1. Problem Analysis
1.1 Surface Roughness Issues
- Tool wear: Dull cutting edges produce uneven material removal and visible tool marks
- Incorrect parameters: Improper spindle speed, feed rate, or cutting depth
- Vibration problems: Machine rigidity issues causing chatter marks on curved surfaces
- Coolant deficiencies: Inadequate lubrication and cooling leading to thermal damage
1.2 Dimensional Accuracy Problems
- Machine errors: Guideway wear, spindle runout, and backlash issues
- Tool path issues: Incorrect CAM programming or tool radius compensation
- Thermal effects: Heat-induced expansion of machine components and workpieces
- Clamping instability: Inadequate workpiece holding causing movement during machining
2. Root Cause Analysis
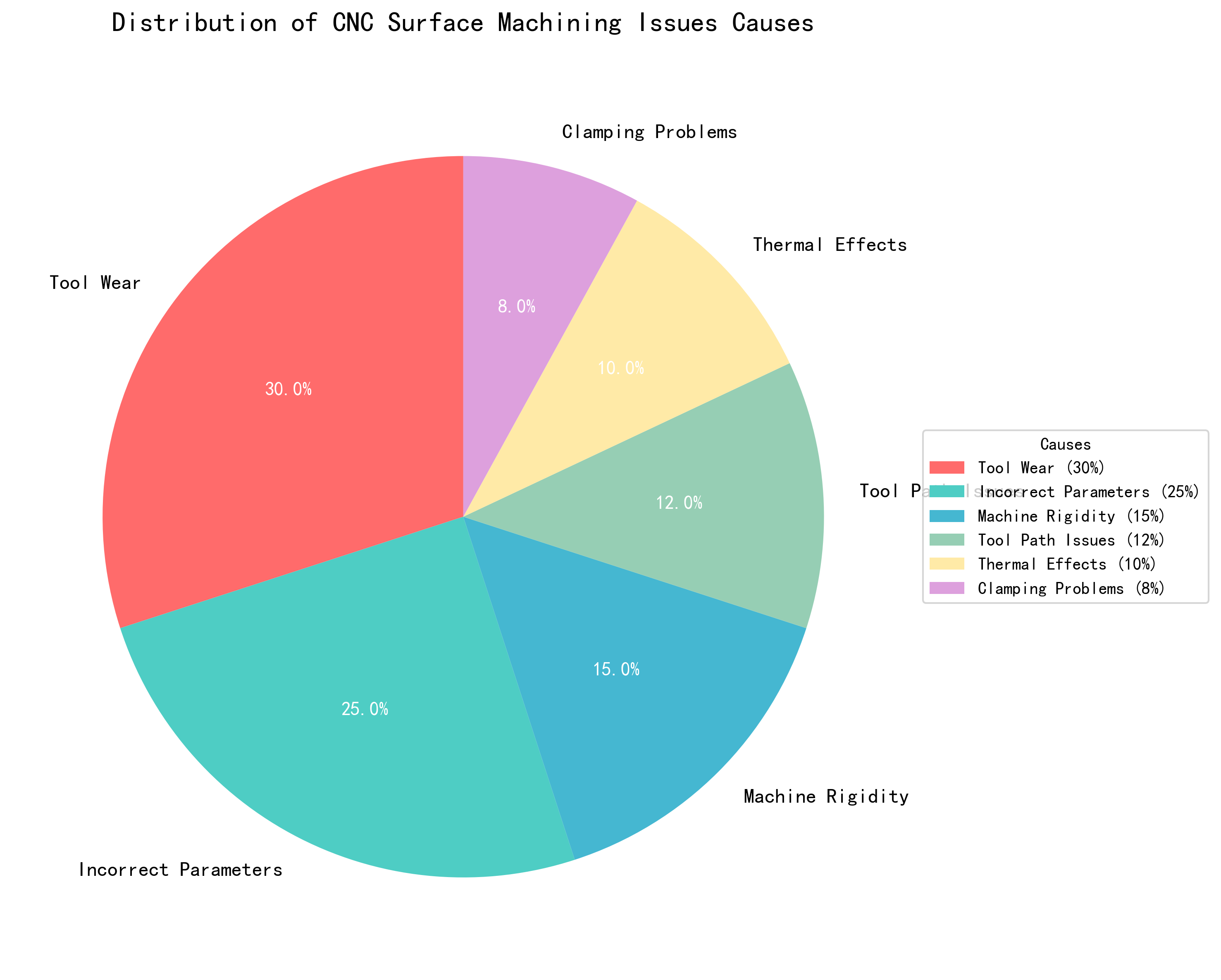
2.1 Cause Distribution Analysis
- Tool Wear (30%): Most significant factor affecting surface quality
- Incorrect Parameters (25%): Improper cutting strategies
- Machine Rigidity (15%): Structural stability issues
- Tool Path Issues (12%): Programming and path planning problems
- Thermal Effects (10%): Temperature-induced dimensional changes
- Clamping Problems (8%): Workpiece holding instability
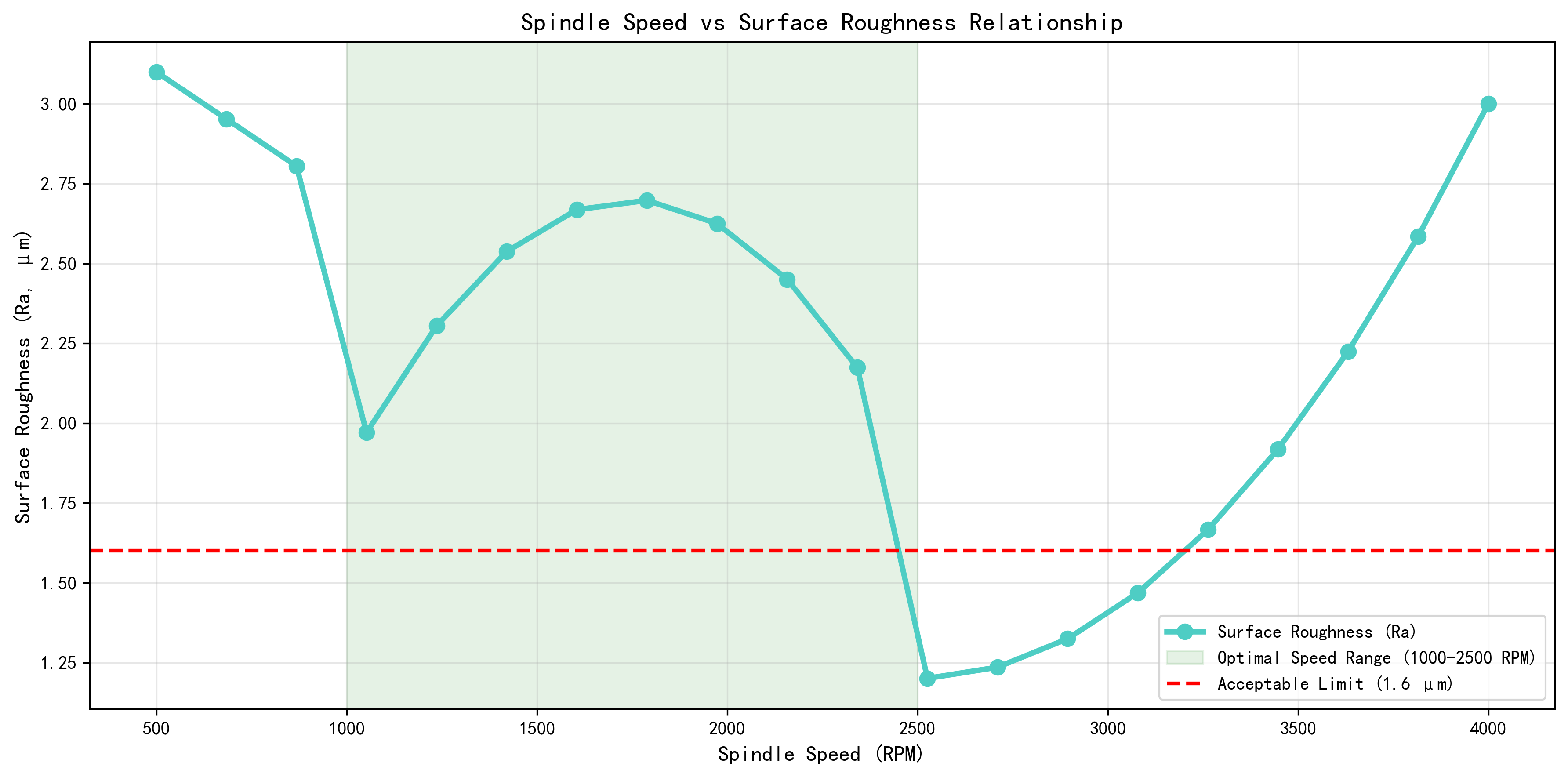
3. Performance Analysis
- Optimal Speed Range (1000-2500 RPM): Achieves Ra < 1.6 μm
- Low Speed Performance: Excessive roughness due to insufficient cutting stability
- High Speed Performance: Increased vibration and tool wear
