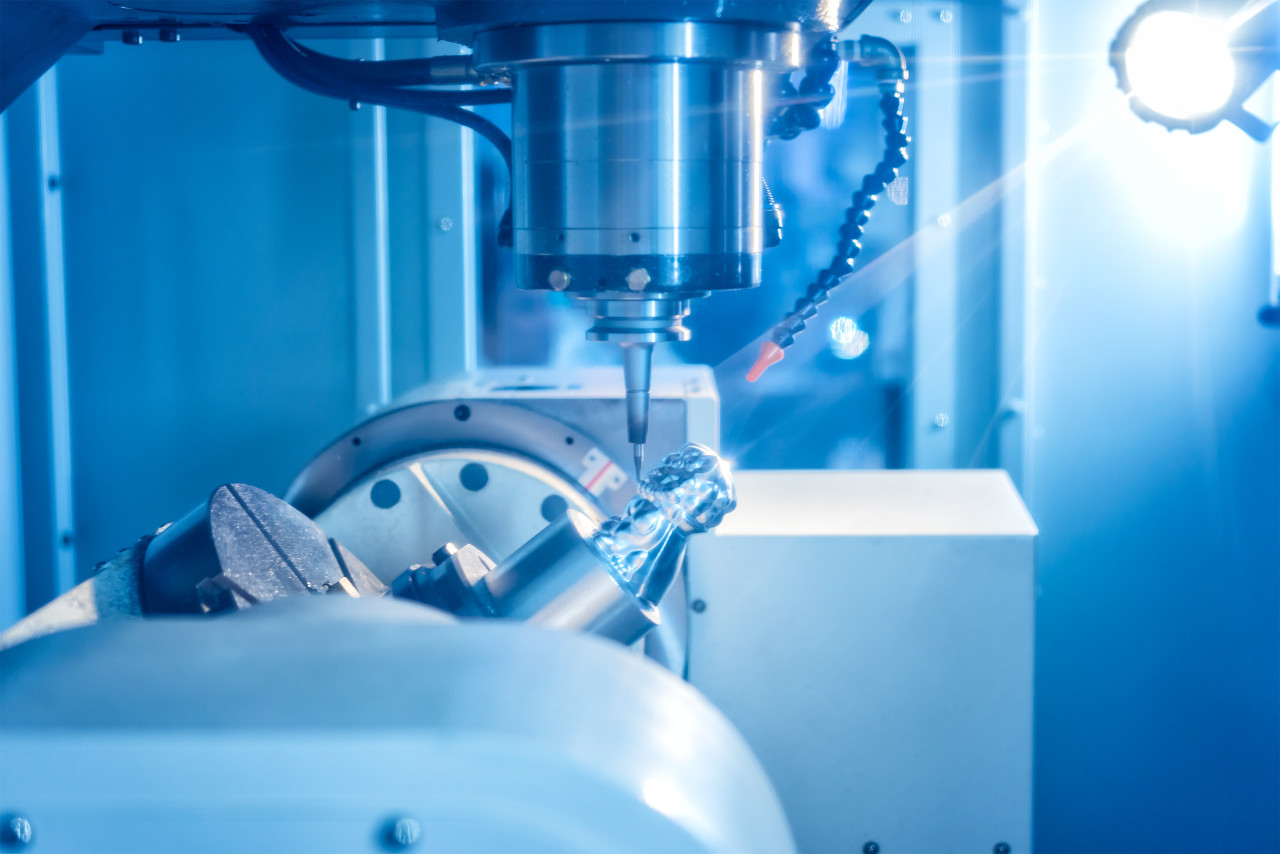
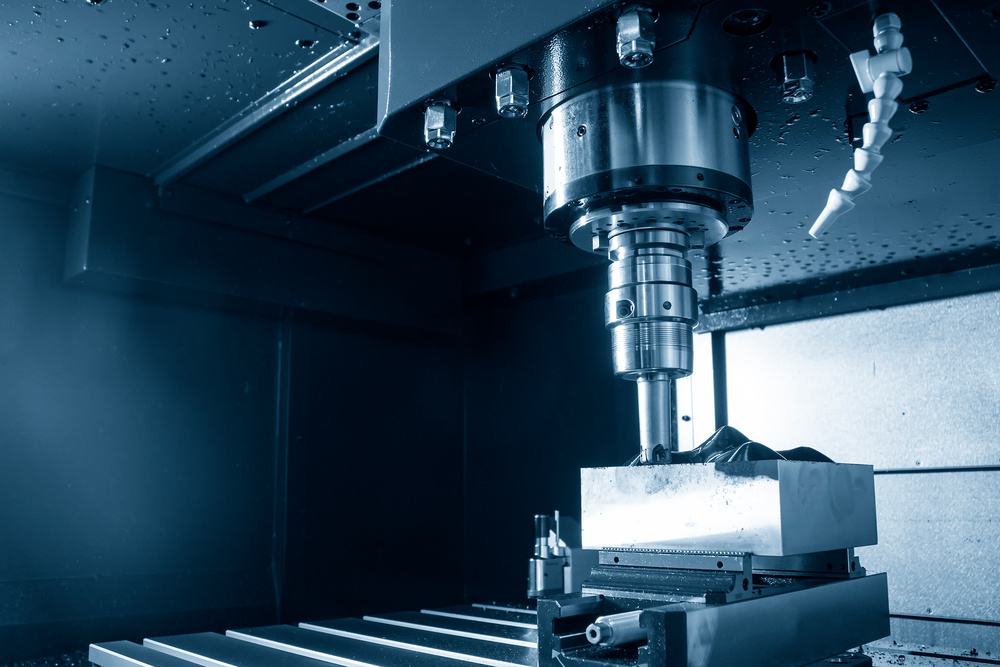
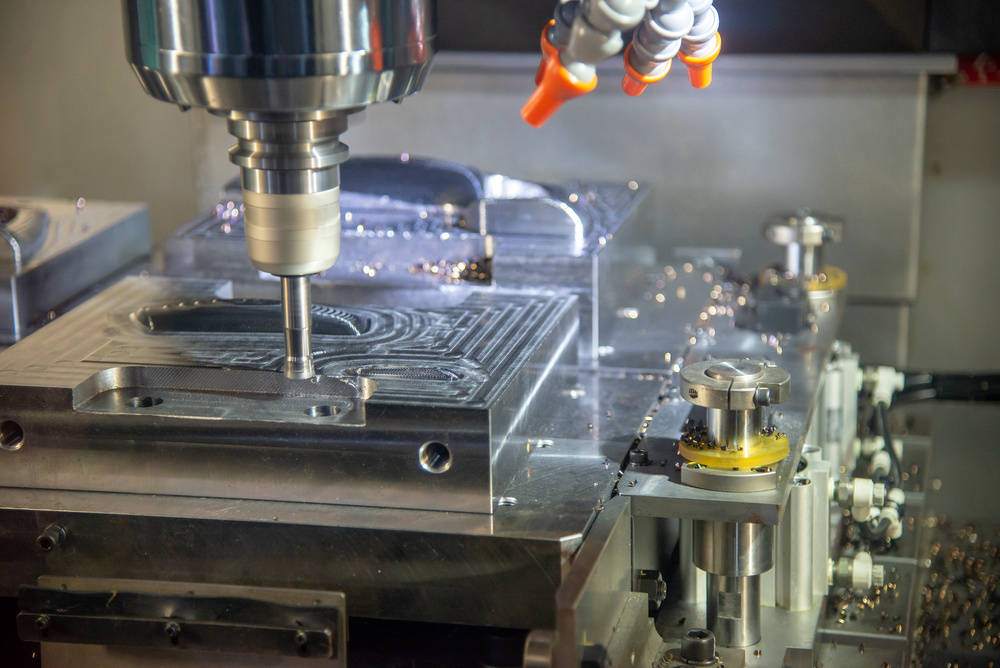
In modern CNC machining workshops, we are often captivated by precision machine tools, complex parts, and advanced technology, yet few people notice the silently working “invisible hero” – cutting fluid. at first glance ordinary, it plays an irreplaceable role in the CNC machining process. This article will take you deep into the mysteries of cutting fluids and explore how they become an indispensable element in CNC machining.
I. Understanding Cutting Fluids: More Than Just “Lubricants”
1.1 What is Cutting Fluid?
Cutting fluid, also known as cutting oil, coolant, or lubricant, is an industrial fluid specifically used in metal cutting processes. It is primarily used to lubricate and cool cutting tools and the metal being processed, making it an essential auxiliary material in CNC machining.
In terms of composition, cutting fluids can be formulated from petroleum distillates, animal fats, vegetable oils, water, air, or other chemical components. These ingredients are scientifically proportioned to form cutting fluid products with specific properties.
1.2 Ten Key Characteristics of High-Quality Cutting Fluids
To be an excellent cutting fluid, it must possess the following key characteristics:
- Excellent thermal conductivity: Capable of effectively transferring heat and quickly reducing temperatures in the cutting area
- High heat capacity: Can absorb large amounts of heat before boiling
- Low viscosity: Good fluidity, easy to distribute in the machining area
- Chemical stability: Does not damage tools or workpiece materials
- Rust and corrosion prevention: Protects workpieces and equipment from rust and oxidation
- Safety: Harmless to humans and the environment
- Chemical inertness: Does not react adversely with machining surfaces
- Low odor: Does not leave pungent odors on equipment
- Transparency: Remains clear for easy observation of the machining process
- Long service life: Does not deteriorate easily during use and storage
II. The Three Core Functions of Cutting Fluids
2.1 Lubrication: The “Lubricant” That Reduces Friction
Cutting fluid forms an oil film on the surfaces of workpieces and tools. This oil film can:
- Reduce tool wear: Extend tool service life
- Lower cutting resistance: Reduce energy consumption during machining
- Improve surface quality: Avoid edge burrs and enhance machining precision
This lubrication effect can even penetrate the smallest metal gaps and irregular areas, ensuring smooth machining processes.
