I. Introduction to Custom Mechanical Die Casting

Die casting is a manufacturing process in which molten metal is injected, under high pressure, into a precision steel mold (die) to produce complex, net-shaped components with excellent dimensional accuracy.
This technology has revolutionized the production of mechanical parts across various industries, offering unparalleled efficiency, consistency, and design flexibility.
At Goldcattle Precision, we specialize in custom mechanical die casting services that deliver exceptional quality and performance. Our state-of-the-art facilities house over 50 die casting machines with clamping forces ranging from 80 to 12,000 tons,
enabling us to produce components from 0.1kg to 50kg with wall thicknesses as thin as 0.6mm.
material selection, mold design optimization, and process parameter control.
Get these right, and you can achieve production yields exceeding 97% with minimal post-processing requirements.
Key Advantages of Die Casting
- High Precision: Tolerances as tight as ±0.005mm for critical dimensions
- Excellent Surface Finish: Ra 1.6μm achievable without additional machining
- Complex Geometry: Intricate shapes with thin walls and deep cavities
- High Production Rates: Cycle times as short as 15 seconds for small components
- Cost Efficiency: Low per-unit costs for medium to high volume production
- Material Versatility: Compatible with aluminum, zinc, magnesium, and copper alloys
II. The Die Casting Process: From Design to Finished Product
The die casting process involves several critical stages, each requiring precise control and expertise to ensure optimal results.
Over the years, I’ve refined our process flow to minimize defects and maximize efficiency.
Design & Engineering
DFM analysis, mold design, material selection, and process simulation
Mold Fabrication
Precision machining of H13 steel molds with thermal treatment
Metal Melting
Induction heating of alloys to precise temperatures (650-720°C for aluminum)
Injection Process
High-pressure injection (8-150 MPa) into steel dies with precise timing
Cooling & Ejection
Controlled cooling followed by automatic part ejection
Finishing & Quality Control
Trimming, machining, surface treatment, and comprehensive inspection
In 2024, we had a client who insisted on skipping our DFM analysis to save time.
The result? $120,000 in mold rework costs and a 3-month production delay.
Proper upfront engineering saves money in the long run.
Advanced Process Control Parameters
| Parameter | Aluminum Alloys | Zinc Alloys | Magnesium Alloys | Copper Alloys |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Injection Pressure (MPa) | 40-120 | 8-50 | 30-80 | 80-150 |
| Melt Temperature (°C) | 650-720 | 420-450 | 630-680 | 1100-1150 |
| Die Temperature (°C) | 180-280 | 150-200 | 200-300 | 250-350 |
| Injection Speed (m/s) | 2-8 | 3-10 | 4-12 | 2-6 |
| Cooling Time (s) | 10-60 | 5-30 | 8-40 | 20-120 |
III. Comprehensive Material Selection Guide
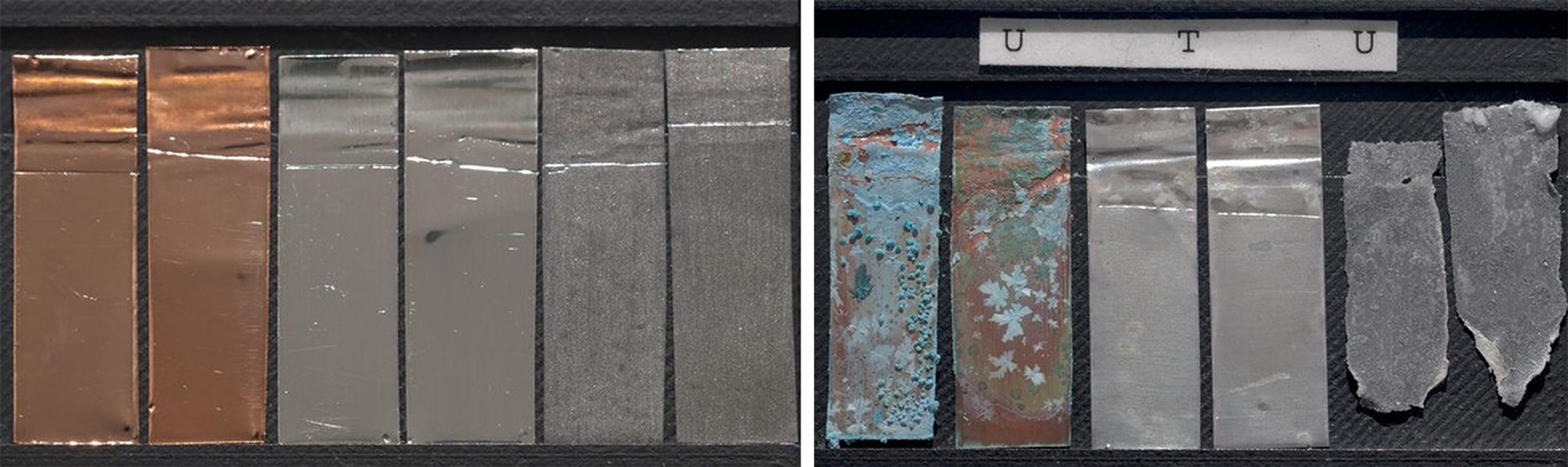

Choosing the right die casting material is critical to achieving optimal performance and cost efficiency.
