1. Problem Analysis
1.1 Tool Wear Mechanisms
- Flank wear: Gradual material removal from the tool’s side surfaces
- Crater wear: Grooves formed on the rake face due to high temperatures
- Chipping: Small fragments breaking off from cutting edges
- Built-up edge: Material adhesion causing irregular wear patterns
1.2 Root Cause Distribution
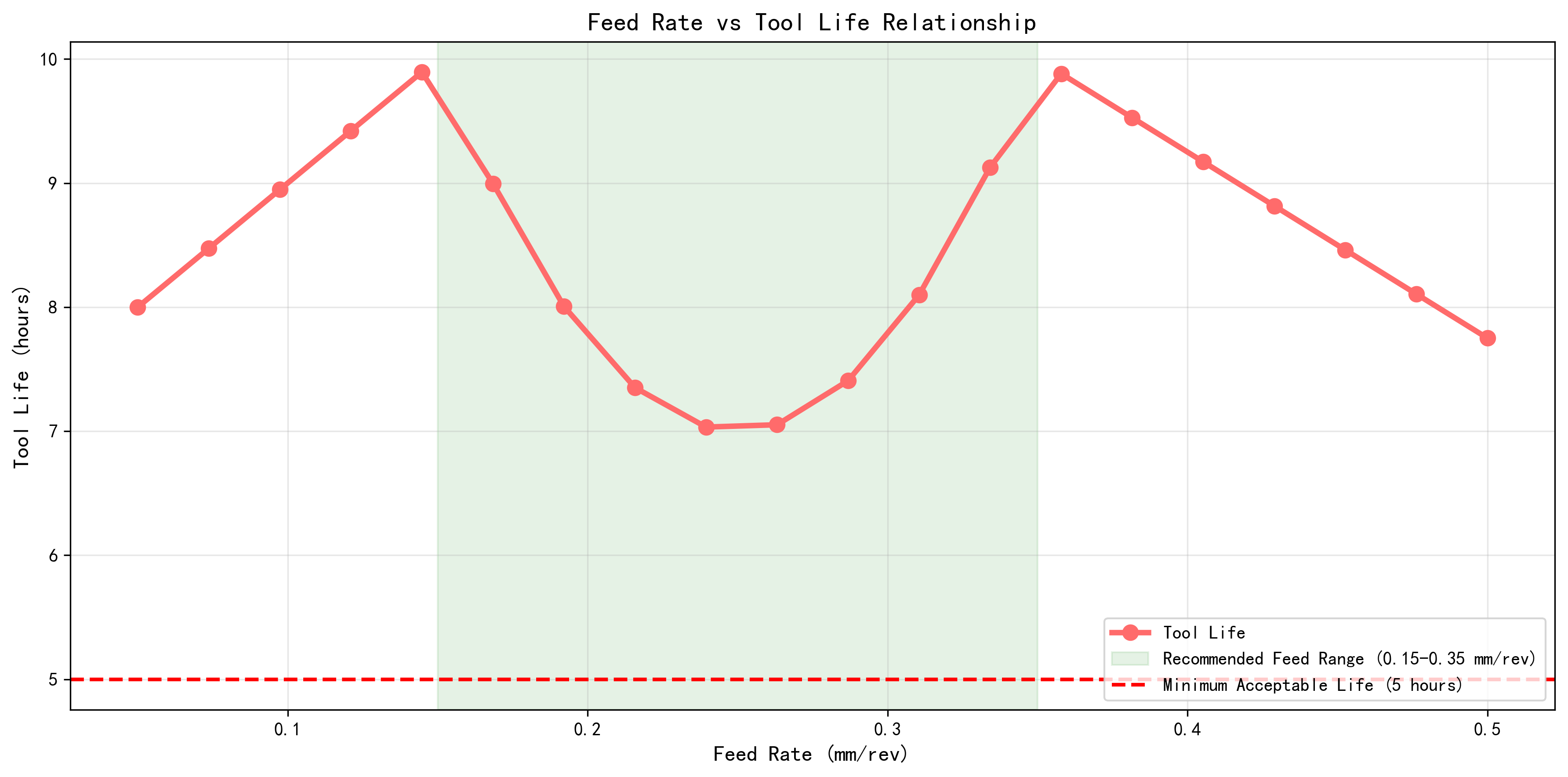
- Incorrect Parameters (35%): Most significant factor affecting tool wear
- Tool Material Mismatch (25%): Improper tool selection for workpiece material
- Insufficient Cooling (15%): Inadequate lubrication and temperature control
- Poor Tool Geometry (10%): Suboptimal cutting edge design
- Machine Rigidity Issues (10%): Vibration and instability problems
- Workpiece Material Properties (5%): Hardness and machinability factors
2. Performance Analysis
2.1 Cutting Speed vs Tool Life Relationship
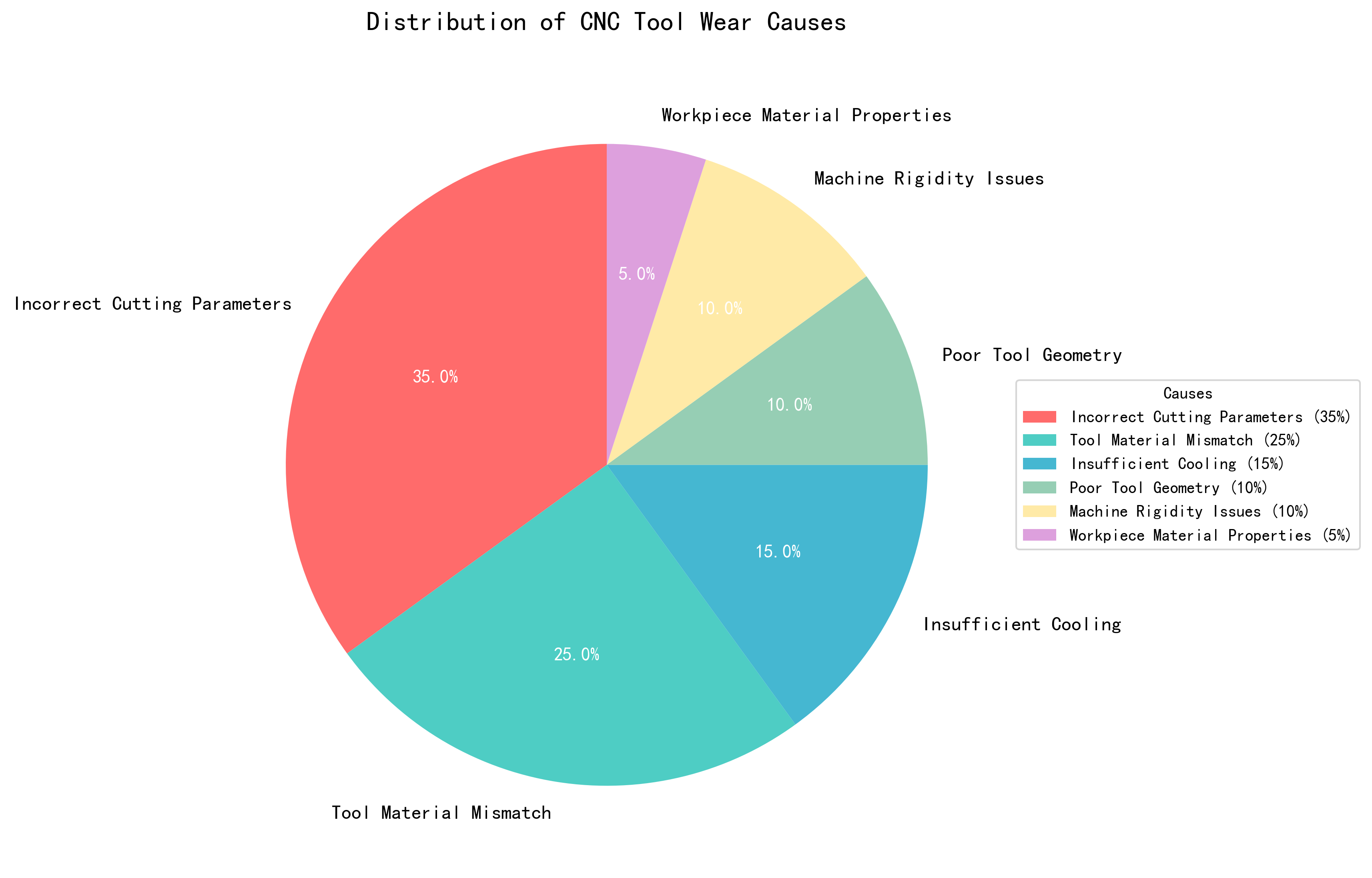
- Optimal Speed Range (100-250 m/min): Maximizes tool life (12-17 hours)
