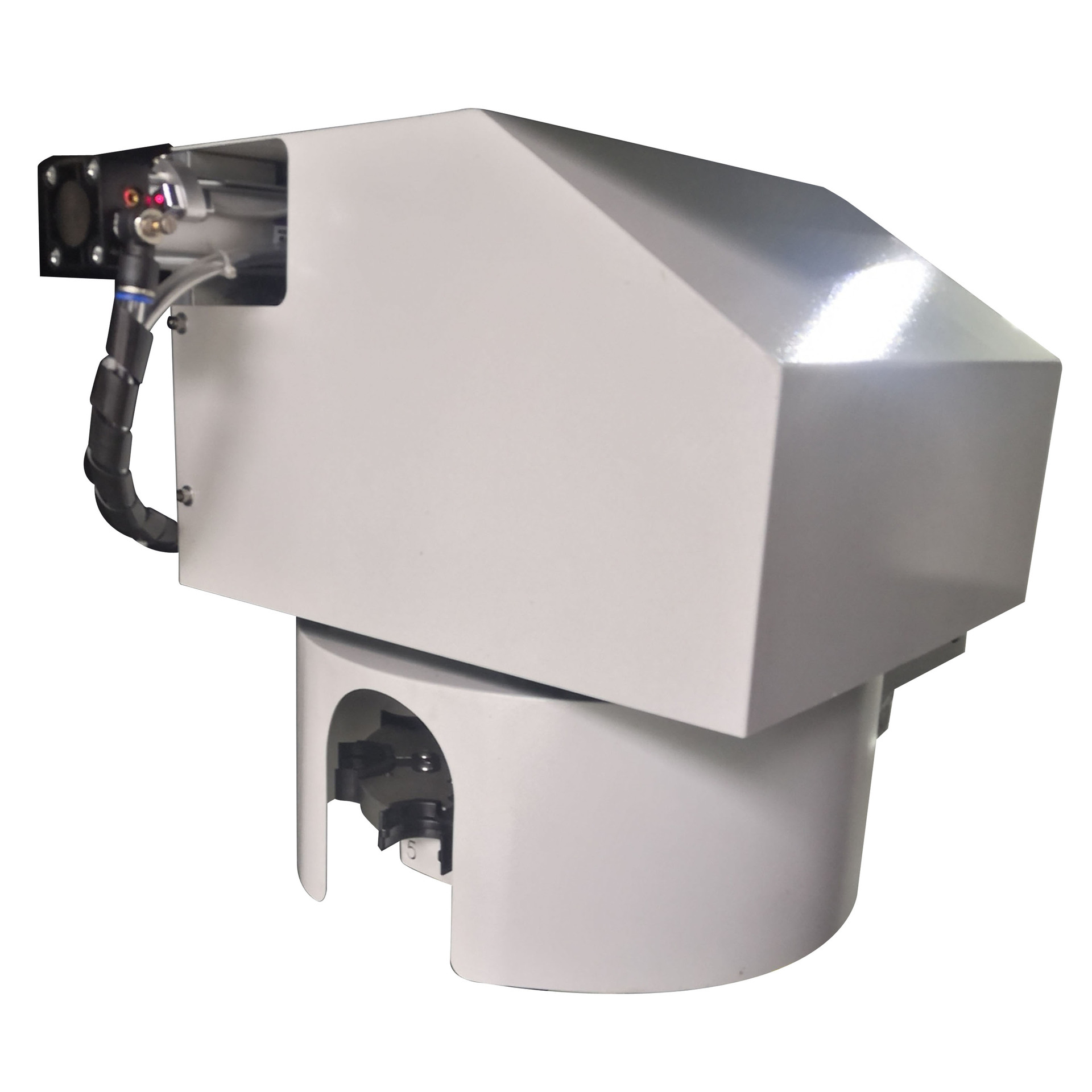

2. Disc-Type Tool Magazine
- Capacity: 20-40 tools
- Tool Change Time: 6-8 seconds
- Structural Features: Compact footprint, fast tool change
- Application: Medium batch production
3. Chain-Type Tool Magazine
- Capacity: 40-120 tools
- Tool Change Time: 12-15 seconds
- Structural Features: Large capacity, expandable
- Application: Large batch complex part machining
- Robot Arm Tool Change – Cam or hydraulic driven, precise movement
- Tool Position Detection – Photoelectric sensors confirm tool position
- Tool Identification – RFID or encoder disc for tool information
- Automatic Tool Length Compensation – Tool length measurement and compensation

