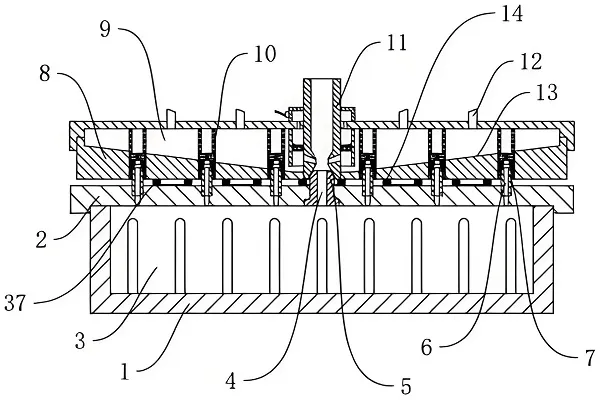
Thermoplastic Molding is a secondary molding technology usingThermoplastic Molding sheets as raw materials. The basic principle is to heat theThermoplastic Molding sheet to the softening temperature (i.e. high elasticity and plasticity), and then by applying pressure (such as gas pressure, liquid pressure or mechanical pressure) to make the blank bending and stretching, until it reaches a certain shape and then cooled and shaped, and finally become the desired shape of the product.

1.Process flow ofThermoplastic Molding molding
Thermoplastic molding process usually includes the following steps:
Raw material preparation: choose suitableThermoplastic Molding sheet as raw material, and according to the need for cutting and pretreatment.
Heating and softening: The cut blanks are placed in a heating system and heated to a softening temperature to make them sufficiently malleable.
Applying pressure: After the blank is softened, it is made to fit on the mold surface or deformed according to a predetermined shape by means of gas pressure, liquid pressure or mechanical pressure.
Cooling and shaping: The blank is kept under pressure for a certain period of time, so that the blank is cooled and shaped to form the desired shape of the product.
Demolding and post-processing: After cooling and shaping, the products are taken out from the molds and necessary post-processing, such as trimming, deburring, sanding, etc., is carried out to improve the surface quality of the products.
2. Introduction ofThermoplastic Molding molding material parameters
Polyethylene (PE)
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE)
Density: about 0.92g/cm³
Melting point: 110~135℃
Heat distortion temperature:60~82℃
Mold temperature:50~70℃
Molding temperature:180~240℃
Characteristics: good flexibility, low temperature resistance, chemical resistance, but relatively low mechanical strength.
High-density polyethylene (HDPE)
Density: 0.94~0.96g/cm³
Melting point: 130~145°C
Heat distortion temperature: higher, depending on the material grade
Mold temperature: 50~95℃
Molding temperature: 180~250℃
Characteristics: Higher mechanical strength, density, tensile strength, high-temperature distortion temperature, viscosity, and chemical stability.
Polypropylene (PP)
Density: about 0.9g/cm³ (different varieties vary slightly)
Melting point: 160 to 170°C (PP-H, PP-B) or higher (e.g., PP-GF)
Heat distortion temperature: Higher, depending on material grade and additives
Mold temperature: 45~55℃ (injection molding process)
Molding temperature: adjusted according to specific varieties and process requirements
Characteristics: good heat resistance, chemical resistance, mechanical strength and processing performance.
Polystyrene (PS)
Density: amorphous density 1.04 ~ 1.06g/cm³, crystalline density 1.11 ~ 1.12g/cm³
Melting temperature: 240℃
Glass transition temperature: 80~90℃
Mold temperature: adjusted according to specific products and process requirements
Molding temperature: higher than the melting temperature
Characteristics: excellent insulation, insulation and transparency, but brittle, easy to crack at low temperature.
Acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene copolymer (ABS)
Density: 1.05~1.08g/cm³.
Melting point: varies according to specific formula and additives, generally between 130~160℃.
Heat distortion temperature: 62~95℃ (normal type) or higher (heat-resistant type)
Mold temperature: 60~80℃
Molding temperature: 180~230℃ (injection molding process)
Characteristics: High strength, low weight, good impact resistance and processing performance.
Nylon (e.g. Nylon 6, Nylon 66)
Density: Nylon 6 is about 1.13g/cm³, Nylon 66 is about 1.15g/cm³.
Melting point: 220-230°C for nylon 6, 255-265°C for nylon 66
Heat distortion temperature: Higher, depending on material grade and additives.
Mold temperature: adjusted according to specific products and process requirements
Molding temperature: higher than the melting point
Characteristics: high strength, high toughness, wear resistance, chemical resistance and good processing performance.
3. Advantages ofThermoplastic Molding molding
High material utilization:Thermoplastic Molding molding can make full use of plastic sheet and reduce material waste.
High molding accuracy: through accurate mold design and control of process parameters, can obtain high precision, high quality products.
