
首页 » Introduction to Injection Services
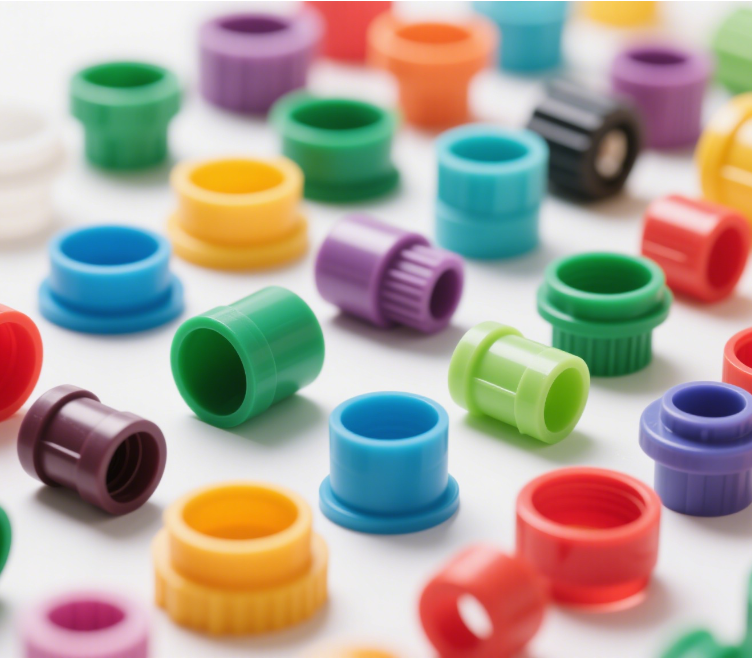

Xiamen Goldcattle Injection Molded services
We provide customized plastic part processing services, capable of achieving high – precision processing results. Our factory has 26 years of experience in injection molding processing and is equipped with advanced injection molding equipment. We use high – quality plastic pellets and can meet the testing requirements of plastic parts in different specifications from customers. Processing can be carried out according to drawings or samples, and samples can be provided for testing. We can endow plastic parts with properties such as high – temperature resistance or corrosion resistance as required by customers. We can also meet customization needs such as coloring plastic parts and printing LOGOs.
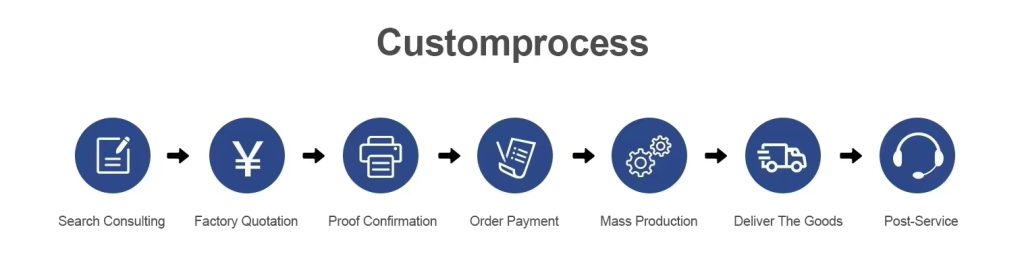
Processed products and injection molding processes

Two - Shot Injection Molding
Introduction: Two sets of molds or a rotating mold are used to inject plastics of different colors or materials in two steps, forming a two – color or two – material product.
Features: It realizes the combination of colors or materials in one – step molding, eliminating the need for later assembly and presenting an exquisite appearance.
Applications: Mobile phone casings (combination of soft and hard rubber), car steering wheels (leather + plastic), transparent buttons with LOGOs, etc.

Multi - Component Injection Molding
Introduction: Three or more materials (such as plastic + metal + rubber) are injected, and composite molding is achieved through multi – station molds or a rotary table.
Features: Integrates multiple properties (such as strength, elasticity, conductivity) and reduces assembly processes.
Applications: Medical devices (plastic + sealing rings), high – end electronic components (structural parts made of composite materials).
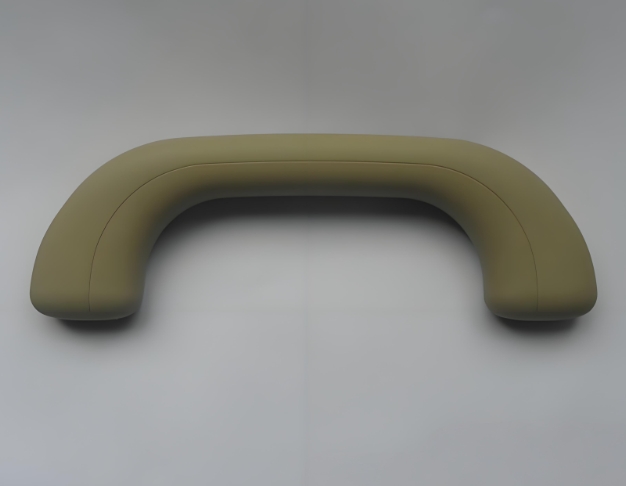