- Tool Life Management – Monitors tool usage time and cutting cycles
- Tool Breakage Detection – Real-time tool condition monitoring
- Tool Presetting – Offline tool parameter setting
- Tool Change Optimization – Optimizes tool change sequence to reduce time
Control System and Programming Technology
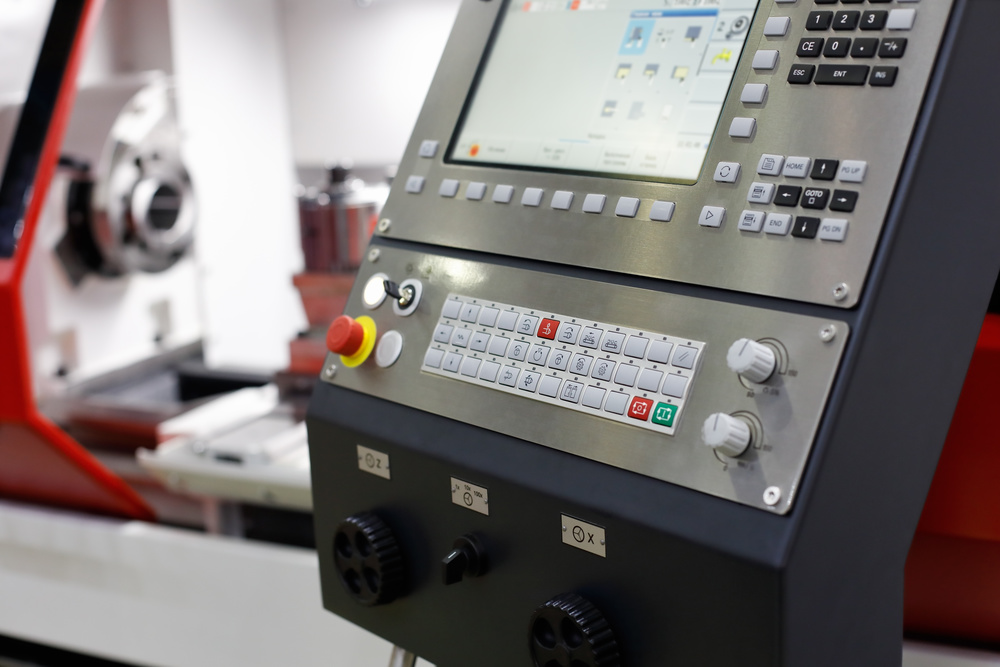

