Introduction
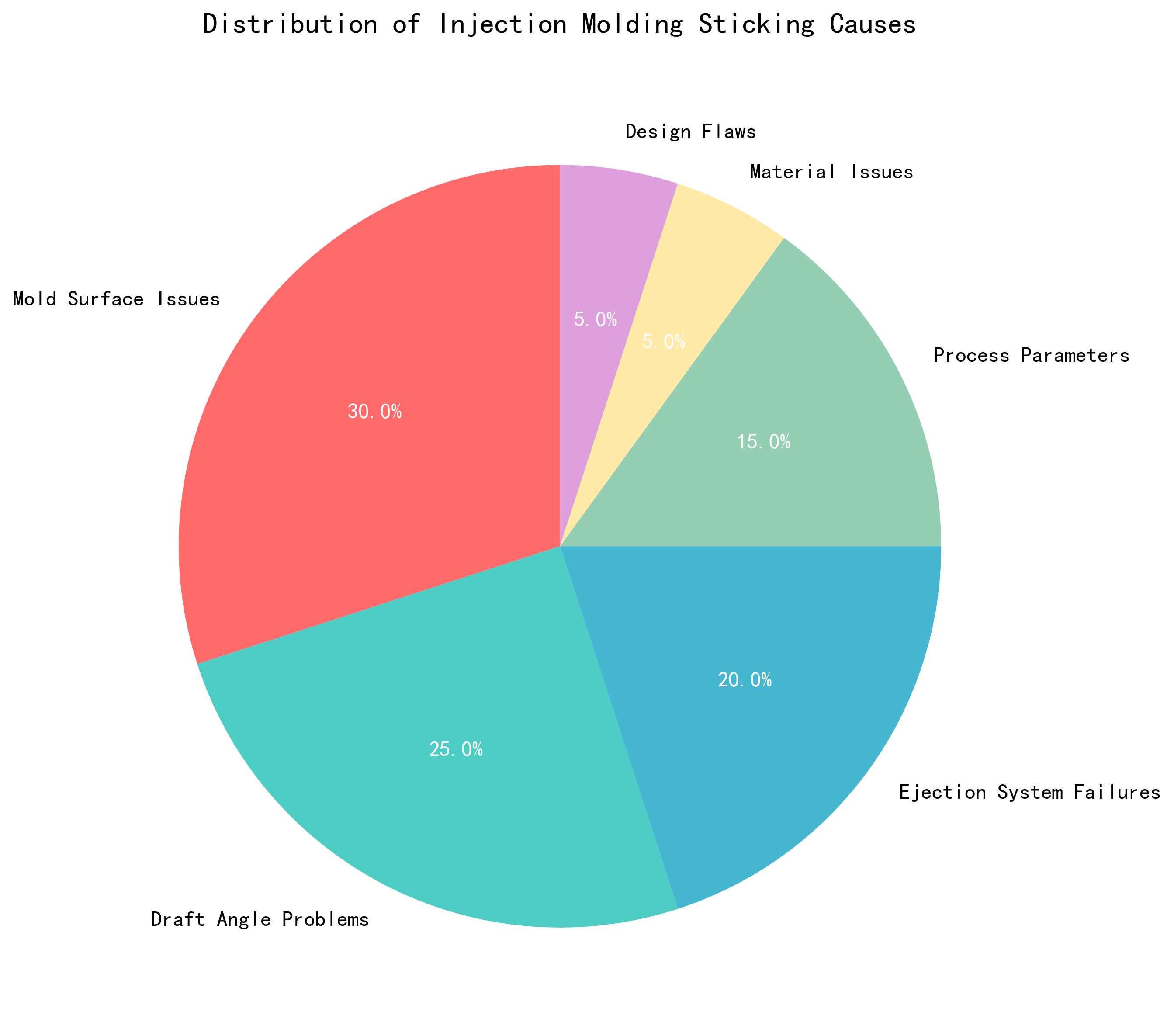
Q1: Why Does Injection Molding Cause Sticking?