Gas - Assisted Injection Molding (GAIM)
Introduction: After injecting the plastic melt into the mold, high – pressure nitrogen gas is injected into the cavity to push the melt for filling and pressure – holding, and finally the gas is discharged. Features: Reduces product shrinkage, decreases weight, and improves surface quality. It is suitable for thick – walled or complex structural parts. Applications: Automotive bumpers, home appliance casings (such as refrigerator doors), large – scale industrial parts.
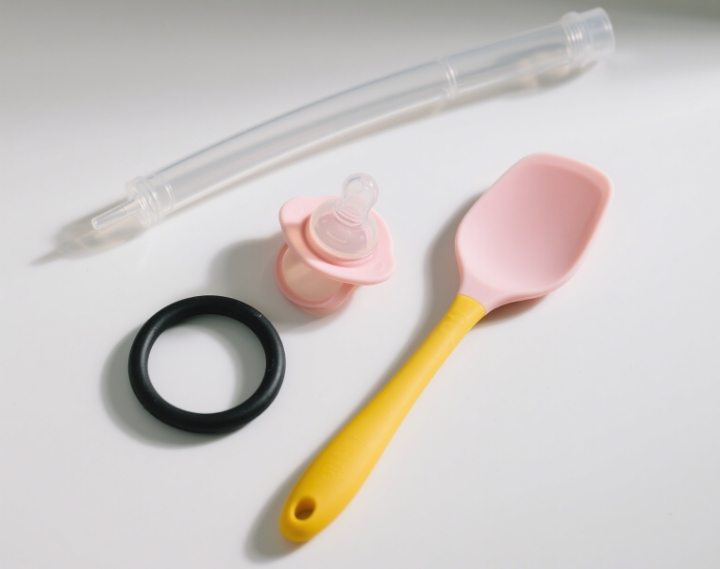
Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding
Introduction: It is an injection molding process for liquid silicone rubber (LSR). The raw materials are precisely metered and mixed before being injected into the mold and then vulcanized at high temperature to form the product.
Features: Silicone products have good elasticity, high – temperature resistance, non – toxicity, and high molding precision.
Applications: Medical catheters, sealing rings, baby products (nipples), kitchen silicone accessories.
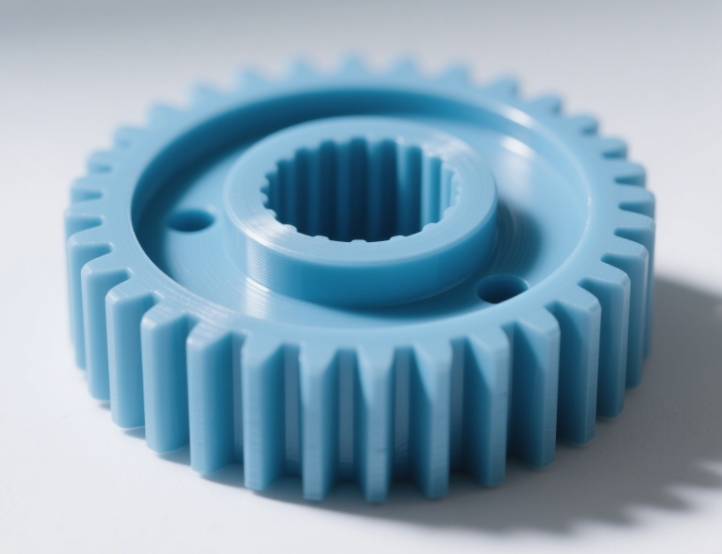
Micro Injection Molding
Introduction: It is used to produce micro – parts ranging from micrometers to millimeters. The mold has extremely high precision, and the injection of a tiny amount of melt needs to be precisely controlled.
Features: The precision can reach the micrometer level. It is suitable for complex and tiny structures and has a high material utilization rate.
Applications: Electronic chip components, medical micro – catheters, precision gears, optical components (such as micro – lenses).
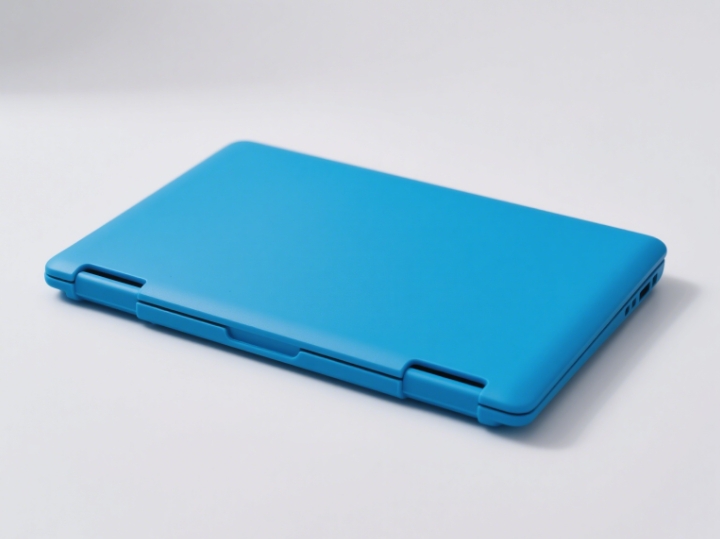