1. Fanuc Series 0i-MF
- Control Axes: Up to 6-axis simultaneous control
- Program Storage: 32MB memory, expandable to 2GB
- Special Features: AI contour control, high-speed high-precision machining
- User Interface: Color LCD display, user-friendly operation
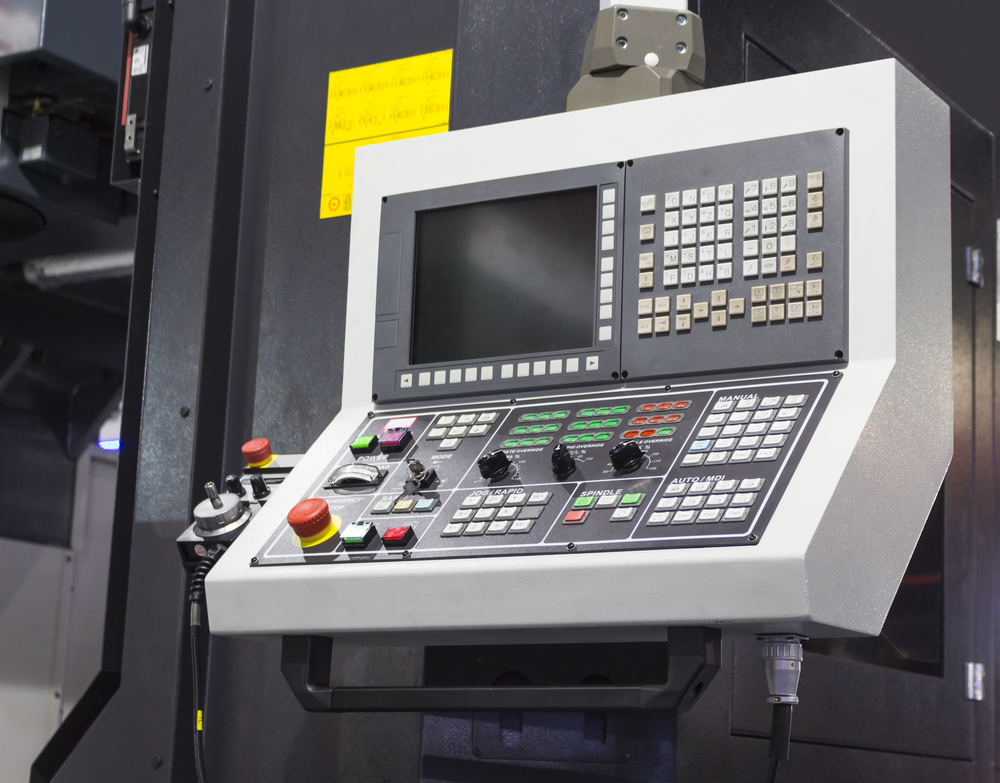

2. Siemens SINUMERIK 828D
- Control Axes: Up to 5-axis simultaneous control
- Programming Method: ShopMill/ShopTurn conversational programming
- Special Features: 3D simulation, collision detection
- Network Functionality: Industrial Ethernet support
3. Mitsubishi M80
- Control Axes: Up to 8-axis simultaneous control
- Processing Speed: 32-bit RISC processor
- Special Features: High-speed look-ahead control
- Communication Interfaces: USB, Ethernet, RS232
- G-code Programming – Standard CNC programming language
- M-code Programming – Auxiliary function control
- Macro Programming – Custom cycle programs
- CAD/CAM Integration – Computer-aided programming
- High-Speed Look-Ahead – Preprocessing of machining paths
- Adaptive Control – Adjusts feed rate based on cutting load
- Error Compensation – Geometric error and thermal error compensation
- Remote Monitoring – Real-time equipment status monitoring
Precision Control and Measurement

