In the fields of medical devices, food machinery, and chemical equipment, stainless steel parts must simultaneously possess high corrosion resistance, precise tolerances, and smooth surfaces. However, the machining challenges of 304/316 stainless steel lie in work hardening (hardness can instantly increase by 1.5–2 times) and low thermal conductivity (cutting temperatures easily reach 800℃), leading to tool breakage, deformation, or surface roughness if not handled properly.
At Goldcattle Workshop, we’ve specialized in stainless steel CNC milling for 26 years. Using 5-axis + high-pressure internal cooling + PCBN finishing tools, we’ve overcome these challenges: thin-walled part deformation controlled within 0.02mm, surface roughness stably at Ra 0.2–0.4μm, and batch qualification rate ≥99.2%.

Our CNC workshop in action – precision machining of stainless steel components
I. Material Characteristics and Machining Challenges
Stainless steels (such as 304, 316, 430, etc.) have unique properties that make them both valuable and challenging to machine. We’ve observed that understanding these characteristics is key to successful machining.
Key Challenges We Face Daily:
- High Strength and Work-Hardening: Tensile strength reaches 520–700MPa, with hardness increasing by 1.5–2 times during machining
- Low Thermal Conductivity: Only 1/3 of carbon steel, leading to cutting temperatures up to 800–1000℃
- High Toughness: Strong plastic deformation ability causes built-up edges during cutting
Stainless Steel Machining Solutions Table
| Stainless Steel Grade | Main Challenges | Our Common Solutions | Typical Improvement Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| 304/304L | Severe work hardening | Low feed + high speed + sharp tools | Hardened layer depth < 0.1mm |
| 316/316L | Corrosion-resistant but sticky | TiAlN coating + MQL minimum quantity lubrication | Tool life increased by 2 times |
| 17-4PH | High strength + hardening | Liquid nitrogen cooling (-196℃) + layered milling | Cutting temperature reduced by over 30% |
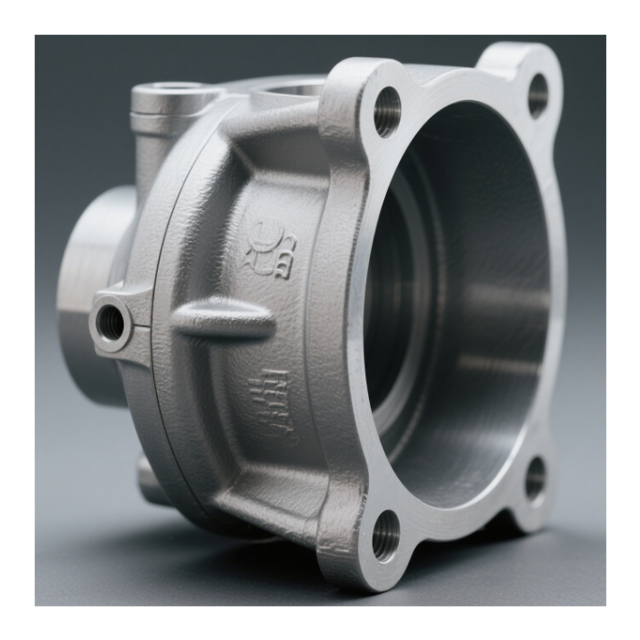
 Example of a complex stainless steel part we machined with tight tolerances
Example of a complex stainless steel part we machined with tight tolerances
II. Full Process of Custom Stainless-Steel Milling Service
Our process is optimized based on material characteristics, with each step refined through years of hands-on experience.
1. Requirement Communication and Feasibility Analysis
Our professional team formulates a process plan based on the type of stainless steel (such as 316L medical-grade stainless steel) and the part’s application (such as corrosion-resistant valves, surgical instruments).
In our daily operations: When customizing a 304 stainless-steel pump body for food machinery, we always recommend using coated tools combined with minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) to ensure hygiene standards and machining accuracy.