Nano Injection Molding
Introduction: The metal frame and plastic are combined through nano – level surface treatment, allowing the plastic to embed into the micro – pores of the metal to achieve a firm connection.
Features: It enables the integrated molding of metal and plastic, with high bonding strength and a seamless appearance.
Applications: The middle frames of smartphones (metal + plastic), laptop computer casings, high – end wearable devices.
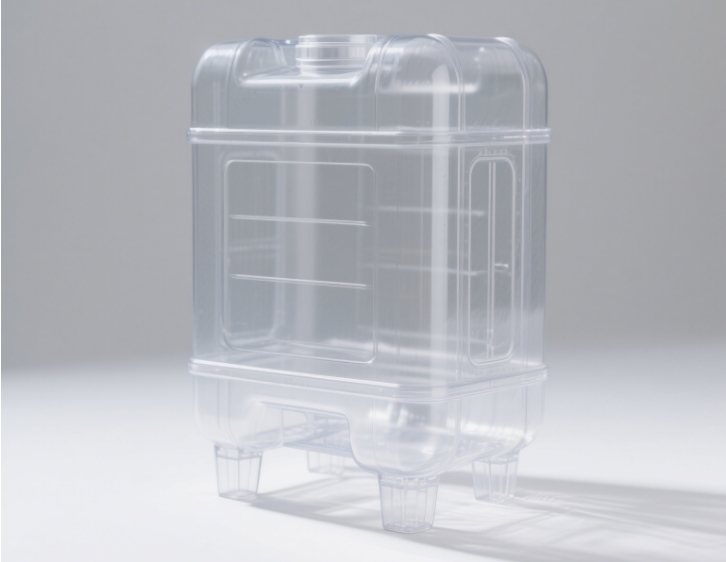

Rotational Molding
Introduction: Plastic powder is added to the mold. The mold rotates along two axes and is heated simultaneously, causing the powder to evenly adhere to the inner wall of the mold and take shape.
Features: It is suitable for large – sized hollow parts. There is no stress concentration, the wall thickness is uniform, and the mold cost is low.
Applications: Plastic water tanks, children’s play facilities, automotive fuel tanks, outdoor furniture.
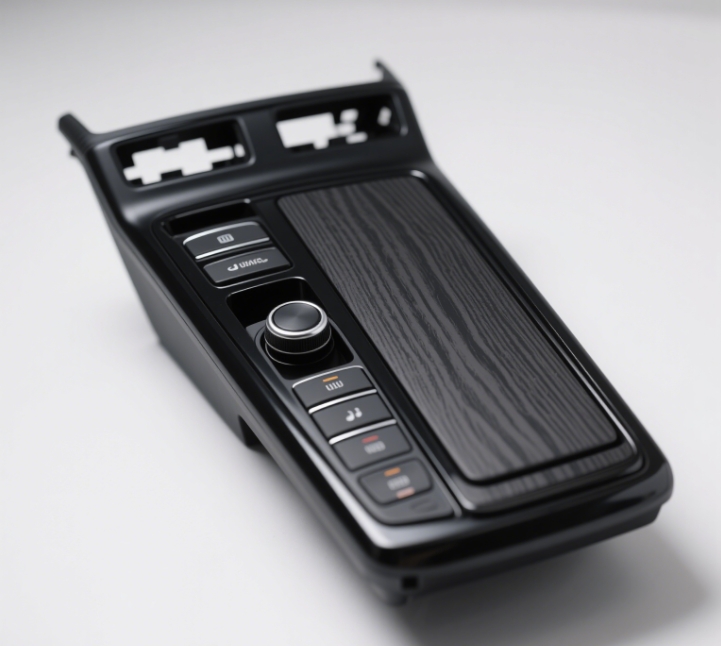