1. Geometric Precision
- Positioning Accuracy: ±0.003-±0.005mm
- Repeatability: ±0.002-±0.003mm
- Straightness: 0.002mm/m
- Perpendicularity: 0.002mm/m
2. Motion Precision
- Circular Interpolation Accuracy: ±0.003mm
- Thread Machining Accuracy: ISO 4H/5g
- Surface Roughness: Ra 0.8-3.2μm
3. Machining Precision
- Dimensional Accuracy: IT5-IT7 grade
- Geometric Tolerances: 0.005-0.01mm
- Surface Quality: Mirror finish achievable
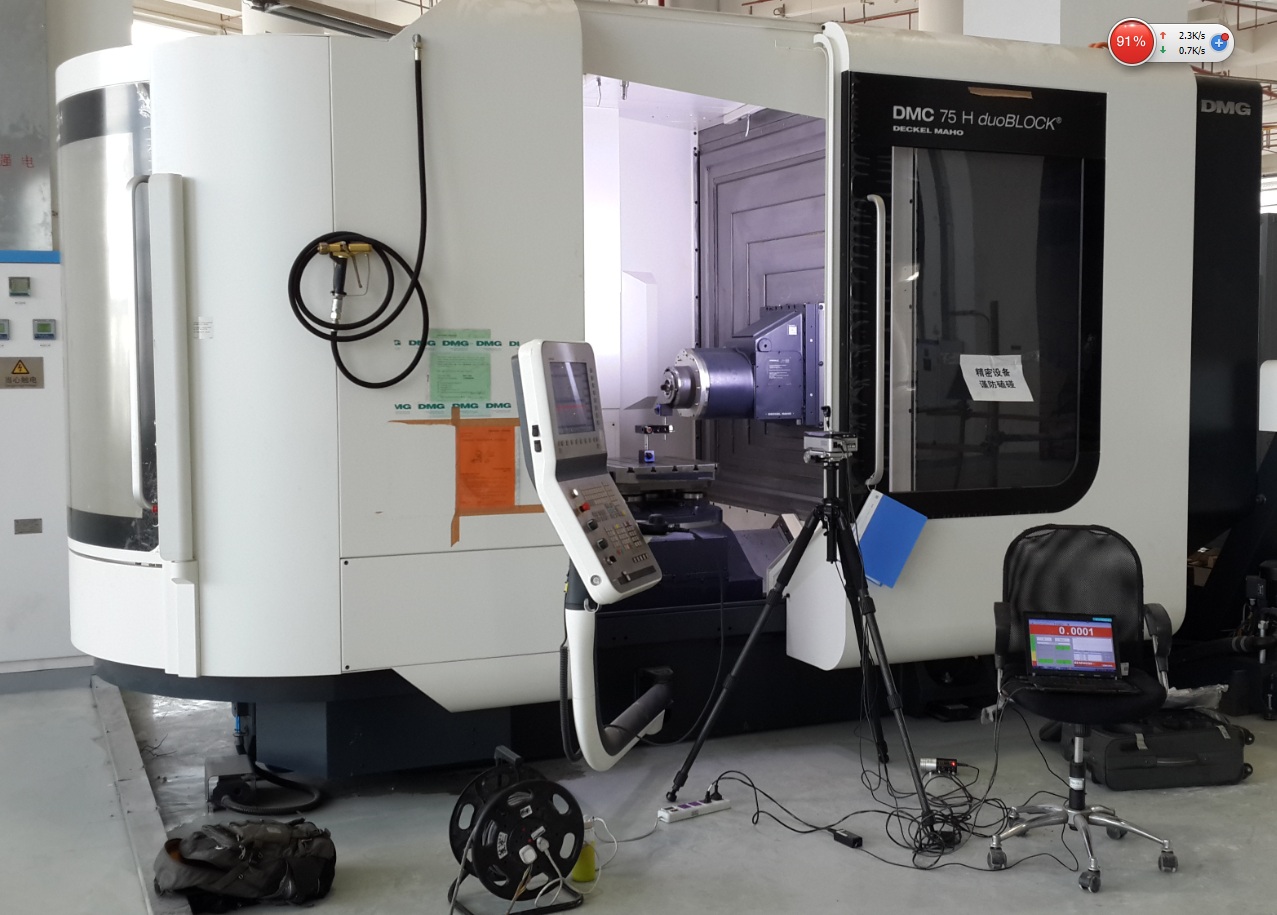

- Laser Interferometer – Measures positioning accuracy and geometric errors
- Ballbar Testing – Evaluates dynamic accuracy and servo performance
- Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) – Verifies final workpiece accuracy
- In-Process Measurement – Real-time precision monitoring during machining
- Temperature Control – Workshop temperature maintained at 20±2°C
- Vibration Isolation – Anti-vibration foundations and damping measures
- Error Compensation – Geometric, thermal, and load error compensation
- Regular Calibration – Precision calibration according to standards
Cooling and Lubrication System

1. Cutting Fluid Cooling System
- Function: Cools tools and workpiece, flushes away chips
- Types: Emulsions, synthetic coolants, oil-based cutting fluids
- Circulation Method: Pump circulation, filtration precision 20-50μm
- Cooling Capacity: 5-20kW cooling capacity