2. Digital Design & Simulation
We use UG/NX for 3D modeling. For thin-walled structures prone to deformation (like 1mm wall thickness), we adopt the “helical milling + residual stress relief” strategy.
Our practical approach: For Thin – walled area, we do stress simulation first and often adjust to spiral milling paths to avoid excessive cutting depth in one pass.
3. Tool & Parameter Optimization
Proper tool selection is critical for stainless steel machining success.
Our standard cutting parameters for different stainless steel grades
Rough Machining
Select CVD-coated carbide tools (such as YBC251) for high-temperature wear resistance.
Finish Machining
Use PCBN tools (cubic boron nitride) suitable for machining stainless steel with hardness ≥ HRC45.
Standard Parameters
- Cutting speed: 50–100m/min (to avoid excessive temperature)
- Feed rate: 0.08–0.15mm/z
- Cutting depth: 0.5–2mm (layer-by-layer cutting to reduce hardening)
4. Precision Machining and Real-time Monitoring
We use high-rigidity CNC machine tools equipped with high-pressure internal cooling systems (5–10MPa pressure) to directly cool the cutting area.
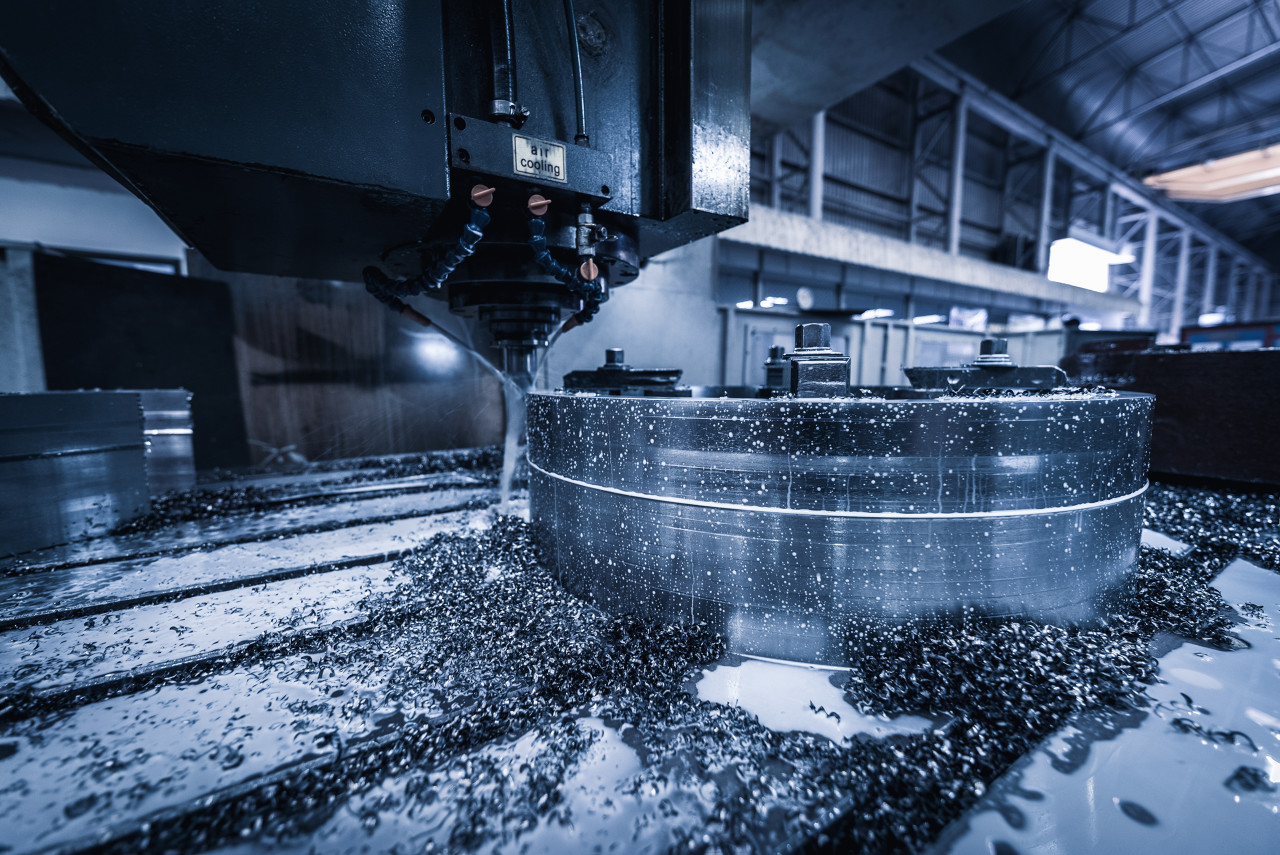

High-pressure internal cooling system in action during stainless steel machining
Our actual measurement: After using 5-10MPa internal cooling, the surface temperature of parts in the same batch dropped from 950℃ to 620℃, and tool life increased from 8 hours to 18 hours.