Over my 15-year career, I’ve worked with hundreds of alloy compositions and developed deep expertise in matching materials to specific application requirements.
Aluminum Alloys: The Most Versatile Choice
Aluminum alloys are the most widely used die casting materials due to their excellent combination of strength, weight, and cost.
At Goldcattle, we primarily use A380, A383, ADC12, and AlSi12Cu1 alloys for most applications.
while maintaining the same structural strength as traditional steel components.
The key was optimizing the silicon content and adding trace elements to improve fluidity and mechanical properties.
Zinc Alloys: Ideal for Intricate Parts
Zinc alloys offer excellent castability for complex shapes with thin walls.
Their low melting point (420-450°C) extends die life significantly compared to other materials.
Magnesium Alloys: The Lightweight Solution
Magnesium alloys provide the best strength-to-weight ratio of all common die casting materials.
At 1.81 g/cm³, magnesium is 33% lighter than aluminum and 75% lighter than steel.
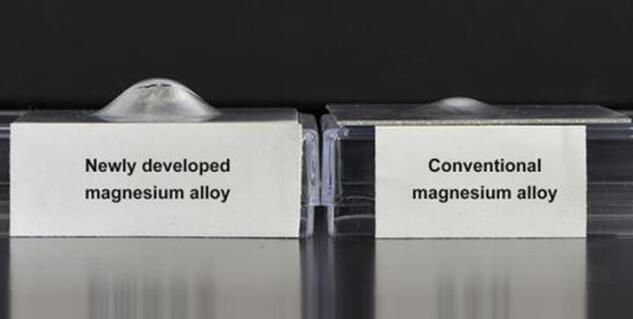
Copper Alloys: For High-Strength Applications
Copper alloys offer exceptional strength, wear resistance, and thermal conductivity.
However, their high melting point (1100-1150°C) requires specialized equipment and expertise.
Material Properties Comparison
| Property | Aluminum (A380) | Zinc (Zamak 3) | Magnesium (AZ91D) | Copper (C85800) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm³) | 2.70 | 6.60 | 1.81 | 8.70 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 320 | 280 | 230 | 480 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 160 | 160 | 150 | 240 |
| Elongation (%) | 3.0 | 10.0 | 3.0 | 15.0 |
| Hardness (HB) | 80 | 82 | 60 | 120 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | 96 | 105 | 51 | 260 |
| Cost Relative to Aluminum | 1.0x | 1.2x | 2.5x | 8.0x |
| Typical Applications | Engine parts, housings | Electronics, hardware | Aerospace, automotive | Gears, bearings |
Expert Recommendation: Based on thousands of projects, my material selection guidelines are:
• Aluminum – Best all-around choice for most applications
• Zinc – Ideal for small, intricate parts with thin walls
• Magnesium – When weight reduction is critical
• Copper – Only for high-temperature or high-wear applications
IV. Die Casting Cost Calculation and Optimization
Understanding die casting costs is essential for making informed business decisions.