2. Spindle Cooling System
- Cooling Method: Oil or water cooling
- Temperature Control Precision: ±1°C
- Flow Control: Automatic adjustment based on spindle load
- Heat Dissipation Capacity: Matches spindle power requirements
3. Machine Cooling System
- Cooling Objects: Electrical cabinet, servo motors, ball screws
- Cooling Method: Air or liquid cooling
- Temperature Control: Maintains stable operating temperature
- Energy-Saving Design: Intelligent temperature control, on-demand cooling
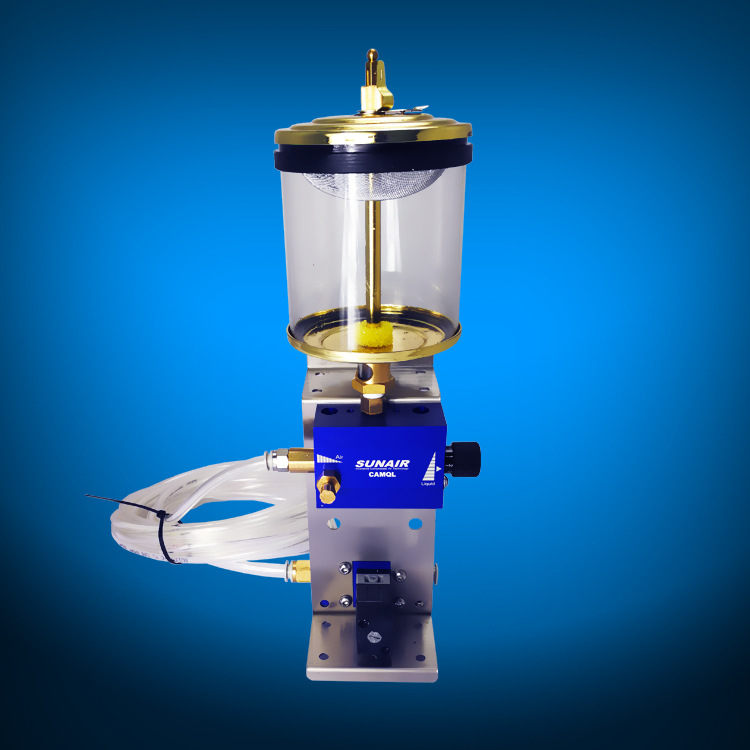

- Lubrication Methods: Oil-air lubrication, grease lubrication
- Lubrication Points: Ball screws, guideways, spindle bearings
- Lubrication Cycle: Programmable automatic lubrication
- Condition Monitoring: Real-time monitoring of lubrication system status
- Intelligent Control – Automatic adjustment based on machining conditions
- Energy Efficiency – Optimized cooling and lubrication parameters, reduced energy consumption
- Maintenance-Friendly – Modular design for easy maintenance
- Environmental Compliance – Meets environmental protection standards
Safety Protection Design

1. Mechanical Protection
- Safety Doors – Interlock protection, machine stops when door opens
- Protective Covers – Prevent chip and coolant splashing
- Emergency Stop Buttons – Rapid machine shutdown in emergency situations
- Safety Locks – Prevent unauthorized operation
2. Electrical Safety
- Overload Protection – Motor overload and short circuit protection
- Earth Leakage Protection – Protection against electrical equipment leakage
- Overvoltage Protection – Voltage anomaly protection
- EMC Protection – Electromagnetic compatibility protection
3. Control System Safety
- Program Protection – Machining program password protection
- Operation Permissions – Multi-level user permission management
- Error Detection – Program error and operation error detection
- Emergency Stop – Multiple emergency stop circuits
- ISO 13849 – Machinery safety standard
- IEC 61508 – Functional safety standard
- CE Certification – European safety certification
- OSHA Standards – American occupational safety standards
- Area Monitoring – Hazardous area intrusion detection
- Status Display – Real-time display of equipment operating status
- Alarm System – Fault and abnormal condition alarms
- Log Recording – Safety event and operation logging
Maintenance and Service Technology