2.2 Cooling: The “Coolant” That Controls Temperature
Extremely high temperatures, reaching 600-1000 degrees Celsius, can be generated during cutting processes. The cooling effect of cutting fluid:
- Reduces thermal deformation: Minimizes thermal deformation of tools and workpieces
- Maintains machining precision: Ensures dimensional stability
- Supports high-speed machining: Allows for higher cutting speeds
Especially for materials with low thermal conductivity like stainless steel, the cooling effect of cutting fluid is particularly important.
2.3 Cleaning: The “Cleaner” That Maintains Cleanliness
Cutting fluid can:
- Flush away chips: Prevent chips from adhering to workpiece surfaces and causing scratches
- Prevent clogging: Avoid machining defects caused by chip accumulation
- Protect tools: Prevent tool damage caused by chip entanglement
III. Main Types of Cutting Fluids
3.1 Emulsion-Type Cutting Fluids
Emulsions are the most common type of cutting fluid, formed by mixing water and mineral oil in specific proportions (usually 10%-20% oil to water).
Characteristics:
- Contains multiple additives: sodium sulfonate (solubilizer), preservatives, bactericides, anti-wear agents
- Excellent cooling performance, suitable for high-speed machining
- Superior lubrication and anti-corrosion performance compared to synthetic cutting fluids
Application scenarios: High-speed drilling, milling, turning, grinding, and other processes requiring rapid cooling
3.2 Straight Oil Cutting Fluids
Straight oil cutting fluids are derived from plants or animals and are considered environmentally friendly products.
Characteristics:
- Excellent lubrication performance
- Almost water-free, with strong rust prevention capabilities
- Higher cost due to organic nature
Application scenarios: Not suitable for heavy cutting and drilling, usually used as additives
3.3 Synthetic Cutting Fluids
Synthetic fluids are made by mixing organic and inorganic chemical components with water.
Characteristics:
- Excellent cooling performance
- Semi-synthetic fluids are common types that combine the advantages of emulsions and synthetic fluids
IV. How to Choose the Right Cutting Fluid
4.1 Consider the Machining Material
Different materials have different requirements for cutting fluids:
- Aluminum alloys: Need good lubricity and cooling properties
- Stainless steel: Focus on cooling performance and rust resistance
- Titanium alloys: Require specially formulated cutting fluids
4.2 Choose Based on Machining Process
- High-speed machining: Prioritize emulsions or synthetic fluids with good cooling performance
- Heavy cutting: Need cutting fluids with excellent lubrication performance
- Precision machining: Choose cutting fluids that have minimal impact on surface quality
4.3 Consider Environmental Requirements
- Choose environmentally friendly products
- Consider waste fluid treatment costs
- Pay attention to the health and safety of operators
V. Usage and Maintenance of Cutting Fluids
5.1 Proper Concentration Control
- Emulsion-type cutting fluids need to maintain appropriate oil-water ratios
- Excessively high concentration affects cooling efficiency and increases costs
- Excessively low concentration reduces lubrication and rust prevention performance
5.2 Regular Testing and Maintenance
- Regularly test the concentration and pH value of cutting fluids
- Timely replenish consumed cutting fluids
- Regularly replace aged cutting fluids
5.3 Storage Precautions
- Store in a cool, dry place
- Prevent contaminants from entering
VI. Development Trends in Cutting Fluid Technology
6.1 Environmentally Friendly Cutting Fluids
With increasing environmental awareness, cutting fluids with good biodegradability and minimal environmental impact are becoming the development direction. Plant-based cutting fluids are receiving more attention due to their renewability and environmental friendliness.
6.2 High-Performance Additives
The development of new additives has enabled cutting fluids to have better lubricity, cooling properties, and rust resistance while reducing environmental impact.
6.3 Intelligent Management Systems
Through sensors and intelligent control systems, real-time monitoring and automatic adjustment of cutting fluid conditions are achieved, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
VII. Conclusion: The Indispensable “Invisible Hero”
Although cutting fluids are not as eye-catching in CNC machining, they are indeed crucial factors in ensuring machining quality, improving production efficiency, and extending equipment life. Choosing the right cutting fluid and using it properly is essential for any CNC machining enterprise.
With the continuous development of manufacturing industry and technological progress, cutting fluid technology is also constantly innovating and improving. From traditional mineral oils to modern environmentally friendly synthetic fluids, from simple lubrication and cooling to intelligent management systems, cutting fluids are serving modern manufacturing in more efficient, environmentally friendly, and intelligent ways.
In the future era of intelligent manufacturing, cutting fluids will continue to play their important role as a crucial bridge connecting design concepts with manufacturing reality, bringing more high-quality products and better experiences to our lives.