Global Market Size
Regional Distribution Pattern
- Asia-Pacific Region: Accounts for approximately 48% of global production capacity, with China, India, and Southeast Asian countries contributing the main growth
- China: Produced about 128 million tons of plastic molded products in 2023, accounting for over 35% of global total production
- North American Market: Reached approximately $98 billion in 2023, representing 16.7% of global market share
- European Market: Valued at around €86 billion in 2023, with Germany, Italy, and France as major production bases
Core Advantages

- Lightweight: Density is only 1/4-1/8 of metal, significantly reducing product weight
- Cost-effective: Low raw material costs, high molding efficiency, suitable for mass production
- Corrosion-resistant: Excellent chemical stability, resistant to various chemical substances
- Easy processing: Mature molding processes, capable of manufacturing complex shapes and precision structures
- High design freedom: Enables complex geometries and multi-functional integrated designs
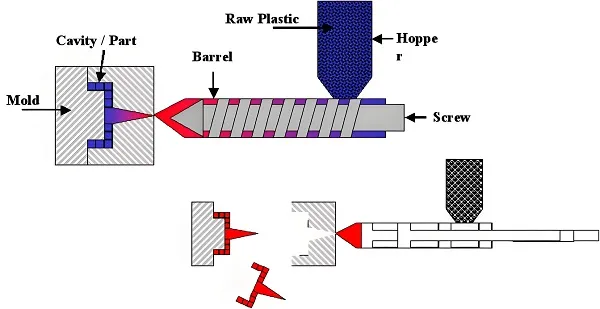
Technical Principles of Plastic Molding
Basic Principles
Technical Characteristics
- Material Melting: Plastic pellets are melted into a viscous flow state in the heating system
- Pressure Injection: Molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure
- Cooling and Solidification: The melt cools and solidifies into a solid state in the mold
- Demolding and Part Removal: The mold opens and the molded part is removed
Detailed Molding Processes
Injection Molding