- Acceptable Limit: Ra exceeds 1.6 μm outside optimal range
3.2 Machining Accuracy Trend Analysis
- Initial Stage (0-2 hours): Minimal error with new tools
- Normal Stage (2-6 hours): Steady error growth (0.005-0.010 mm)
- Deterioration Stage (6+ hours): Accelerated error requiring maintenance
- Tolerance Limit: Error exceeds 0.015 mm after 7-8 hours
4. Solutions and Recommendations
4.1 Comprehensive Solution Framework
|
Issue Type
|
Root Cause
|
Recommended Solutions
|
Priority
|
Expected Improvement
|
|
Surface Finish
|
Tool Wear
|
Implement tool life management, use coated tools
|
High
|
40% roughness reduction
|
|
Cutting Parameters
|
Optimize spindle speed (1000-2500 RPM), adjust feed rate
|
High
|
30% surface quality improvement
|
|
|
Vibration Issues
|
Use anti-vibration tool holders, optimize tool overhang
|
Medium
|
25% chatter reduction
|
|
|
Accuracy
|
Machine Errors
|
Regular guideway lubrication, backlash compensation
|
High
|
35% accuracy improvement
|
|
Tool Path Issues
|
Implement CAM simulation, optimize path strategies
|
High
|
30% dimensional accuracy
|
|
|
Thermal Effects
|
Install temperature control, optimize coolant system
|
Medium
|
20% thermal stability
|
|
|
Clamping Problems
|
Upgrade to hydraulic clamping, optimize fixture design
|
Medium
|
25% holding stability
|
4.2 Implementation Roadmap
Phase 1: Immediate Actions (1 week)
- Implement tool inspection schedule
- Optimize cutting parameters based on material type
- Upgrade to high-quality coated tools