Wide range of application: It is applicable to the molding of variousThermoplastic Moldings, such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and so on.
High production efficiency:Thermoplastic Molding molding process is simple, short cycle, can quickly produce a large number of products.
4. Application areas ofThermoplastic Molding molding
Thermoplastic molding technology is widely used in the following fields:
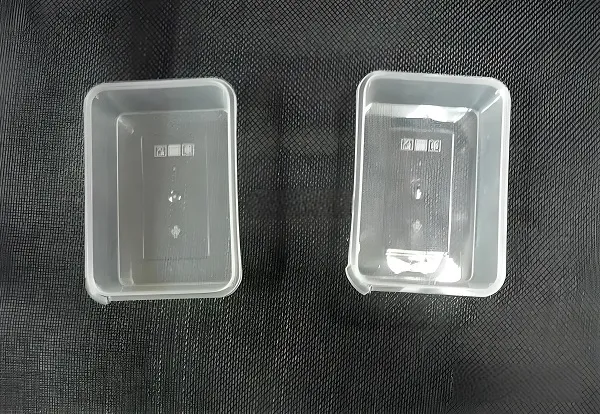
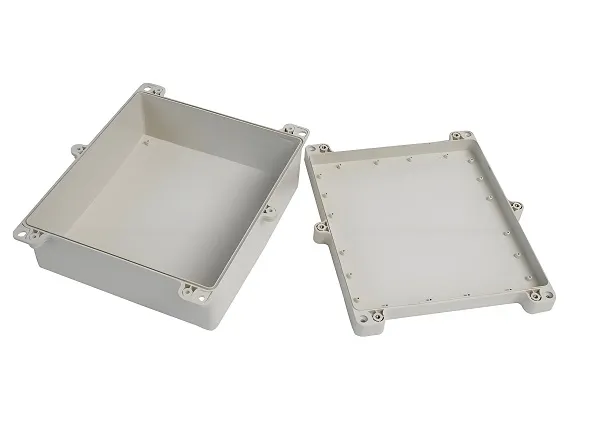
Packaging industry: used in the manufacture of various packaging containers, such as trays, caps, containers, etc.
Automotive industry: In the manufacture of automotive parts,Thermoplastic Molding molding technology is used to manufacture parts such as instrument panels and inner door panels.
Home appliance industry: It is used to manufacture shells and internal parts of home appliances such as washing machines and refrigerators.
Construction industry: In the manufacture of construction materials,Thermoplastic Molding molding technology is used to produce products such as insulation boards and waterproof boards.
CustomThermoplastic Molding Molding Parts FAQ
What isThermoplastic Molding molding?
A:Thermoplastic Molding molding is a plastics processing technique in whichThermoplastic Molding sheets or pellets are heated to a softened state, then pressure is applied to deform them and fit them to the surface of a mold, and they are eventually cooled and shaped into a part of the desired shape. This technique is widely used to manufacture plastic products of various complex shapes and designs.
What materials isThermoplastic Molding molding applicable to?
A:Thermoplastic Molding molding is applicable to a wide range ofThermoplastic Molding materials, such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (PS), ABS, nylon (e.g., nylon 6, nylon 66) and so on. These materials have good plasticity, chemical resistance, mechanical strength and processing properties.
How to ensure the quality ofThermoplastic Molding molded parts?
A: To ensure the quality ofThermoplastic Molding molding parts need to start from the following aspects:
Material selection: Selection of high-qualityThermoplastic Molding materials to ensure that the physical properties and chemical stability of the material.
Mold design: design a reasonable mold structure to ensure the accuracy and durability of the mold, while taking into account the release of parts and molding efficiency.
Process control: Strictly control the process parameters such as heating temperature, molding pressure, cooling time, etc. to ensure the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of the parts.
Post-treatment: Necessary post-treatment is performed on the part to improve the surface quality and dimensional accuracy of the part.
What is the process of customThermoplastic Molding molding parts?
Answer:
Demand Confirmation: Communicate with customers to clarify the specific requirements, quantity and material of the parts.
Mold design: Design the mold according to the part drawings or samples to ensure mold accuracy and molding quality.
Mould Manufacturing: Manufacture the mould according to the design drawings, and carry out debugging and optimization.
Raw Material Preparation: Select suitableThermoplastic Molding raw materials and carry out pre-treatment (e.g. drying, coloring, etc.).
Molding Processing: Heat the raw material to a soft state, put it into the mold for molding, and take out the parts after cooling.
Post-treatment: Necessary post-treatment (e.g. trimming, deburring, sanding, etc.) is carried out on the parts to improve the quality of appearance and usability.
Quality Inspection: Conduct quality inspection on the finished parts to ensure compliance with customer requirements and industry standards.
Delivery to customers: Deliver qualified parts to customers and provide after-sales service and technical support.