1. Daily Maintenance
- Cleaning – Equipment exterior and work area cleaning
- Lubrication Check – Lubrication system oil level and quality inspection
- Cooling System – Coolant level and concentration check
- Air Pressure System – Air pressure and leakage inspection
2. Periodic Maintenance
- Guideway and ball screw cleaning and lubrication
- Filter inspection and cleaning
- Electrical cabinet cooling inspection
- Safety device function check
- Spindle system condition inspection
- Servo motor temperature check
- Hydraulic system pressure inspection
- Tool clamping system check
- Precision measurement and calibration
- Transmission system backlash inspection
- Electrical system insulation test
- Software backup and updates
3. Annual Maintenance
- Comprehensive precision measurement and adjustment
- Spindle bearing condition assessment
- Servo system performance testing
- Control system function check
|
Maintenance Interval
|
Maintenance Item
|
Maintenance Content
|
Responsible Person
|
|
Daily
|
Routine Inspection
|
Cleaning, lubrication, level checks
|
Operator
|
|
Weekly
|
Regular Inspection
|
Guideway lubrication, filter cleaning
|
Technician
|
|
Monthly
|
In-depth Inspection
|
Spindle inspection, hydraulic system
|
Engineer
|
|
Annual
|
Comprehensive Maintenance
|
Precision calibration, system testing
|
Professional Service
|
- Fault Codes – System fault code analysis
- Condition Monitoring – Equipment operating status monitoring
- Diagnostic Tools – Specialized diagnostic software and tools
- Spare Parts Management – Critical spare parts inventory management
Application Fields and Technical Advantages
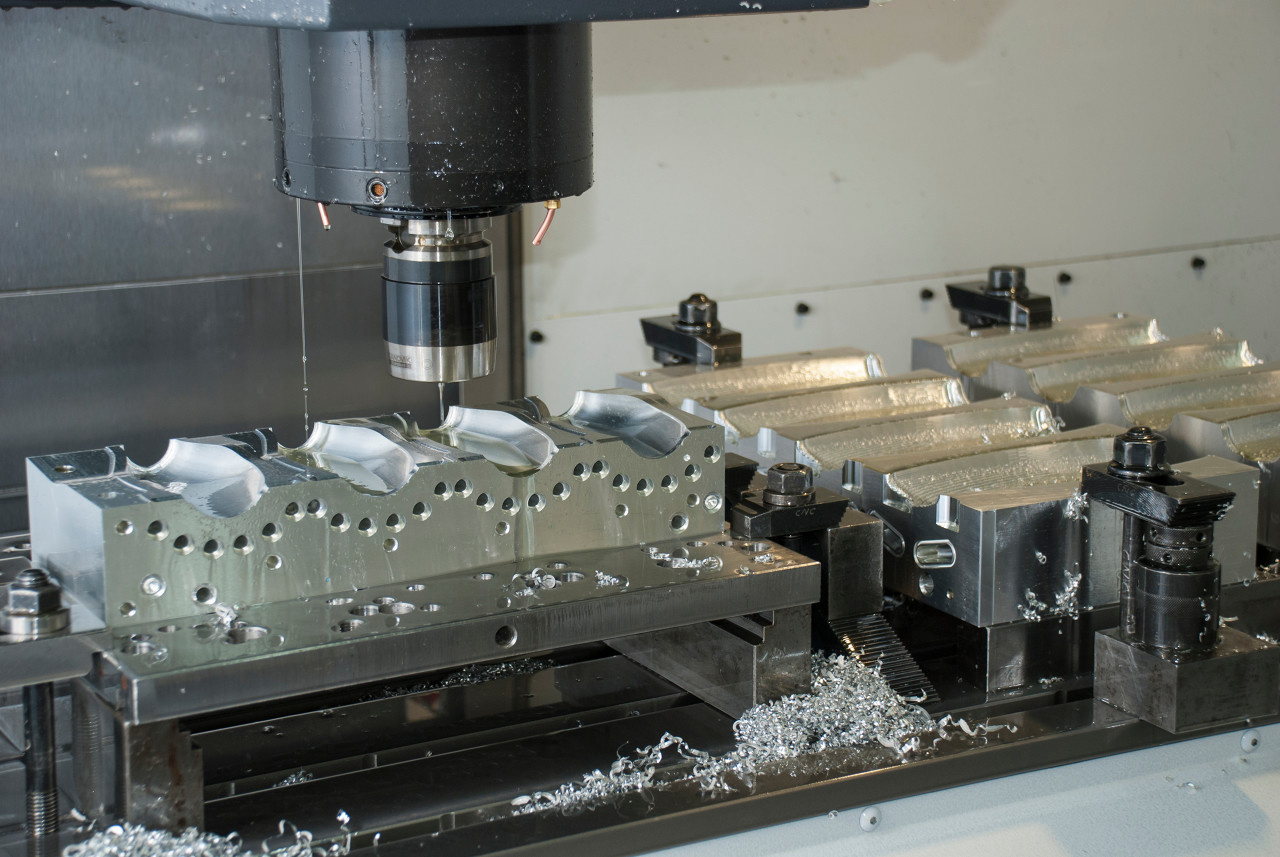