5. Quality Inspection and Surface Treatment
Quality control is embedded in every step of our process.

Our quality inspection process ensures every part meets specifications
Inspection Standards
We use coordinate measuring machines (accuracy ±0.001mm) to detect hole diameters and geometric tolerances, with a full-size pass rate ≥ 99.2%.
Surface Treatment
We provide electropolishing (Ra≤0.2μm) and passivation treatment (salt-spray test ≥ 1000 hours) to improve corrosion resistance.
6. Delivery and Application Support
Regular orders are delivered within 3–10 working days. For complex parts (such as multi-stage centrifugal pump impellers), we provide process verification reports and material certifications (such as ASTM A276).
III. Advantages of Our Stainless-Steel Milling Processes
Our core technologies break through material limitations, developed through years of practical experience in our workshop.
Key Advantages
- Coating Technology: We commonly use TiAlN coating in our workshop, which can withstand temperatures up to 1100℃ and extends tool life by 2 times compared to ordinary carbide. When machining 304 stainless steel, tool life reaches 15–20 hours without chipping.
- Cooling Optimization: High-pressure oil mist lubrication (MQL) uses only 1/50 of traditional cutting fluids, reducing cutting temperature by 30%
- Multi-axis Precision: 5-axis machining achieves ±0.005mm accuracy, 40% more efficient than traditional 3-axis machining
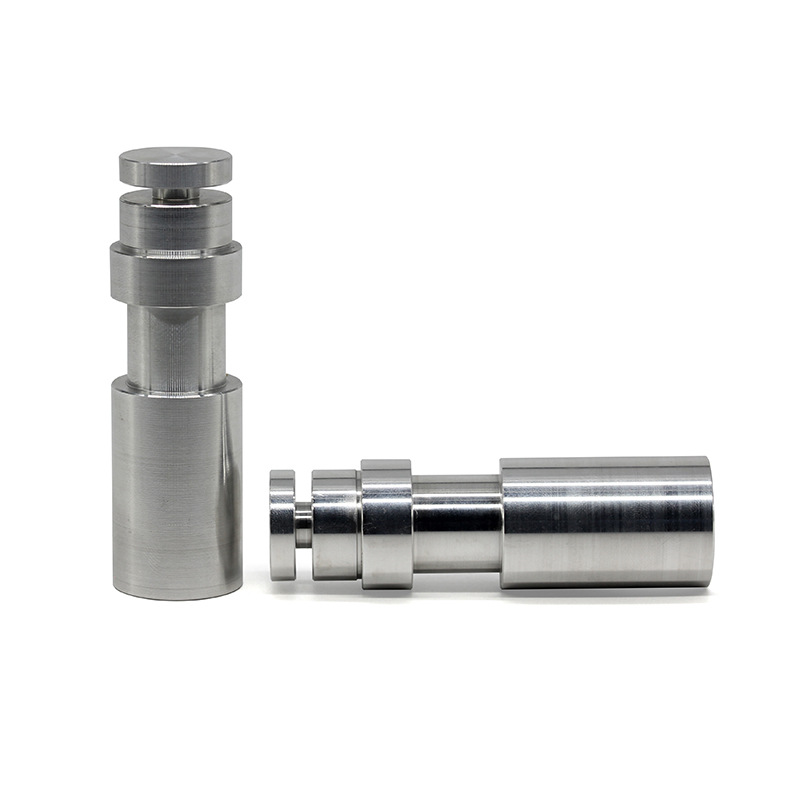

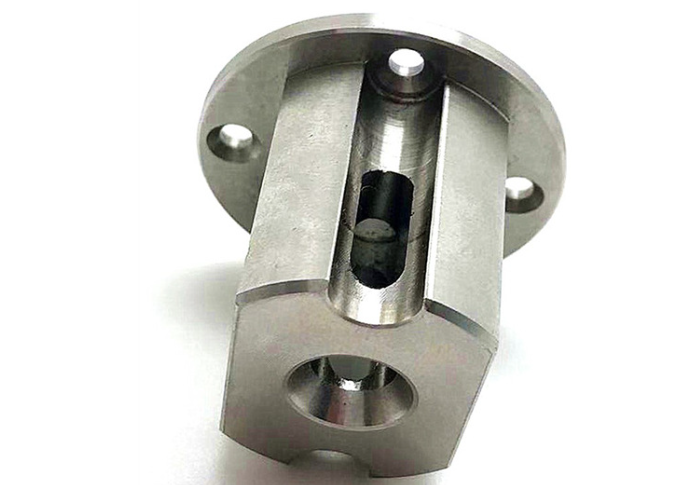
Examples of our precision stainless steel components with tight tolerances
IV. Verification by Practical Cases
While we can’t share specific client details due to confidentiality, we can demonstrate our capabilities through anonymized case studies with actual data from our workshop.
