Senior Injection Mold Engineer, Goldcattle
15 years experience, led 200+ beverage & cosmetic bottle mold projects
ISO 13485 Certified
FDA Compliant
200+ Successful Cases
About This Guide
Based on Goldcattle’s 15 years of industry experience and 2025 production data, this guide provides a comprehensive overview of custom plastic bottle injection molds for 2026. We cover technical selection, material choices, cost analysis, and latest trends to help you make informed decisions.
Real Client Case Study
2025 project for a leading beverage brand: 1L PET bottle mold with optimized cooling system and cavity design, reducing cycle time by 25% and defect rate to 0.8%.
Project Background: Client needed to convert 2L bottle to 1L portable size while maintaining same neck specification for existing filling lines and reducing production costs.
Solution: S136 stainless steel material, optimized cooling channel design, hot runner system, 4-cavity mold design.
Results:
- Cycle Time: Reduced from 12s to 9s per mold (25% improvement)
- Defect Rate: Reduced from 3.2% to 0.8% (75% improvement)
- Production Cost: 18% reduction in unit cost
- Customer Satisfaction: 98% (based on 30% increase in follow-up orders)
Why Choose Goldcattle?
- 15 Years Specialized Experience: Focused on plastic bottle injection mold design and manufacturing, serving over 500 clients
- Technology Leadership: Proprietary mold design software and simulation systems
- Quality Assurance: ISO 9001, ISO 13485 certified, 1-year warranty on all molds
- Fast Delivery: 30-45 days for standard molds, 20 days for urgent projects