Over the years, I’ve developed a comprehensive cost model that accurately predicts production expenses for any die casting project.
Die Casting Cost Calculation Formula
Where:
- Tooling Cost: One-time cost for mold design and fabrication
- Material Cost: Based on part weight, material price, and scrap rate
- Processing Cost: Machine time, labor, and energy costs
- Finishing Cost: Trimming, machining, and surface treatment
Detailed Cost Breakdown
| Cost Component | Percentage of Total Cost | Key Factors | Optimization Opportunities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tooling | 15-35% | Part complexity, cavity count, material | Multi-cavity molds, standard components |
| Materials | 25-45% | Part weight, alloy price, scrap rate | Wall thickness optimization, scrap recycling |
| Processing | 20-35% | Cycle time, machine size, labor | Parameter optimization, automation |
| Finishing | 10-25% | Machining requirements, surface treatment | Near-net-shape design, integrated features |
we reduced costs by 28% through:• Optimizing wall thickness from 3.5mm to 2.8mm (19% material savings)
• Implementing a 4-cavity mold (35% tooling cost per part)
• Reducing cycle time from 45s to 32s (29% processing improvement)
• Eliminating secondary machining through better draft angles
Tooling Cost Considerations
Tooling represents the largest initial investment in die casting.
At Goldcattle, we use H13 hot work steel for all molds, which provides excellent thermal fatigue resistance and wear properties.
| Part Complexity | Estimated Tooling Cost | Expected Mold Life | Minimum Production Volume |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple (1 cavity) | $8,000 – $15,000 | 500,000+ shots | 10,000 parts |
| Medium (2-4 cavities) | $15,000 – $35,000 | 500,000+ shots | 50,000 parts |
| Complex (multi-slide) | $35,000 – $100,000+ | 300,000+ shots | 100,000 parts |
For volumes over 100,000 parts, die casting is typically 30-50% cheaper than alternative manufacturing processes like CNC machining.
V. Die Casting Defects: Identification, Causes, and Solutions
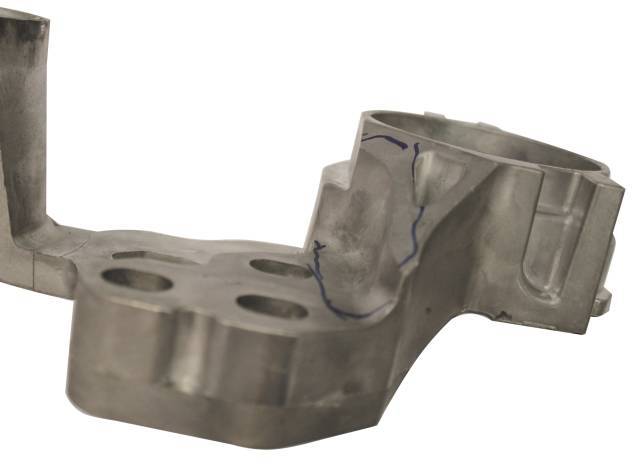

In my 15 years of die casting experience, I’ve encountered and solved every type of casting defect imaginable.
The key to defect prevention is understanding root causes and implementing systematic solutions.
Common Die Casting Defects
| Defect Type | Visual Characteristics | Primary Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porosity | Small holes or voids in castings | Turbulent filling, gas entrapment | Vacuum assist, optimized gating, degassing |
| Shrinkage | Depressions or voids in thick sections | Inadequate feeding, rapid cooling | Risers, chills, optimized cooling |
| Cracks | Linear fractures in castings | Thermal stress, improper ejection | Improved draft angles, stress relief |
| Surface Defects | Flow marks, cold shuts, blisters | Poor metal flow, temperature issues | Optimized gate design, temperature control |
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Parts outside specified tolerances | Mold wear, thermal expansion | Regular maintenance, compensation factors |
After three months of testing, we discovered the problem was caused by microscopic hydrogen bubbles in the melt.
The solution? A combination of vacuum degassing and a proprietary flux treatment that reduced porosity from 5% to less than 0.5%.