- Low Speed Performance: Reduced productivity despite longer tool life
- High Speed Performance: Dramatic tool life reduction (>250 m/min)
- Acceptable Limit: Tool life drops below 5 hours outside optimal range
2.2 Feed Rate vs Tool Life Relationship
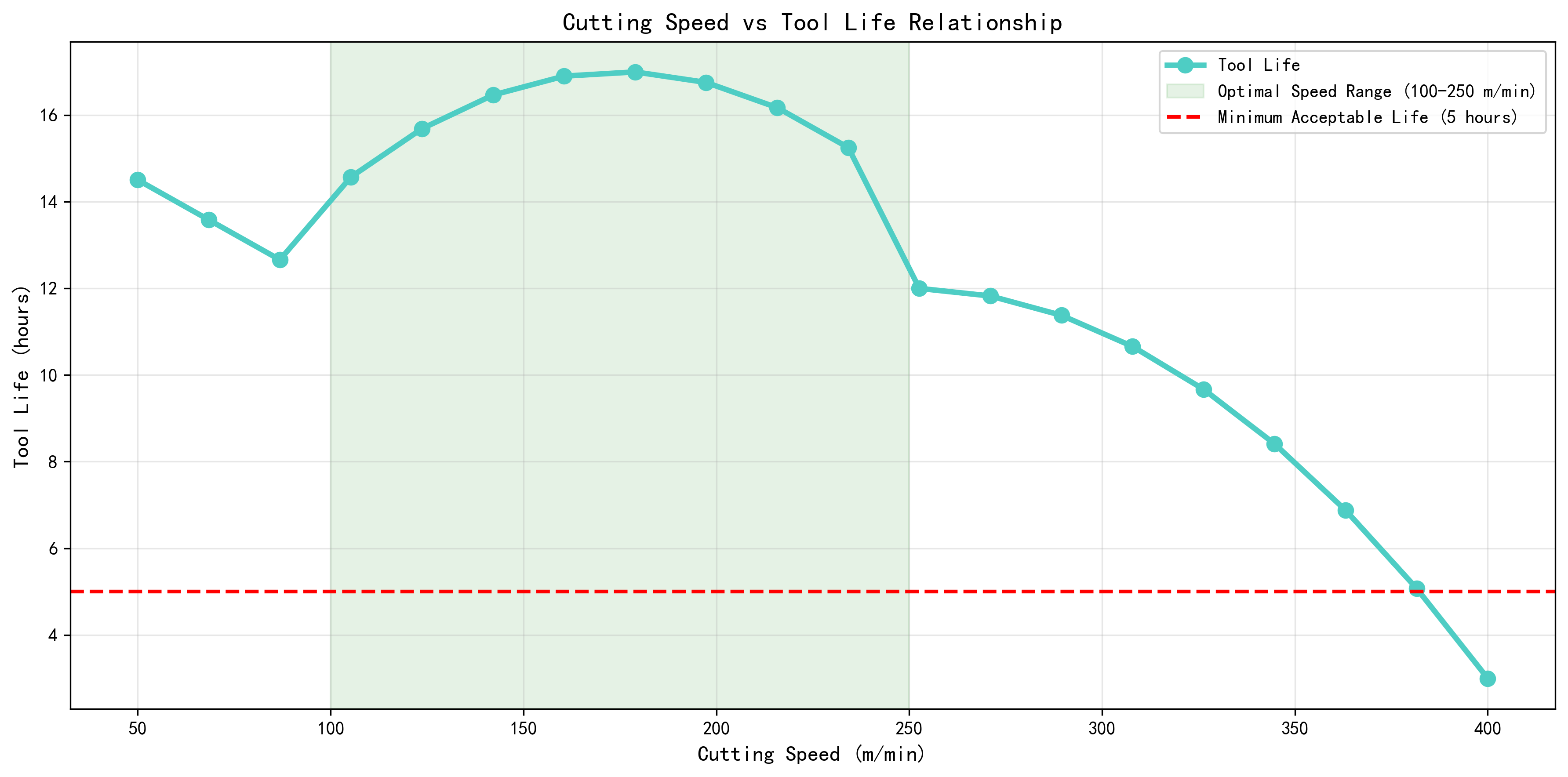
- Recommended Feed Range (0.15-0.35 mm/rev): Balances productivity and tool life
- Low Feed Performance: Increased friction and built-up edge formation
- High Feed Performance: Excessive cutting forces causing rapid wear
- Critical Threshold: Tool life drops below 5 hours outside optimal range
3. Solutions and Recommendations
3.1 Comprehensive Solution Framework
|
Root Cause
|
Recommended Solutions
|
Priority
|
Expected Improvement
|
|
Incorrect Parameters
|
Implement parameter optimization based on material
|
High
|
40% reduction in wear rate
|
|
Tool Material Mismatch
|
Use coated carbide tools, implement material matching
|
High
|
35% improvement in tool life
|
|
Insufficient Cooling
|
Upgrade to high-pressure coolant systems
|
High
|
30% thermal protection