1. Aerospace Manufacturing
- Application Components: Engine parts, structural components, landing gear parts
- Technical Requirements: High precision, high reliability, complex shapes
- Material Processing: Titanium alloys, aluminum alloys, high-temperature alloys
- Quality Standards: AS9100 certification, strict quality control

2. Automotive Manufacturing
- Application Components: Engine blocks, transmission parts, chassis components
- Technical Requirements: High volume, high efficiency, good consistency
- Production Features: High automation, flexible manufacturing
- Quality Standards: IATF16949 certification
3. Medical Device Manufacturing
- Application Components: Surgical instruments, implants, medical equipment parts
- Technical Requirements: Ultra-high precision, excellent surface quality, biocompatibility
- Material Requirements: Titanium alloys, stainless steel, ceramic materials
- Quality Standards: ISO13485 certification
4. Mold Manufacturing
- Application Components: Plastic molds, stamping dies, die casting molds
- Technical Requirements: Complex surface machining, high precision, surface quality
- Processing Features: Single-piece small batch, high customization
- Technical Challenges: Deep cavity machining, micro-machining
- High-Precision Machining – Positioning accuracy up to ±0.003mm
- High-Efficiency Production – Automatic tool change, reduced auxiliary time
- Flexible Manufacturing – Rapid changeover, adaptable to multiple product types
- Complex Shape Machining – Multi-axis simultaneous machining of complex surfaces
- High Automation Level – Enables unmanned production
- Stable Quality – Consistent machining quality and reliability
- Production Efficiency – 3-5 times improvement compared to traditional machines
- Labor Costs – Reduced labor requirements, lower labor costs
- Quality Costs – Reduced scrap rates, lower quality costs
- Return on Investment – Typically 2-3 year payback period
Summary and Future Outlook
- Higher Precision – Positioning accuracy moving toward nanometer level
- Higher Speed – Continued increase in spindle speeds and feed rates
- Intelligentization – Integration of AI technology for adaptive machining
- Green Technology – Continuous improvement of energy-saving and environmental protection technologies
- Integration – Deep integration with CAD/CAM systems
- Networking – Implementation of factory network management
- 5-Axis Machining Technology – Complex parts completed in single setup
- Additive Manufacturing Integration – Combination of CNC machining with 3D printing technology
- Digital Twin Technology – Synchronization of virtual simulation with actual machining
- Industry 4.0 Integration – Core component of smart factories
- ISO 230-1:2012 – Test code for machine tools
- ISO 10791-1:2014 – CNC milling machines
- GB/T 18400.1-2010 – Machine tools safety standards
- DIN 8603 – Accuracy of machine tools