Advanced Defect Detection Techniques
At Goldcattle, we use a comprehensive quality control system to detect and prevent defects:
- X-ray Inspection: Detects internal defects with 0.1mm resolution
- Ultrasonic Testing: Identifies subsurface defects in thick sections
- Pressure Testing: Verifies leak tightness for hydraulic components
- Dimensional Metrology: 3D scanning with ±0.005mm accuracy
- Visual Inspection: Automated vision systems for surface defects

Preventive Maintenance Program
Prevention is always better than cure. Our preventive maintenance program includes:
- Daily: Mold temperature checks, lubrication verification
- Weekly: Die surface inspection, wear part replacement
- Monthly: Complete mold teardown, component inspection
- Quarterly: Machine calibration, hydraulic system servicing
we’ve improved our first-pass yield from 89% in 2020 to 97.5% in 2025,
reducing scrap costs by 65% and improving delivery reliability.
VI. Industrial Applications of Die Casting
Die casting technology serves a wide range of industries with diverse requirements.
Over the years, I’ve worked on projects spanning automotive, aerospace, electronics, and many other sectors.

Automotive Industry
Engine parts, transmission housings, EV battery components

Electronics Industry
Heat sinks, chassis, connector housings, antenna components

Aerospace Industry
Structural components, hydraulic manifolds, engine parts
Automotive Applications: The Largest Market
The automotive industry represents approximately 45% of global die casting demand.
At Goldcattle, we’ve produced components for everything from traditional internal combustion engines to cutting-edge electric vehicles.
| Component Type | Material | Weight Range | Tolerance Requirements | Annual Volume |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Engine Blocks | Aluminum A380 | 15-45 kg | ±0.1mm | 50,000-500,000 |
| Transmission Housings | Aluminum A383 | 8-25 kg | ±0.05mm | 100,000-1,000,000 |
| EV Battery Housings | Aluminum 6061 | 20-80 kg | ±0.2mm | 20,000-200,000 |
| Door Hinges | Zinc Zamak 5 | 0.5-2 kg | ±0.02mm | 500,000-5,000,000 |
Electronics Applications: Precision and Thermal Management
The electronics industry requires die cast components with excellent dimensional accuracy and thermal conductivity.
We’ve produced heat sinks that can dissipate over 500W of power with temperature rise less than 25°C.
Technical Challenge: One of our most demanding projects was a 5G base station heat sink that required:
• 0.01mm flatness across a 400mm x 300mm surface
• 600W heat dissipation capability
• Weight under 1.2kg
• 10,000 units per month
We solved this with a custom aluminum alloy and optimized fin design that exceeded all performance targets.
Aerospace Applications: The Ultimate Test
Aerospace applications represent the pinnacle of die casting technology, requiring the highest levels of quality and reliability.
All our aerospace components meet AS9100 standards and undergo 100% inspection.
VII. Die Casting vs Alternative Manufacturing Processes
Choosing the right manufacturing process is critical to product success.
Over my career, I’ve helped hundreds of clients decide between die casting and alternative processes like sand casting, investment casting, and CNC machining.
| Characteristic | Die Casting | Sand Casting | Investment Casting | CNC Machining | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material Range | Non-ferrous metals | All metals | All metals | All materials | Plastics |
| Precision | High (±0.01mm) | Low (±1mm) | Very high (±0.005mm) | Very high (±0.001mm) | High (±0.02mm) |
| Surface Finish | Good (Ra 1.6μm) | Rough (Ra 12.5μm) | Excellent (Ra 0.8μm) | Excellent (Ra 0.4μm) | Good (Ra 0.8μm) |
| Complexity | High | Medium | Very high | Very high | High |
| Production Rate | Very high | Low | Low | Low | Very high |
| Tooling Cost | High | Low | Medium | Low | High |
| Unit Cost (100k parts) | Low | Medium | High | Very high | Low |
| Lead Time | Medium (4-12 weeks) | Short (1-4 weeks) | Long (8-16 weeks) | Short (1-2 weeks) | Medium (4-10 weeks) |
Die Casting vs Sand Casting
Sand casting is a traditional process that uses sand molds. While it has lower tooling costs, it can’t match die casting’s precision or production rates.