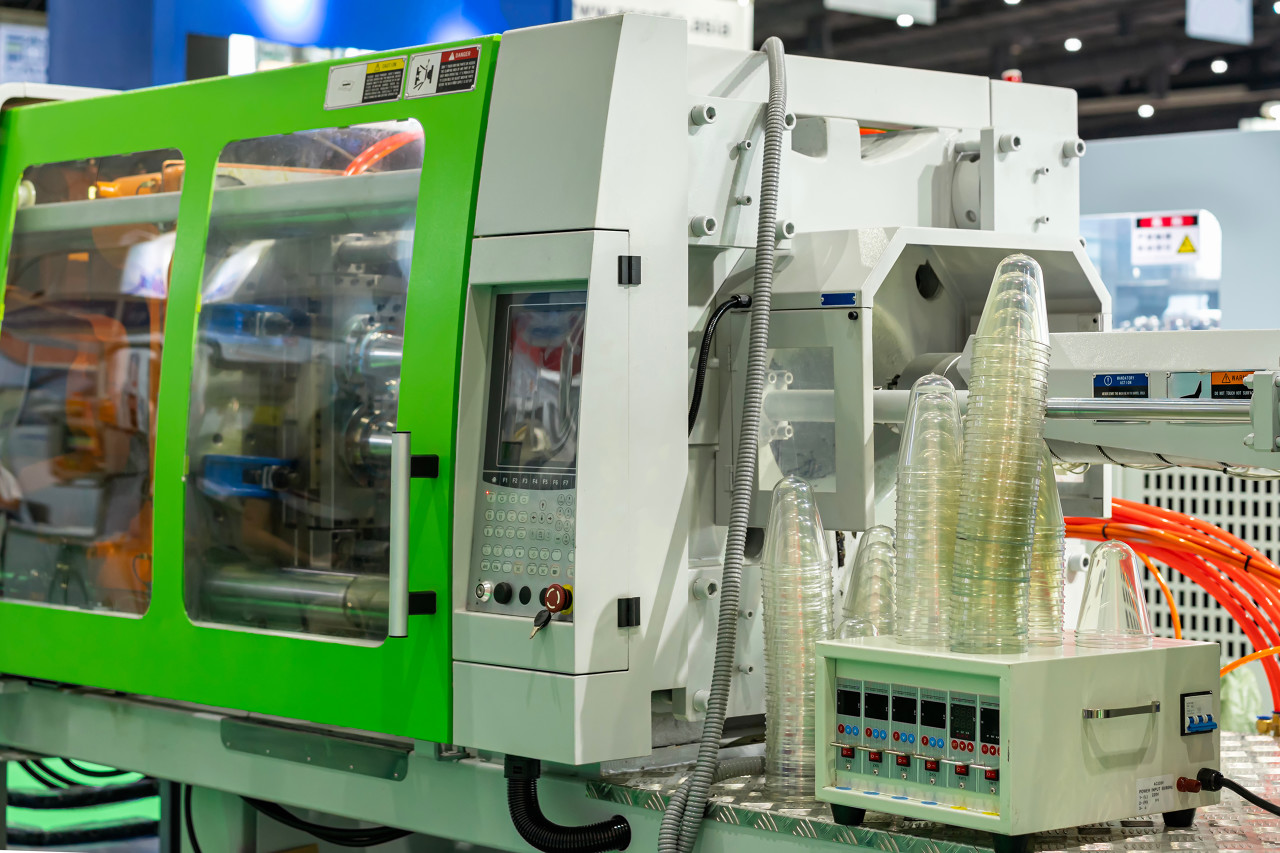

Technical Parameters
- Injection Pressure: 50-150MPa
- Injection Speed: 50-200mm/s
- Barrel Temperature: 150-300°C (varies by material)
- Cycle Time: 30 seconds – 5 minutes
Application Scope
- Precision Components: Electronic connectors, medical device parts
- Large Structural Parts: Automotive bumpers, instrument panels
- Thin-wall Products: Mobile phone cases, home appliance components
Extrusion Molding
Process Characteristics
- Continuous Production: 24-hour continuous production capability with extremely high efficiency
- Diverse Profiles: Can manufacture pipes, sheets, rods, films, etc.
- Low Equipment Investment: Relatively lower investment cost compared to injection molding equipment
Application Fields
- Construction Sector: Plastic window/door profiles, water supply pipes
- Packaging Sector: Plastic films, strapping bands
- Electronics Sector: Wire/cable insulation, heat shrink tubes
Blow Molding
Main Types
- Extrusion Blow Molding: Used for manufacturing hollow products like bottles and containers
- Injection Blow Molding: Used for manufacturing high-precision hollow products
- Stretch Blow Molding: Used for manufacturing high-strength transparent bottles
Technical Advantages
- Specialized for Hollow Products: The only process capable of manufacturing hollow plastic products
- Excellent Integrity: Seamless products with high strength
- Cost-effective: Suitable for mass production with low unit cost
Compression Molding
Suitable Materials
- Thermosetting Plastics: Phenolic resins, epoxy resins, etc.