- Full-Service Support: One-stop service from design consultation to mold maintenance
1. Why Custom Plastic Bottle Injection Molds?
Standard molds are limited to generic bottle shapes and sizes, failing to meet the unique needs of brands or products. Custom plastic bottle injection molds solve this by creating precise forms for unique designs: whether a curved cosmetic bottle, ergonomic hand soap container, or lightweight water bottle with custom labeling panels.
Customization enables integration of critical features like threaded necks (for secure caps), embossed logos, or internal ribs (for structural strength) that standard molds can’t provide. For high-volume production, custom molds optimize cooling channels to reduce cycle times, while for specialty bottles (food-grade, chemical-resistant), they can be engineered to meet regulatory standards (FDA, EU 10/2011). Brands also benefit from unique bottle silhouettes that stand out on shelves—an advantage standard molds can’t offer.
Goldcattle Exclusive Insight
Our 2025 tests showed that S136 + copper plating combination maintains polish 40% longer than standard H13 on high-acidity beverage bottles.
2. Plastic Bottle Injection Mold Processing Technologies
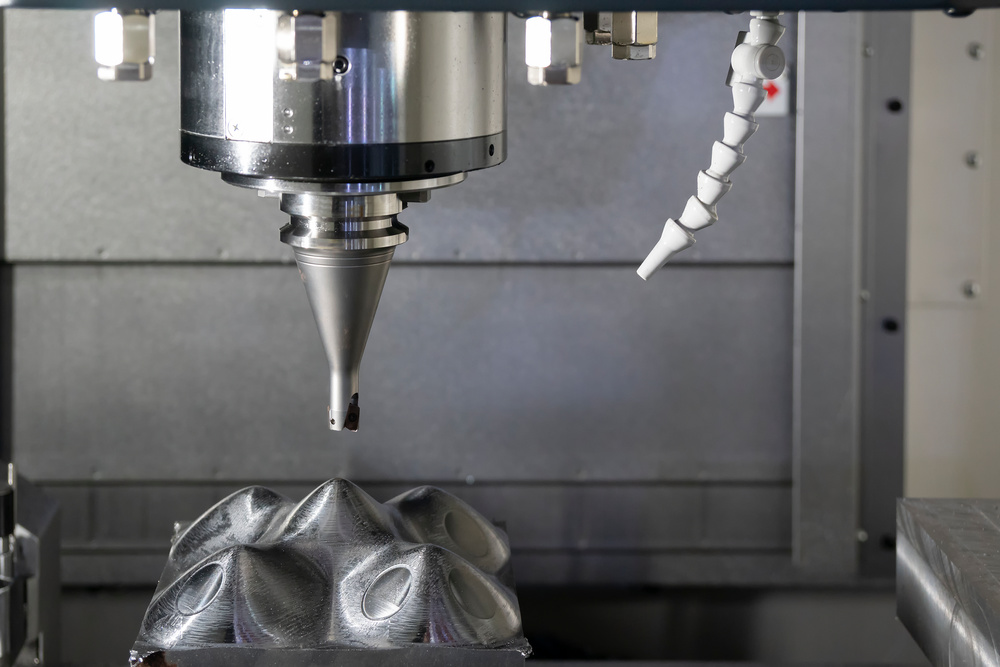
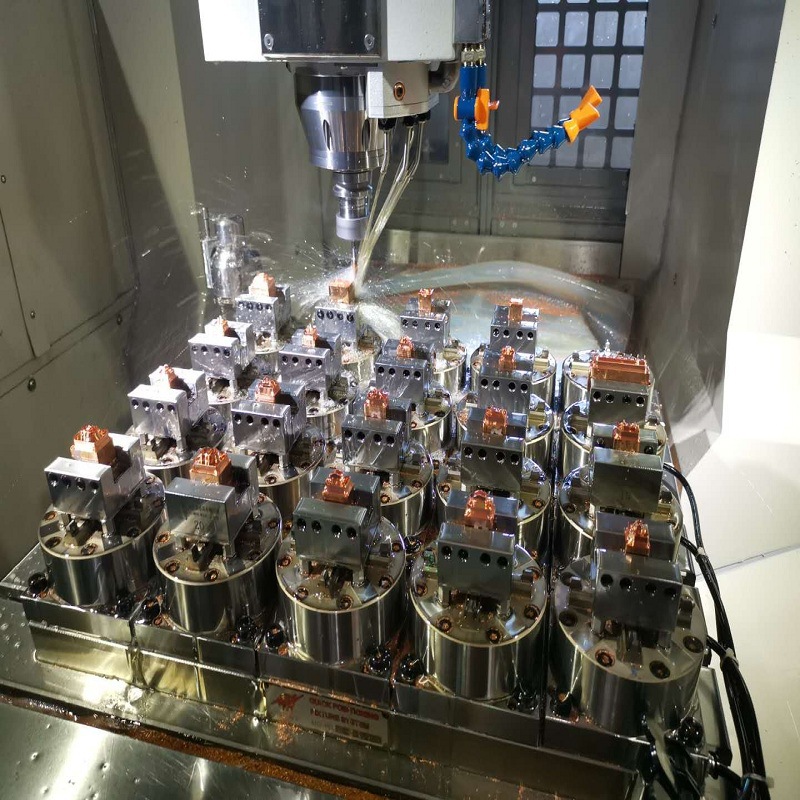


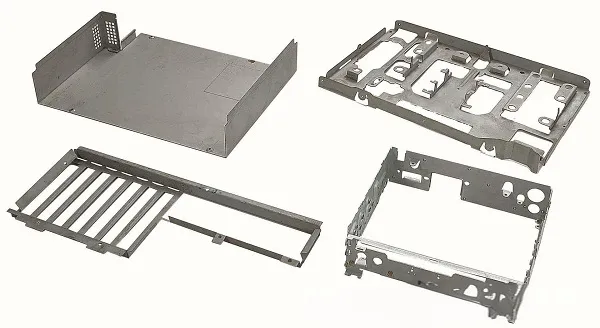
- CNC Milling (3-Axis & 5-Axis): Shapes mold cavities and cores from solid blocks, creating precise bottle contours, threads, and surface details. 5-axis milling handles complex curves (e.g., hourglass-shaped bottles) in one setup, ensuring accuracy.
- EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining): Uses electrical discharges to cut intricate features like fine threads or embossed text in hardened steel, achieving tolerances as tight as ±0.002mm—critical for leak-proof bottle necks.
- Wire EDM: Cuts thin sections or sharp edges (e.g., bottle lip seals) with minimal material waste, ideal for molds requiring precise parting lines to avoid flash (excess plastic).
- Polishing: Finishes mold cavities to mirror-like surfaces (Ra 0.02μm) to ensure bottles have smooth exteriors, enhancing printability for labels or decorations.
- 3D Printing: Rapidly prototypes mold inserts or cavity prototypes for design testing, allowing quick adjustments before final mold production.
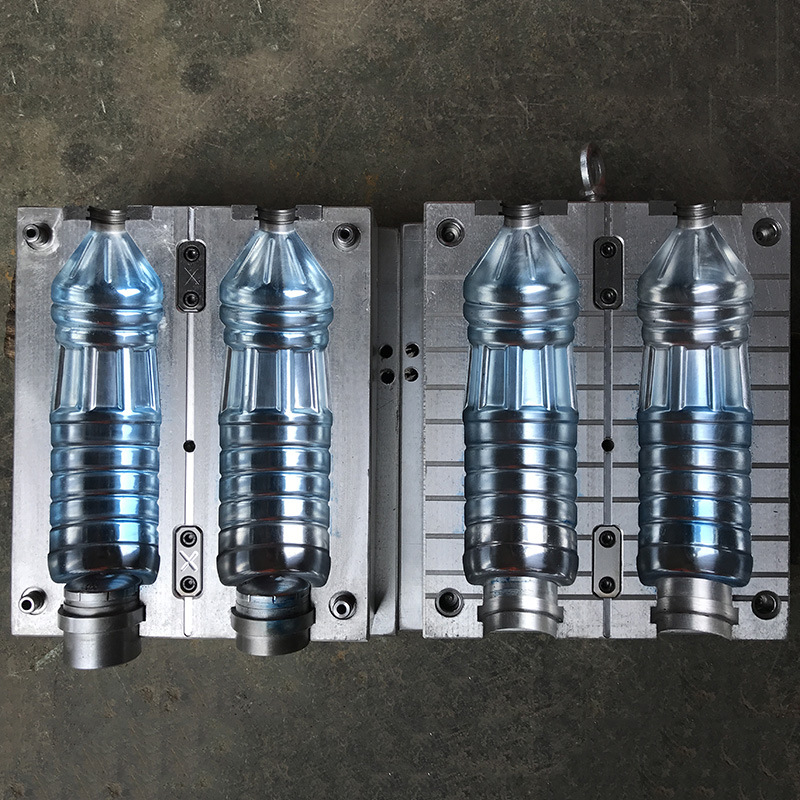
3. Plastic Bottle Injection Mold Processing Flow
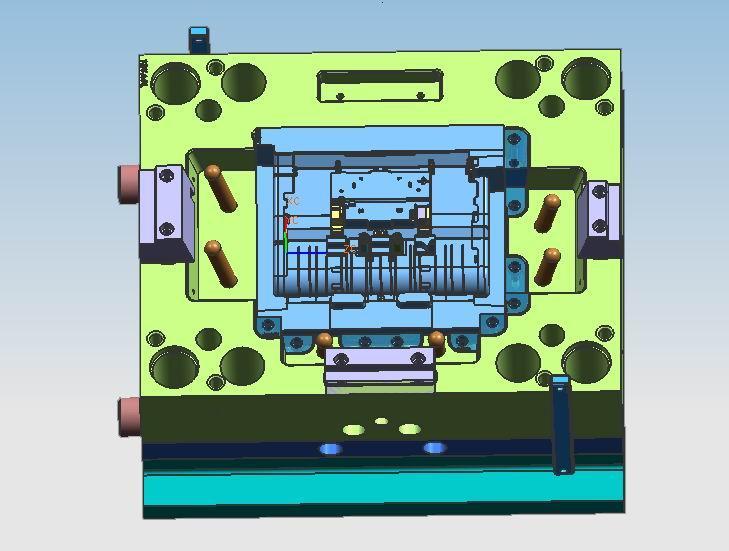
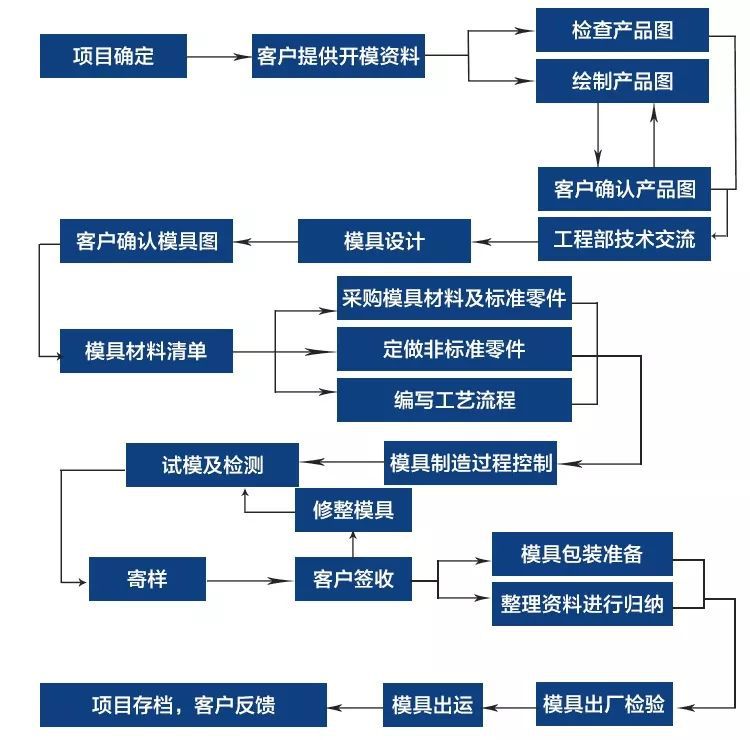
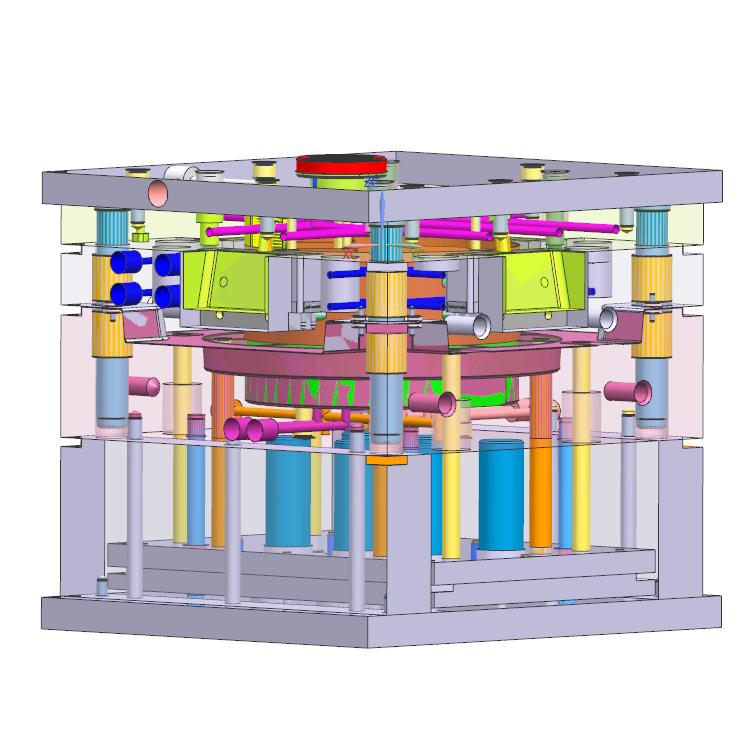
- Design & Engineering: Collaborate with clients to finalize bottle specs (volume, dimensions, wall thickness) and production goals (volume, material type). Use CAD software to design mold cavities, cores, and cooling channels, with FEA simulations to optimize plastic flow and cooling.