The Main Culprits:
- Mold Surface Issues (30% of cases)
-
- Rough surfaces, scratches, or poor polishing
-
- Lack of proper coatings or treatments
-
- Mold wear and tear over time
- Draft Angle Problems (25% of cases)
-
- Insufficient draft angles (less than 3°)
-
- Incorrect angle direction
-
- Complex part geometries
- Ejection System Failures (20% of cases)
-
- Weak ejection force
-
- Improper ejector pin placement
-
- Vacuum issues in deep cavities
- Process Parameters (15% of cases)
-
- Incorrect temperature settings
-
- Too much injection pressure
-
- Improper cooling times
- Material Issues (5% of cases)
-
- Wrong material selection
-
- Contamination or moisture
-
- Material degradation
- Design Flaws (5% of cases)
-
- Poor mold design
-
- Inadequate venting
-
- Unbalanced gating
Q2: How to Properly Adjust for Injection Molding Sticking?
Step-by-Step Adjustment Process:
- Check the Basics First
-
- Verify mold temperature settings
-
- Check injection pressure and speed
-
- Ensure proper cooling time
- Optimize Process Parameters
-
- Reduce injection pressure by 10-15%
-
- Lower melt temperature slightly
-
- Extend cooling time by 10-20%
-
- Adjust holding pressure and time
- Inspect Mold Condition
-
- Check for surface damage or wear
-
- Verify draft angles with a protractor
-
- Ensure proper venting
- Test and Validate
-
- Run small test batches
-
- Document all changes
-
- Monitor results carefully

Q3: How to Solve Parts Sticking to the Mold?
Quick Fixes for Immediate Relief:
- Use Mold Release Agents
-
- Apply silicone-based release agents
-
- Use PTFE sprays for high-temperature materials
-
- Remember: less is more!
- Manual Intervention
-
- Gently tap stuck parts with soft tools
-
- Use compressed air to blow parts free
-
- Never use excessive force!