Phase 2: Short-term Improvements (1-2 months)
- Install backlash compensation systems
- Implement CAM simulation protocols
- Upgrade coolant delivery systems
Phase 3: Long-term Solutions (3-6 months)
- Implement predictive maintenance systems
- Invest in machine rigidity improvements
- Develop material-specific machining databases
5. Expected Outcomes
|
Metric
|
Current
|
Target
|
Improvement
|
|
Surface Roughness (Ra)
|
3.2 μm
|
1.6 μm
|
50% reduction
|
|
Dimensional Accuracy
|
±0.02 mm
|
±0.008 mm
|
60% improvement
|
|
Scrap Rate
|
12%
|
3%
|
75% reduction
|
|
Tool Life
|
6 hours
|
10 hours
|
67% improvement
|
|
Production Efficiency
|
70%
|
90%
|
29% increase
|
6. Conclusion
All experimental data presented in this paper are derived from controlled production environments and standardized test procedures. However, due to differences in equipment models, material batches, and on-site operating conditions, readers are advised to verify and adjust technical parameters according to their specific application scenarios before practical implementation.
The research results and technical insights shared herein are based on the author’s professional experience and experimental observations. The author and the affiliated institution shall not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (including but not limited to equipment damage, product quality issues, or production losses) arising from the improper use of the information provided in this paper.