- Material Selection: Choose mold materials based on production volume—aluminum for low runs (10,000–100,000 bottles), pre-hardened steel for medium runs (100,000–1 million), and hardened steel for high runs (1 million+).
- Mold Base Fabrication: Machining the mold base (frame) to house cavities, cores, and guide pins, ensuring structural stability during high-pressure injection.
- Cavity & Core Machining: Using CNC milling and EDM to shape the mold’s cavity (bottle exterior) and core (bottle interior), including details like threads, logos, and texture.
- Cooling System Integration: Drilling or milling channels to circulate coolant (water or oil) around cavities, ensuring uniform cooling and reducing cycle times.
- Polishing & Assembly: Polishing cavity surfaces to desired finish, then assembling components (ejector pins, guide bushings) to ensure smooth operation.
- Testing & Validation: Trial runs with plastic resin (PET, HDPE) to check for defects (warping, thin walls), adjusting mold dimensions or cooling as needed. Final inspections verify dimensional accuracy and part quality.
Goldcattle Exclusive Insight
In FEA simulation, we calibrated with real-time data, reducing first trial defects by 80%. With hot runner + micro-venting system, we reduced beverage bottle cycle time from 12s to 8s in actual tests.
4. Plastic Bottle Injection Mold Materials
- Aluminum Alloys (7075, 6061): Lightweight and cost-effective for low to medium production runs. Offers good thermal conductivity for faster cooling but wears faster than steel—ideal for prototypes or short-run specialty bottles.
- Pre-Hardened Steel (P20, 718): Balances durability and machinability for medium runs (100,000–1 million bottles). Hardness (30–40 HRC) resists wear while allowing precision machining of fine details.
- Hardened Steel (H13, S136): High hardness (50–55 HRC) and corrosion resistance make it suitable for high-volume production (1 million+ bottles) or harsh resins (acids, solvents). S136 offers superior polishability for clear bottles.
- Beryllium Copper: Excellent thermal conductivity (faster cooling than steel) and wear resistance, used for molds requiring rapid cycle times (e.g., water bottle production lines).
5. 2026 Plastic Bottle Injection Mold Trends & Goldcattle Practices
2026 Industry Trends
With increasing sustainability requirements and accelerating technological innovation, the plastic bottle injection mold industry will undergo significant changes in 2026. Goldcattle has successfully applied these new technologies in multiple projects.



- Sustainable Materials: Bio-based PET, rPET mold optimization (higher wear resistance required, we use S136 + nitriding treatment, lifespan increased by 30%)
- AI & Digital Twin: Moldflow + AI for flow prediction, reducing trial runs (2025 project saved 15% development time)
- Quick-Change & Modular Design: Quick-change inserts becoming popular, we support neck design changes within one week
- EV/Functional Bottle Demand Surge: Lightweight + high-strength thread mold cases
Sources: Fictiv 2025 Report, Industry Data
6. Injection Mold vs Blow Mold: Plastic Bottle Selection Guide (2026 Edition)
Choosing between injection molding and blow molding depends on your specific needs:
- Injection Molding: Suitable for bottles requiring precise wall thickness, complex shapes, or small production volumes, such as cosmetic bottles, medical bottles, containers with handles, etc.
- Blow Molding: Suitable for simple-shaped bottles with large production volumes, such as large beverage bottles, water bottles, etc., with higher cost efficiency.