- Temperature Adjustments
-
- Increase mold temperature by 5-10°C
-
- Reduce melt temperature if possible
-
- Check for temperature inconsistencies
Long-Term Solutions:
- Improve Mold Surface Finish
-
- Polish mold surfaces to mirror finish
-
- Apply hard chrome plating
-
- Consider PVD coatings for durability
- Optimize Ejection System
-
- Increase number of ejector pins
-
- Add air ejection for deep cavities
-
- Ensure proper ejector plate alignment
- Redesign Problem Areas
-
- Increase draft angles to minimum 3°
-
- Add radii to sharp corners
-
- Improve venting systems

Q4: How to Handle Nozzle Sticking Issues?
Common Causes of Nozzle Sticking:
- Temperature Problems
-
- Nozzle temperature too high or too low
-
- Inconsistent heating
-
- Cold slugs forming
- Pressure Issues
-
- Too much back pressure
-
- Inconsistent injection pressure
-
- Improper decompression
- Mechanical Problems
-
- Worn nozzle components
-
- Misalignment with mold
-
- Contamination buildup
Solutions:
- Temperature Adjustment
-
- Optimize nozzle temperature profile
-
- Ensure proper heat distribution
-
- Preheat nozzle before production
- Pressure Optimization
-
- Reduce back pressure
-
- Implement proper decompression
-
- Stabilize injection pressure
- Mechanical Fixes
-
- Replace worn nozzle tips
-
- Realign nozzle to mold
-
- Clean nozzle regularly

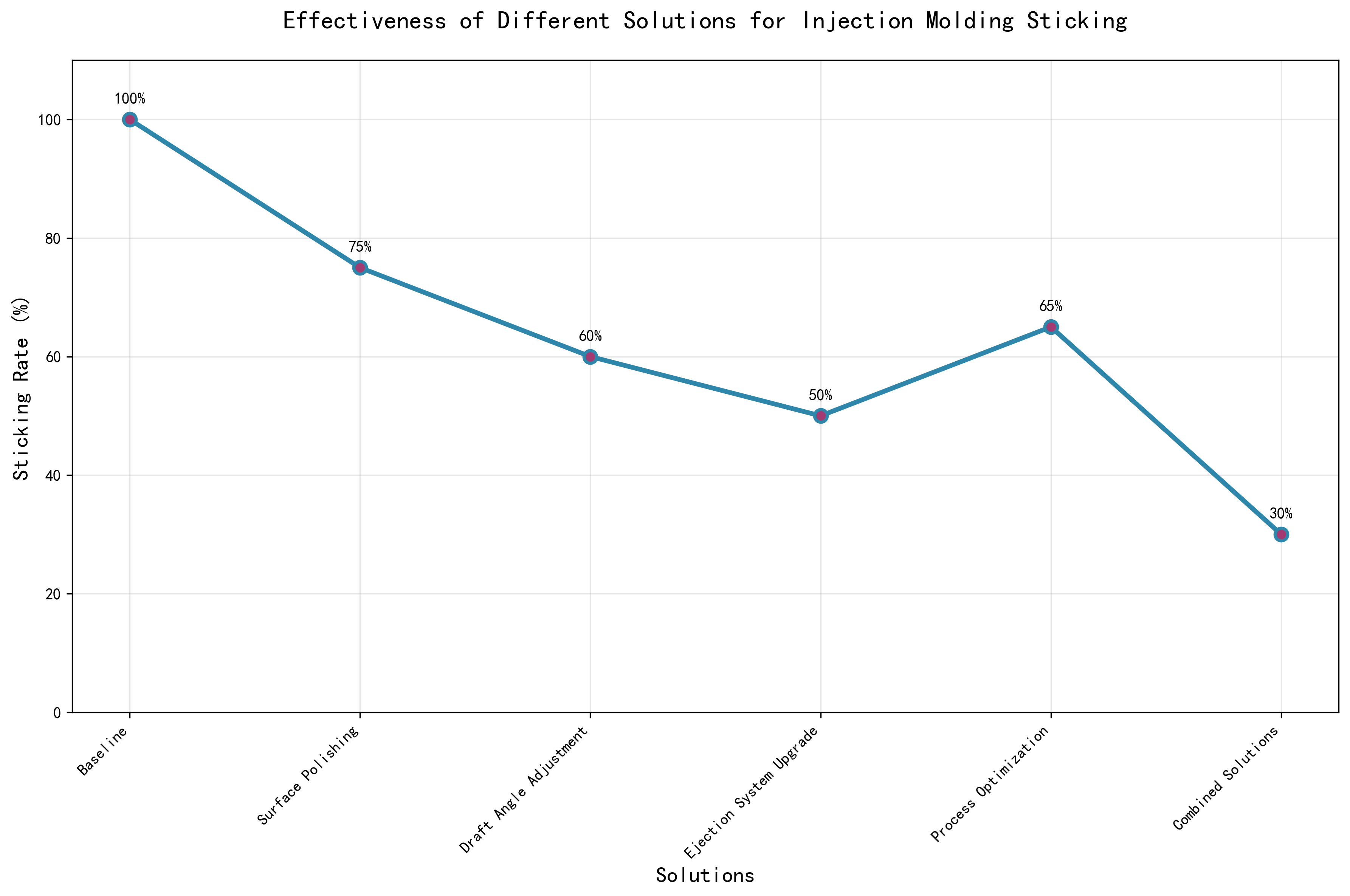
Q5: How Effective Are Different Solutions?
Key Takeaways from the Chart:
- Combined Solutions work best (30% sticking rate)
- Ejection System Upgrade is very effective (50% sticking rate)
- Draft Angle Adjustment is also great (60% sticking rate)
- Process Optimization helps significantly (65% sticking rate)
- Surface Polishing provides good improvement (75% sticking rate)
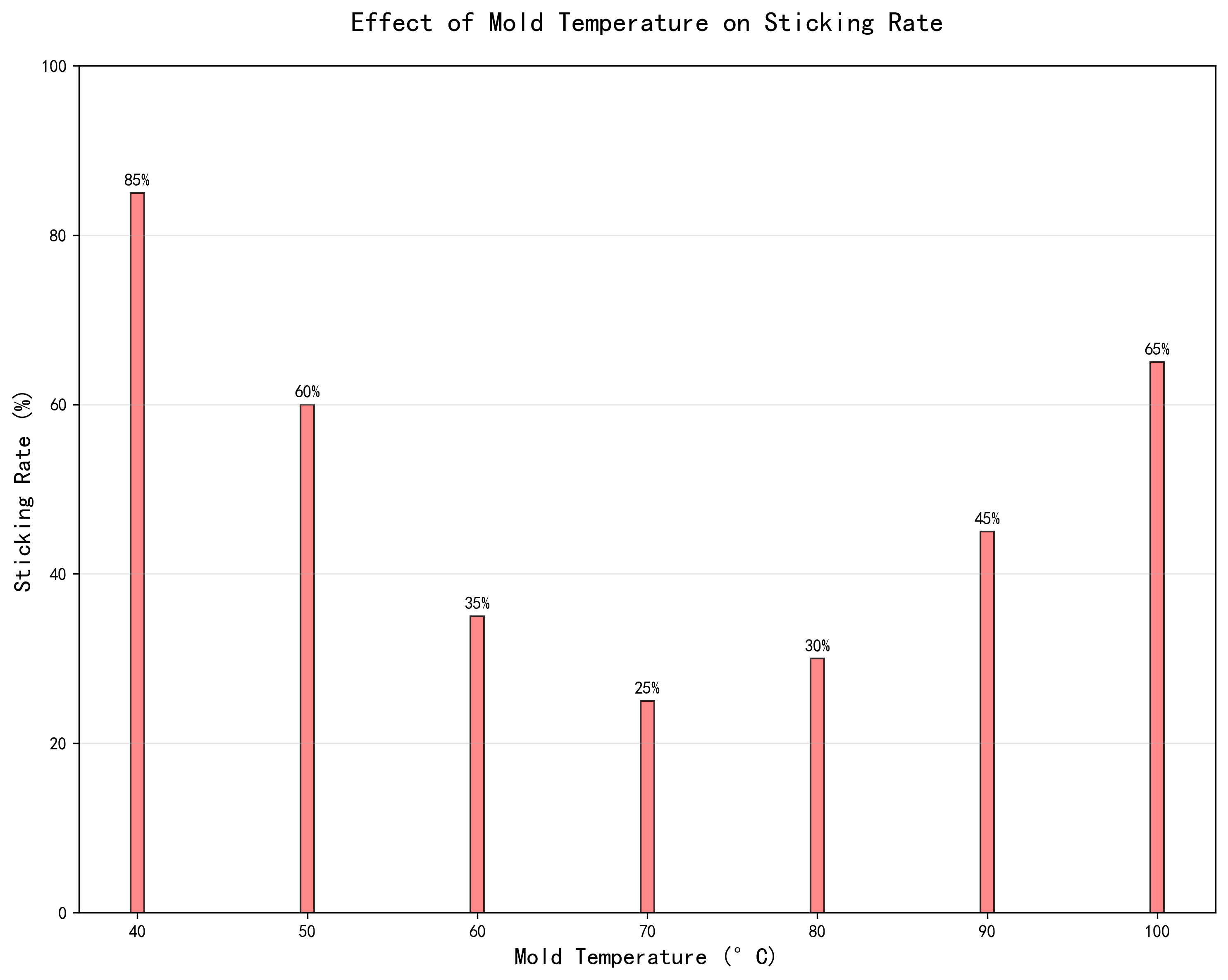