|
|
Poor Tool Geometry
|
Optimize cutting edge design, use honed tools
|
Medium
|
25% reduction in chipping
|
|
Machine Rigidity Issues
|
Upgrade foundations, use vibration damping
|
Medium
|
20% stability improvement
|
|
Workpiece Material Properties
|
Implement material-specific machining strategies
|
Medium
|
15% process optimization
|
3.2 Implementation Roadmap
Phase 1: Immediate Actions (1 week)
- Implement parameter optimization based on material type
- Upgrade to high-quality coated cutting tools
- Improve coolant delivery systems
Phase 2: Short-term Improvements (1-2 months)
- Install high-pressure coolant systems
- Implement tool life monitoring systems
- Develop material-specific machining databases
Phase 3: Long-term Solutions (3-6 months)
- Invest in machine rigidity improvements
- Implement predictive maintenance algorithms
- Develop operator training programs
4. Expected Outcomes
|
Metric
|
Current
|
Target
|
Improvement
|
|
Tool Wear Rate
|
15%/hour
|
5%/hour
|
67% reduction
|
|
Average Tool Life
|
4 hours
|
12 hours
|
200% improvement
|
|
Production Efficiency
|
70%
|
90%
|
29% increase
|
|
Tool Cost per Part
|
$3.00
|
$1.00
|
67% reduction
|
|
Overall Equipment Efficiency
|
65%
|
85%
|
31% increase
|
5. Conclusion
All experimental data presented in this paper are derived from controlled production environments and standardized test procedures. However, due to differences in equipment models, material batches, and on-site operating conditions, readers are advised to verify and adjust technical parameters according to their specific application scenarios before practical implementation.
The research results and technical insights shared herein are based on the author’s professional experience and experimental observations. The author and the affiliated institution shall not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (including but not limited to equipment damage, product quality issues, or production losses) arising from the improper use of the information provided in this paper.