Foam Injection Molding
Introduction: A foaming agent (physical or chemical foaming agent) is injected into the plastic melt. During the molding process, the foaming agent decomposes to produce gas, creating a microporous structure inside the product.
Features: The products are lightweight, have good heat and sound insulation properties, and reduce material consumption.
Applications: Automotive interior parts (such as instrument panels), packaging materials, mid – soles of sports shoes.
Classification and Characteristics of Common Plastic Materials
| Chemical Name | Abbreviation | Key Properties | Common Uses | Recyclable? | Recycling Notes | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene Terephthalate | PET | High transparency, resistant to water and acids, moderate heat resistance (≤70℃), good chemical resistance but prone to deformation at high temperatures. | Mineral water bottles, beverage bottles, snack packaging, textile fibers (e.g., polyester). | Yes | Must be cleaned, flattened, and free of oil; some regions only accept bottle recycling. | Difficult to degrade, prone to microplastic formation; may release trace harmful substances (e.g., antimony) at high temperatures. |
| High-Density Polyethylene | HDPE | Resistant to acids, alkalis, and low temperatures; high hardness and chemical corrosion resistance; moderate heat resistance (≤120℃). | Milk jugs, detergent bottles, trash cans, plastic bags, water pipes, cutting boards. | Yes | Must be clean and dry; avoid mixing with other plastics; can be recycled into containers, pipes, etc. | Highly stable and non-biodegradable; incineration may produce harmful gases (e.g., carbon monoxide). |
| Polyvinyl Chloride | PVC | Flexible (with plasticizers), flame-retardant, resistant to water and oil, but poor heat resistance (≤60℃); releases harmful substances at high temperatures. | Plastic wrap (rarely used), water pipes, raincoats, plastic doors/windows, artificial leather, wire insulation. | Recyclable in some areas | Difficult to recycle, requires professional handling; chlorine-containing, emits dioxins (highly toxic) when incinerated. | Plasticizers (e.g., phthalates) may be carcinogenic; high risk of microplastic pollution. |
| Low-Density Polyethylene | LDPE | Soft, transparent, resistant to low temperatures, good ductility, but poor heat resistance (≤90℃) and prone to aging. | Plastic bags, food wrap, plastic films, flexible hoses, cosmetic bottles. | Recyclable in some areas | Must be cleaned to avoid tangling; can be recycled into garbage bags, plastic flowers, etc. | Prone to aging and breaking into microplastics, posing a risk of marine life ingestion. |
| Polypropylene | PP | Best heat resistance (≤160℃), chemical corrosion resistance, and bend resistance, but brittle at low temperatures and low transparency. | Microwave-safe food containers, yogurt cups, baby bottles, plastic tableware, automotive parts, ropes. | Yes | Can be reused; recycled into stationery, furniture, fibers, etc. | Relatively environmentally friendly but difficult to degrade; produces minor harmful substances when burned. |
| Polystyrene | PS | Transparent, hard, and brittle; good insulation, poor heat resistance (≤70℃); releases styrene monomer at high temperatures. | Disposable food containers, foam packaging (EPS), CD cases, toys, lamp covers. | Recyclable in some areas | Foam (EPS) requires separate collection and is prone to fragmentation; recycled into photo frames, building materials, etc. | Foam products easily break into microplastics and are non-biodegradable; incineration produces toxic gases (e.g., styrene). |
| Other Plastics (e.g., PC, ABS) | PC/ABS, etc. | Diverse properties (e.g., PC is transparent and heat-resistant but contains BPA; ABS is strong and impact-resistant). | PC: Water bottles, baby bottles, eyeglass lenses; ABS: Electronic casings, toys, automotive parts. | Partially recyclable | PC should avoid high temperatures (BPA risk); recycling systems are unimproved, check local policies. | BPA in PC may disrupt endocrine systems; ABS emits toxic gases when burned; both are non-biodegradable. |
Customized injection molding parts process
Requirement Communication and Project Evaluation
1. Clear Product Requirements