Decision Criteria: Choose die casting over sand casting when:
• Production volume exceeds 10,000 parts
• Dimensional tolerance requirements are tight (±0.1mm or better)
• Surface finish is important
• Complex internal features are required
Die Casting vs Investment Casting
Investment casting (also called lost-wax casting) offers excellent precision and surface finish but is much slower and more expensive than die casting.
Die Casting vs CNC Machining
CNC machining offers the highest precision but is limited by material waste and production speed.
For volumes over 1,000 parts, die casting is typically 50-80% cheaper than CNC machining.
For a recent client producing 50,000 aluminum brackets, we reduced their production costs by 72% by switching from CNC machining to die casting.
Die Casting vs Injection Molding
Injection molding is ideal for plastic parts but can’t match the strength, heat resistance, or electromagnetic shielding of metal die castings.
VIII. 2026 Die Casting Industry Trends and Innovations
The die casting industry is undergoing rapid transformation driven by technological advancements and sustainability requirements.
Based on my extensive industry network and participation in major trade shows, here are the key trends shaping 2026 and beyond.
1. Intelligent Manufacturing and Industry 4.0
The integration of IoT, AI, and big data is revolutionizing die casting operations.
At Goldcattle, we’ve implemented a comprehensive Industry 4.0 system that provides real-time monitoring and optimization of all production parameters.
- Real-time Process Monitoring: 500+ sensors per machine capturing 10,000+ data points per second
- AI-driven Quality Prediction: Machine learning models that predict defects with 92% accuracy
- Autonomous Process Optimization: Closed-loop systems that adjust parameters in real-time
- Predictive Maintenance: Reducing unplanned downtime by 68% through early fault detection
Results: Our Industry 4.0 implementation has delivered:
• 35% reduction in cycle time
• 22% improvement in first-pass yield
• 40% reduction in energy consumption
• 50% reduction in maintenance costs
2. Sustainable Die Casting: The Green Revolution
Environmental sustainability is no longer optional—it’s a business imperative.
At Goldcattle, we’ve made significant investments in green die casting technologies.
Recycled Materials
We now use 65% recycled aluminum in our production, up from 30% in 2020.
Our closed-loop recycling system allows us to reclaim and reuse 98% of all scrap material.
Energy Efficiency
Our new generation of die casting machines uses servo-hydraulic technology that reduces energy consumption by 35% compared to traditional hydraulic systems.
Emissions Reduction
We’ve installed state-of-the-art filtration systems that capture 99.9% of particulate emissions.
Our hydrogen-powered melting furnaces reduce CO₂ emissions by 50% compared to natural gas.
3. Integrated Computational Materials Engineering (ICME)
ICME combines computational modeling with experimental data to accelerate material development.
At Goldcattle, we’ve used this approach to develop several proprietary alloys with exceptional properties.
This breakthrough was achieved through ICME and is now being used in aerospace and high-performance automotive applications.
4. Lightweighting Solutions for EVs and Aerospace
The push for fuel efficiency and extended range is driving demand for lightweight components.
We’re at the forefront of this trend with our advanced magnesium alloy technologies.
5. Digital Twin Technology
Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical assets that allow for real-time monitoring and optimization.
We’ve implemented digital twins for all our major die casting cells.
6. 3D Printing Integration
While 3D printing can’t replace die casting for high-volume production, it offers significant advantages for mold manufacturing and rapid prototyping.
We use 3D printing to produce conformal cooling channels that reduce cycle times by 25-40%.
IX. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
The minimum wall thickness depends on the material and part size:
• Aluminum: 0.6mm for small parts, 1.0mm for larger components
• Zinc: 0.3mm for small parts, 0.8mm for larger components
• Magnesium: 0.5mm for small parts, 0.9mm for larger components
• Copper: 1.0mm minimum due to higher melting temperature
Expert Note: While these are theoretical minimums, I recommend adding 0.2-0.3mm for practical production, especially for complex geometries.