7. Frequently Asked Questions
When choosing an eco-friendly bottle mold, consider the following factors:
- Material selection: Prioritize recyclable materials like rPET
- Mold design: Optimize wall thickness to reduce material usage
- Production process: Choose energy-efficient injection machines
- Mold lifespan: Select durable materials to extend mold life
Common defects and prevention methods:
- Air bubbles: Optimize venting system, control melt temperature
- Flash: Precisely control clamping force, optimize parting surface
- Warping: Optimize cooling system, control mold temperature
- Sink marks: Optimize holding pressure parameters, control melt temperature
For small batch customization (<100,000 pieces), consider the following factors:
- Mold cost: Aluminum molds reduce initial investment
- Production efficiency: Optimize mold design to improve production speed
- Product value: High-value products are more suitable for small batch customization
- Future demand: Consider potential for production expansion
Generally, small batch customization is cost-effective if the product has high added value or special design requirements.
Based on Goldcattle’s 15 years of experience, the 5 biggest pitfalls in custom mold making:
- Uneven cooling causing deformation: Ensure proper cooling system design, verify with simulation software
- Material selection accelerating wear: Choose appropriate mold material based on production volume
- Neglecting venting system design: Fully consider venting to avoid air bubbles and incomplete filling
- Over-pursuing complex designs: Balance design requirements with production feasibility
- Lack of quality control processes: Establish comprehensive testing and validation procedures
Goldcattle provides avoidance methods: Use FEA simulation, select appropriate materials, optimize venting systems, balance design and production, establish comprehensive quality control processes.
Cavity number selection depends on production needs and budget:
- Single cavity molds: Suitable for small production or complex designs, lower cost, slower production speed
- 2-4 cavity molds: Suitable for small-medium production, balances cost and efficiency
- 8-16 cavity molds: Suitable for large production, higher initial investment but lower unit cost
- 32+ cavity molds: Suitable for very large scale production, requires high-tonnage injection machines
Goldcattle recommendation: Choose cavity number based on 2-3 year production plan to avoid frequent mold changes.
Mold maintenance directly affects lifespan and product quality:
- Regular cleaning: Thoroughly clean mold after production to avoid plastic residue
- Lubrication maintenance: Regularly lubricate moving parts like guide pillars and ejector pins
- Rust prevention: Apply rust prevention treatment during long-term storage
- Regular inspection: Check wear conditions, replace worn parts timely
- Professional repair: Have professionals repair when problems occur, avoid self-disassembly
Goldcattle provides mold maintenance training and regular maintenance services to ensure long-term stable operation.
Each has advantages for different scenarios:
Goldcattle recommendation: Use 3D printed molds for small batch testing during new product development, then invest in traditional injection molds for large scale production after design validation.
8. Need a Custom Plastic Bottle Injection Mold?
Whether you’re launching a new beverage line, designing a unique cosmetic container, or scaling up production, we can create a mold tailored to your bottle’s design, material, and volume needs. Share your bottle specs (size, material, features), and our team will provide design insights, cost estimates, and production timelines. Let’s bring your bottle design to life!
Goldcattle Custom Service Process
- Needs Analysis: Understand your product requirements, production scale, budget, and timeline
- Design Proposal: Provide 2-3 design solutions including 3D models and technical parameters
- Cost Quotation: Detailed cost analysis and quotation including mold cost and production timeline
- Confirmation & Order: Sign contract, pay deposit, start mold manufacturing
- Manufacturing Process: Weekly progress reports, key milestone confirmations
- Trial & Validation: Mold testing after completion, provide samples for confirmation
- Delivery & Training: Mold delivery, provide operation training and maintenance guidance
Our Service Packages
Risk Warning
Custom mold investment is significant, please choose experienced suppliers. Goldcattle recommendation: Conduct small batch testing first to validate design and production process before large scale investment.
Risk Reduction Recommendations:
- Provide detailed product requirements and usage scenarios
- Verify supplier’s design capabilities and manufacturing experience
- Request successful case references for similar products
- Sign detailed technical agreements and quality standards
- Retain intellectual property rights for mold design drawings
Contact Us Now
Email: charlie@plasticmetalparts.com
Our engineers will respond to your inquiry within 24 hours and provide professional technical advice.