Q6: What’s the Impact of Mold Temperature?
Temperature Sweet Spot:
- 70°C is optimal (25% sticking rate)
- Too cold (40-50°C): High sticking rates (60-85%)
- Too hot (90-100°C): Increased sticking (45-65%)
- Golden range: 60-80°C for most materials
Preventive Maintenance Tips
Daily Checks:
- Clean molds thoroughly after each run
- Inspect for wear and damage
- Check temperature settings
- Verify ejection system functionality
Weekly Maintenance:
- Lubricate moving parts
- Check alignment and parallelism
- Test mold release agents
- Inspect cooling channels
Monthly Maintenance:
- Polish mold surfaces
- Check for material degradation
- Calibrate temperature controls
- Review process parameters
Final Recommendations
- Start with process adjustments before modifying the mold
- Invest in proper mold surface treatments for long-term results
- Train operators on proper setup and troubleshooting
- Document everything to identify patterns
- Consider professional help for persistent issues

All experimental data presented in this paper are derived from controlled production environments and standardized test procedures. However, due to differences in equipment models, material batches, and on-site operating conditions, readers are advised to verify and adjust technical parameters according to their specific application scenarios before practical implementation.
The research results and technical insights shared herein are based on the author’s professional experience and experimental observations. The author and the affiliated institution shall not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (including but not limited to equipment damage, product quality issues, or production losses) arising from the improper use of the information provided in this paper.