Medical Device Field: 316L Hip Joint Component
Requirements: Wall thickness 1.2mm, tolerance ±0.01mm, Ra 0.2μm surface finish
Our Solution: 5-axis machining + vacuum fixtures + layered precision milling
Results: Deformation controlled at 0.015mm, passed biocompatibility testing

Examples of medical-grade stainless steel components we’ve manufactured
Food Machinery Field: 304 Stainless Steel Centrifugal Pump Impeller
Requirements: FDA food-contact standard, high efficiency, long service life
Our Solution: High-pressure internal cooling + coated tools, material removal rate 200cm³/min
Results: Pump efficiency increased by 15%, maintenance cycle extended to 2 years
Chemical Equipment Field: 316 Stainless Steel Corrosion-Resistant Valve
Requirements: Sealing surface accuracy ±0.003mm, salt-spray test ≥ 1000 hours
Our Solution: PCBN tool finish machining + passivation treatment
Results: Valve leakage rate ≤ 0.01%, service life 3 times longer than ordinary processes
V. FAQ: Professional Answers for Stainless-Steel Milling
Adopt the “low-feed + high-speed” strategy (feed rate ≤ 0.1mm/z) and use sharp tools (rake angle 10°–15°) to reduce the hardened depth of the cutting layer (controlled within 0.1mm).
During finish machining, using PCBN tools combined with ultra-precision milling, the surface roughness Ra can reach 0.1–0.4μm, meeting the requirements of medical devices, optical accessories, etc.
Use vacuum fixtures (clamping force ≤ 0.5N/mm²) + layer-by-layer cutting (each layer cutting depth ≤ 0.3mm). In one case, the deformation of a 0.5mm-thick stainless-steel shell was only 0.02mm.
Electropolishing can reduce surface roughness Ra from 3.2μm to 0.2μm, reducing adhesion of corrosive media. After passivation treatment, salt-spray resistance time of 316 stainless steel increases from 500 hours to 1200 hours.