- High-viscosity Thermoplastics: Some engineering plastics
Application Characteristics
- Suitable for Thick-walled Products: Can manufacture large thick-walled structural parts
- Fiber-reinforced Materials: Suitable for glass fiber-reinforced plastics
- Low-cost Molds: Relatively simple mold structure with lower cost
Material Selection and Performance Analysis
Comparison of Common Materials
|
Performance Indicator
|
PP Polypropylene
|
ABS Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
|
PC Polycarbonate
|
|
Density
|
0.9g/cm³
|
1.05g/cm³
|
1.2g/cm³
|
|
Melting Point
|
160°C
|
105-110°C
|
220-230°C
|
|
Heat Resistance
|
100-150°C
|
70-80°C
|
130°C
|
|
Impact Strength
|
Low (requires modification)
|
High (8-30kJ/m²)
|
Very High (60-80kJ/m²)
|
|
Transparency
|
Semi-transparent
|
Opaque
|
Highly transparent (>90%)
|
|
Cost
|
Low ($1,200-1,500/ton)
|
Medium ($1,800-2,200/ton)
|
High ($3,000-4,500/ton)
|
|
Processing Difficulty
|
Easy (low-temperature injection)
|
Easy molding (good flowability)
|
High (requires high temperature/pressure)
|
|
Environmental Friendliness
|
Food-grade (non-toxic)
|
Contains styrene (requires treatment)
|
Recyclable (needs sorting)
|
Material Selection Guide
PP Polypropylene
- High-temperature Resistance: Smart sockets, lamp structural components (150°C resistance)
- Food Contact: Food packaging containers, medical device housings
- Low-cost Mass Production: Daily necessities, packaging materials
ABS Plastic
- High Appearance Requirements: Appliance housings, automotive interior components
- High Dimensional Stability Requirements: Instrument panel frames, center console panels
- Cost-performance Priority: Smart switches, remote control housings
PC Polycarbonate
- High Transparency Requirements: Smart panels, camera housings (>90% light transmission)
- High Strength Requirements: Safety protection equipment, helmet visors
- Optical Applications: Optical lenses, VR glasses
Product Customization and Quality Control
Customization Process

- Requirements Analysis
-
- In-depth communication to clarify product shape, dimensions, and performance requirements
-
- Analysis of usage environment and functional needs
-
- Development of technical specifications and acceptance criteria
- Mold Design
-
- Mold structure design based on customer requirements
-
- Optimization of mold cooling and venting systems
-
- Ensuring reasonable mold structure and ease of processing
- Mold Manufacturing
-
- CNC machining centers for mold manufacturing
-
- Precision machining to ensure mold accuracy and durability
-
- Mold testing and adjustments
- Molding Production
-
- Raw material preprocessing (drying, color matching, etc.)
-
- Process parameter optimization and setting
-
- Mass production and process monitoring
- Quality Inspection
-
- Dimensional accuracy testing (coordinate measuring machine)
-
- Appearance quality inspection
-
- Performance testing and certification
Quality Control System
ISO9001 Quality Management System
Key Quality Indicators
- Defect Rate: ≤2% (industry average 3-8%)
- Customer Complaint Rate: ≤1 complaint/month
- Process Parameter Compliance Rate: ≥98%
- Mold Maintenance Plan Completion Rate: 100%
Testing Equipment
- Coordinate Measuring Machine: Dimensional accuracy testing (±0.01mm)
- Colorimeter: Color consistency testing
- Impact Testing Machine: Mechanical performance testing
- Heat Deflection Temperature Tester: Heat resistance performance testing
Application Fields and Market Prospects
Automotive Industry Applications
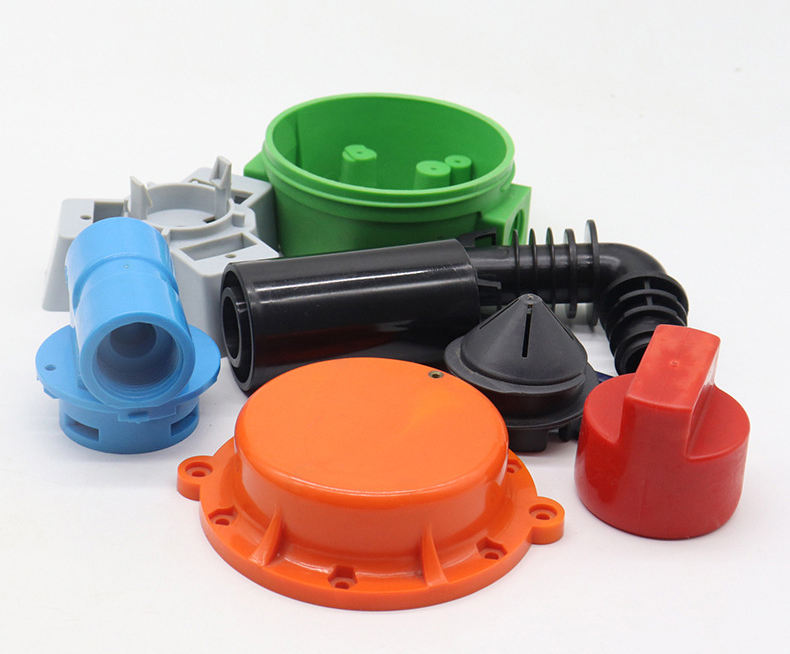

Main Applications
- Body Structural Components: Bumpers, door panels, instrument panels
- Interior Components: Seats, center consoles, steering wheels
- Functional Components: Intake manifolds, fuel tanks, electronic module housings
Technical Requirements
- Lightweighting: New energy vehicles use up to 186kg of engineering plastics per vehicle
