Core Question: What is LSR Injection Molding? Why Can It Produce Precision Products?
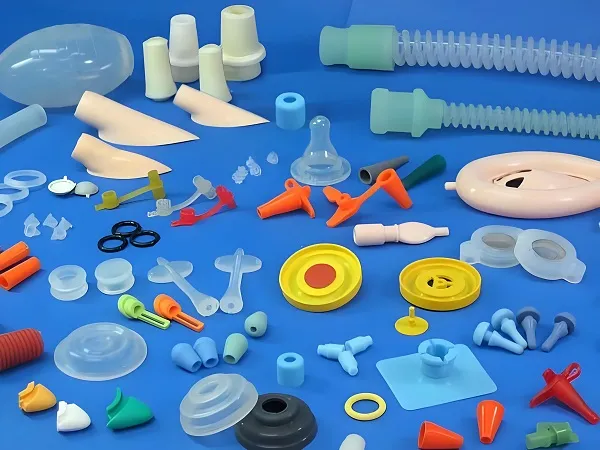

I. What is Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR)?
- Excellent temperature resistance: Maintains elasticity between -50℃ and 250℃, withstanding microwave heating and outdoor exposure;
- Safety and durability: Chemically stable (resistant to acids, alkalis, and UV rays) and biocompatible, making it suitable for human contact;
- High precision: Its liquid state allows it to fill micro-scale mold details easily, with a molding shrinkage rate of only 2%-3% (lower than ordinary plastics);
- Permanent curing: Curing involves irreversible chemical changes, ensuring stable structure and long service life.
II. LSR Injection Molding: Complete Process and Key Technologies for Precision Molding
(1) Detailed Explanation of Three Basic Steps
- Precise Mixing
- High-Temperature Curing
- Intelligent Demolding
(2) Easily Overlooked Key Links
- Raw material pretreatment: Check humidity after opening new materials (ambient humidity must be <60%); damp materials require drying before use;
- Equipment debugging: Clamping force is calculated based on the product’s projected area (5-8 tons of clamping force per cm²) to prevent mold expansion during high-pressure injection;
- Post-processing: Medical-grade products require ultrasonic cleaning + ethylene oxide sterilization. Some products need secondary vulcanization at 150-200℃ for 2-4 hours to remove low-molecular by-products and improve aging resistance.
III. LSR Material Selection: Practical Guide for Scenario Matching
(1) Targeted Selection by Industry Needs
|
Industry
|
Core Requirement Indicators
|
Recommended Material Properties
|
|
Medical/Maternal-Infant
|
FDA/ISO 10993 certification, sterilization resistance
|
Cytotoxicity ≤ Grade 1, performance retention ≥95% after gamma ray sterilization
|
|
Automotive
|
Resistance to high/low temperatures (-60℃~200℃) and oil
|
Compression set ≤15% (150℃×22h)
|
|
Consumer Electronics
|
High light transmittance (>90%), antistatic
|
Surface resistivity 10⁶-10⁹Ω·cm
|
|
Industrial Sealing
|
Chemical corrosion resistance, high hardness
|
Performance retention ≥95% after 24h immersion in 10% NaOH
|
(2) Matching Key Performance Parameters
- Hardness (Shore A): Soft rubber (10-40A) is suitable for tactile parts (e.g., phone cases); hard rubber (50-80A) for seals (e.g., O-rings). Overmolded parts with a hardness difference >50A require stress relief structures;
- Tensile strength: ≥6MPa for medical-grade, ≥8MPa recommended for industrial-grade;
- Flowability: High-flow grades (MFR >150g/10min) for thin-walled parts (<0.5mm).
(3) Substrate Adhesion Matching Solutions
|
Substrate Type
|
Recommended LSR Properties
|
Auxiliary Process
|
|
ABS/PC
|
Contains acrylate functional groups
|
Silane coupling agent (e.g., TC-5985)
|
|
Nylon/PP
|
High surface energy modified LSR
|
Plasma treatment + titanate primer
|
|
Stainless Steel
|
Contains carboxylic acid groups
|
Chromium-free passivation + silane primer
|
IV. 4 Core Application Scenarios of LSR Injection Molding
- Medical & Healthcare
- Maternal-Infant Products
- Consumer Electronics
- Automotive Industry
V. Common Defects and Solutions
|
Defect Type
|
Main Causes
|
Solutions
|
|
Surface Bubbles
|
Poor mold venting, air in materials
|
Add 0.015-0.025mm vent grooves, conduct vacuum degassing
|
|
Poor Adhesion
|
Oil contamination on substrates, poor material compatibility
|
Clean with alcohol + plasma treatment, select dedicated LSR
|
|
Dimensional Deviation
|
Fluctuations in process parameters, mold deformation
|
Stabilize temperature and pressure, calibrate molds regularly
|
|
Flow Marks
|
Insufficient flowability, uneven mold temperature
|
Increase material temperature, optimize conformal cooling system
|
VI. Selecting Services/Equipment: Dual Guide for Avoiding Pitfalls & Selection
(1) 3 Criteria for Selecting Service Providers
- Certifications: Food-grade products require FDA/LFGB reports; medical-grade products need ISO 13485 certificates + Material Test Certificates (MTC). Avoid providers without certifications.
- Equipment Check: Prioritize manufacturers with cold runner molds and automatic mixing systems (flash control <0.01mm). For micro-parts (e.g., 10mg electronic components), confirm they have needle injection and CCD visual inspection equipment.
- Process Inquiry: For complex parts, confirm “mold compensation solutions” (e.g., segmental temperature control for parts with uneven wall thickness to ensure uniform curing); for multi-material parts (silicone overmolded plastics), confirm they have 90-110℃ low-temperature vulcanization technology to prevent substrate deformation.
(2) Core Parameters for Injection Molding Machine Selection
- Clamping force: Calculated as (product projected area × injection pressure × 1.2 safety factor). Example: 100cm² projected area requires 500-800 tons of clamping force;
- Injection volume: 10%-20% larger than the product weight to avoid insufficient filling;
- Temperature control accuracy: Mold temperature fluctuation ≤±1℃, barrel temperature control range 20-80℃.
VII. Clarifying Misconceptions
- “Can LSR only be mixed at 1:1?”
- “Can any release agent be used?”
- “Higher hardness means better sealing performance?”