- The customer provides information such as the part’s purpose, appearance requirements, dimensional specifications, and usage environment (e.g., temperature, humidity, chemical resistance).
- Example: If the part is used for a car hood, high – temperature resistance and mechanical strength should be emphasized. If it is a daily – use product, attention should be paid to the surface finish and feel.
2. Feasibility Analysis
- Evaluate the applicability of the injection – molding process (e.g., whether a complex structure requires a multi – slider mold), and preliminarily estimate the production cost.
3. Quotation and Contract Signing
- Quote based on factors such as material cost, mold complexity, and production quantity, and confirm the delivery time and technical standards.
Product Design and Material Selection
1. 3D Modeling and Drawing Design
- Use CAD software (such as SolidWorks, UG) to draw a 3D model, and mark details such as tolerances, draft angles, and gate positions.
- Key points: Avoid sharp corners (to prevent stress concentration), and design a reasonable draft angle (usually 1° – 3°).
2. Material Selection
- Select plastic materials according to the usage scenario. Common materials include:
- General – purpose plastics: PP (good weather resistance), PE (flexible), ABS (balanced comprehensive performance).
- Engineering plastics: PC (high transparency, impact – resistant), POM (wear – resistant), PA (high strength).
- Example: Choose PP or PE for food – grade parts, and flame – retardant ABS for electronic component housings.
3. Mold Flow Analysis (CAE)
- Simulate melt flow, cooling, and shrinkage through software to predict defects such as sink marks, air bubbles, and weld lines, and optimize the design.
Mold Design and Manufacturing
1. Mold Structure Design
- Determine the mold type (such as two – plate mold, three – plate mold), the number of cavities (single – cavity or multi – cavity), and the gate form (point gate, submarine gate).
- Core components: fixed mold, moving mold, ejection system, cooling system, and gating system.
2. Mold Processing
- Steps:
- Mold material selection: Commonly used steels include S136 (corrosion – resistant) and 718H (pre – hardened steel, suitable for high – precision molds).
- Processing techniques: CNC milling, electrical discharge machining (EDM), wire – cutting (slow – wire), and polishing.
- Example: Complex surfaces require EDM processing, and parts with a mirror – like appearance need the mold surface to be polished to Ra0.01μm.
3. Mold Assembly and Trial – run
- Assemble the mold and conduct the first trial – run to check whether the part’s dimensions and appearance meet the design requirements.
Preparation for Injection – molding Production
1. Equipment Debugging
- Select an appropriate injection – molding machine (based on part weight and clamping force requirements), and set parameters:
- Barrel temperature: Adjust according to the material’s melting point (e.g., the barrel temperature for ABS is 200 – 240℃).
- Injection pressure: Usually 80 – 150MPa to prevent flash or insufficient filling.
- Cooling time: Depends on the part thickness to avoid deformation during demolding.
2. Raw Material Pretreatment
- Hygroscopic materials (such as PA, PC) need to be dried (the drying temperature for PA is 80 – 100℃ for 4 – 6 hours) to prevent hydrolysis.
Injection – molding Production and Process Control
1. Trial – run and Parameter Optimization
- First Article Inspection (FAI): Use a coordinate measuring machine to check dimensions, and visually inspect for defects such as flash and sink marks.
- Adjust parameters: For example, increase the injection pressure if there is insufficient filling, and lower the barrel temperature if there are silver streaks on the surface.
2. Mass Production
- Continuously monitor the production process, sample parts every hour, and record equipment operation data (such as pressure and temperature fluctuations).
3. Mold Maintenance
- Regularly clean the mold surface residues and spray rust – preventive agents to avoid a decline in part accuracy due to mold wear.
Injection
Molding
Manufacturers





Xiamen Goldcattle Injection Molded Parts Display

Plastic Toy

Automotive injection

3C Injection

Cosmetic plastic parts

Household plastic parts
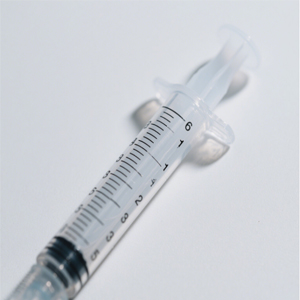
Medical plastic parts
Injection Molding equipment/workshop