- Heat Resistance: Components around the engine need to withstand temperatures above 120°C
- Impact Resistance: Bumper cantilever beam impact strength needs to be ≥20kJ/m²
Electronics Industry Applications

Precision Electronic Housings
- Mobile Phone Cases: Thickness 0.3-0.8mm, precision ±0.05mm
- Smart Watches: Complex curved surface design, high-gloss surface
- Connectors: Miniaturized design, multi-cavity mold molding
Technical Challenges
- Miniaturization: Wearable devices demand micron-level precision
- Thin-wall Technology: 0.3mm ultra-thin structural parts with ±0.01mm tolerance control
- High Gloss: Surface roughness Ra ≤0.2μm
Medical Industry Applications
Medical-grade Material Requirements
- Biocompatibility: Compliant with ISO10993 standards
- Cleanliness: Class 7 cleanroom production
- Traceability: Complete production records and batch management
Typical Applications

- Syringe Components: High-precision fit, leak-proof
- Surgical Instruments: High strength, sterilization-resistant
- Diagnostic Equipment: Optical-grade transparent parts, high precision
Packaging Industry Applications
Sustainable Development Trends
- Recycled Plastics: Approximately 22% of global plastic molded products used recycled materials in 2023
- Bio-based Materials: Growing applications of biodegradable materials like PLA and PHA
- Lightweight Design: Reducing material usage, lowering costs and environmental impact
Technology Development Trends
Intelligent Production
- AI-optimized Processes: AI algorithms optimize injection parameters and predict defect risks
- IoT Monitoring: Real-time equipment status monitoring and predictive maintenance
- Digital Twin: Establishing digital models of production processes to optimize efficiency
Green Manufacturing
- Servo Energy-saving Injection Molding Machines: Account for 78% of market, reducing energy consumption by 30%
- Closed-loop Waste Recycling: 100% recycling of production waste
- Chemical Recycling Technology: Establishing commercial channels for high-end recycled materials
Material Innovation
- Bio-based Plastics: Corn starch-based PP reduces carbon footprint by 30%
- Nanocomposites: 50% increase in surface hardness, replacing some metals
- Paint-free Technology: Reducing VOC emissions and lowering costs
Process Innovation
- 3D Printing Molds: Rapid prototyping, shortening development cycles
- Multi-material Injection: Achieving integrated molding of different materials
- Micro-injection Technology: Manufacturing micron-level precision components
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What are the main advantages of plastic molded parts?
Q2: How to select the appropriate plastic material?
- Product functional requirements (strength, heat resistance, transparency, etc.)
- Operating environment conditions (temperature, chemical exposure, mechanical stress, etc.)
- Cost budget and production volume
- Processing technology requirements
Q3: How to ensure dimensional accuracy of plastic molded parts?
- Precision mold design and manufacturing (±0.01mm accuracy)
- Strict process parameter control (temperature, pressure, time)
- Advanced testing equipment (coordinate measuring machine)
- Continuous process monitoring and adjustments
Q4: What is the typical tolerance range for plastic molded parts?
- Standard precision: ±0.1mm
- Medium precision: ±0.05mm
- High precision: ±0.02mm
- Ultra-high precision: ±0.01mm
Q5: What are the environmental requirements and development trends in plastic molding?
- EU imposes high tariffs on plastic packaging with recycled content below 30%
- California SB 54 mandates 65% packaging recycling rate by 2032
- China’s “14th Five-Year Plan” plastic pollution control action completely bans non-degradable single-use products
- Recycled plastic penetration rate increasing from 22% in 2023 to over 35% by 2028
- Rapid growth in bio-based and biodegradable plastic applications
- Establishment of circular economy models