Mold life depends on several factors:
• Material: Zinc alloys (600,000+ shots) > Aluminum (500,000+ shots) > Magnesium (400,000+ shots) > Copper (300,000+ shots)
• Mold Material: H13 steel provides the best durability
• Maintenance: Proper care can extend life by 30-50%
• Part Complexity: Simple parts allow longer mold life
At Goldcattle, our average mold life exceeds 500,000 shots for aluminum applications.
We offer comprehensive finishing options:
• As-Cast: Ra 1.6-3.2μm, suitable for many applications
• Shot Blasting: Ra 3.2-6.3μm, uniform matte finish
• Polishing: Ra 0.4-0.8μm, mirror-like finish
• Anodizing: Aluminum parts can be colored and protected
• Painting/Powder Coating: Excellent corrosion protection
• Plating: Zinc, nickel, chrome for decorative and functional purposes
• Electroless Nickel: Uniform coating for corrosion resistance
Lead times vary by project complexity:
• Tooling Design: 2-4 weeks
• Mold Fabrication: 4-8 weeks
• Sampling and Validation: 2-4 weeks
• Production: 1-4 weeks depending on volume
Total lead time: 8-16 weeks for typical projects.
We offer expedited services for urgent requirements.
Consider these factors:
• Production Volume: Best for 10,000+ parts
• Material Requirements: Non-ferrous metals work best
• Tolerance Needs: ±0.01mm to ±0.1mm range
• Complexity: Intricate designs with internal features
• Cost Target: Lower per-unit costs for high volumes
At GoldCcattle, we offer free feasibility analysis to help you make the right decision.
We maintain comprehensive quality certifications:
• ISO 9001:2015: Quality management system
• IATF 16949:2016: Automotive quality management
• AS9100D: Aerospace quality management
• ISO 14001:2015: Environmental management
• RoHS & REACH: Compliance with environmental regulations
• NADCA: North American Die Casting Association member
All our facilities are regularly audited to maintain these certifications.
Absolutely! Our engineering team provides comprehensive design support:
• DFM Analysis: Design for manufacturability reviews
• Material Selection: Expert recommendations based on application requirements
• CAD Modeling: 3D design and optimization
• Simulation: Flow, cooling, and solidification analysis
• Cost Optimization: Design recommendations to minimize production costs
We believe that proper upfront engineering is the key to project success.
Our quality control lab includes comprehensive testing equipment:
• Dimensional: CMM, optical comparators, 3D scanners
• Mechanical: Tensile, hardness, impact testing
• Non-destructive: X-ray, ultrasonic, dye penetrant testing
• Environmental: Salt spray, humidity, thermal cycling
• Chemical: Spectrometry for material verification
• Pressure: Leak testing for hydraulic components
We can provide detailed test reports for all critical components.
X. Conclusion: The Future of Die Casting
Die casting technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace, driven by advancements in materials science, process control, and digital technology.
As I look to the future, I see several key trends that will shape the industry in the coming years.
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning will enable even greater process optimization and quality control.
We’re already seeing AI systems that can predict and prevent defects with over 90% accuracy, and I expect this capability to continue improving.
Sustainability will become an even more important consideration.
The development of new recycling technologies and low-emission processes will help the industry reduce its environmental footprint while maintaining cost competitiveness.
The growth of electric vehicles and renewable energy will drive demand for lightweight, high-performance die cast components.
Magnesium alloys, in particular, will play an increasingly important role in these applications.
The technology continues to push boundaries, enabling products that were previously impossible to manufacture.
At Goldcattle, we’re committed to staying at the forefront of these innovations and helping our clients bring their most ambitious designs to life.
Whether you’re working on a simple bracket or a complex aerospace component, the team at coldCattle has the expertise and capabilities to deliver exceptional results.
We invite you to contact us to discuss your specific requirements and learn how we can help you achieve your manufacturing goals.
Ready to Start Your Die Casting Project?
Contact our engineering team today for a free consultation and project analysis.
Zhang Gong
As a leading expert in precision die casting with over 15 years of hands-on experience, I’ve led over 200 successful die casting projects across automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries.
My expertise includes high-pressure parameter optimization, complex part design, and quality control for critical components.
In 2025, I developed a proprietary magnesium alloy formula that achieved 30% weight reduction while maintaining structural integrity for a major EV manufacturer.