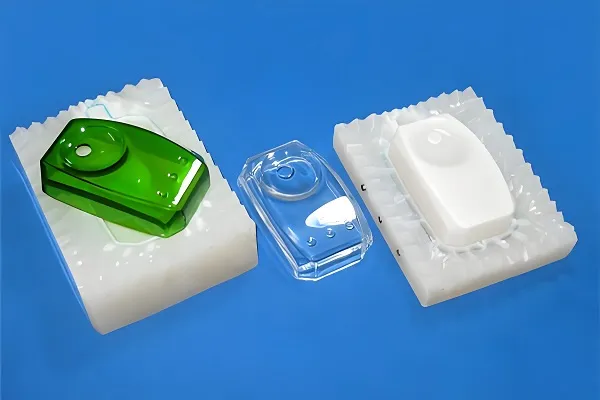
With the increasing demand for miniaturization and precision manufacturing, the application of micro injection molding technology has become more and more widespread in several industries. The purpose of this paper is to analyze the current status, challenges and future trends of micro injection molding technology. By citing the latest industry data and case studies, this paper details the application of micro-injection molding in medical devices, automotive electronics, consumer electronics and other fields, and discusses the impact of technological advances on production efficiency and market demand.

1. Introduction
Micro-injection molding technology is an efficient method used to produce tiny, complex plastic parts. With the rapid development of nanotechnology and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), micro injection molding technology has become an integral part of manufacturing. According to a new report by market research firm 168Report, the global micro injection molding plastics market size was estimated at USD 865.7 million in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 11.3% to reach USD 1,845.3 million by 2029. This figure highlights the importance and potential of micro injection molding technology in the global market.
2 Characteristics of Micro Injection Molding Technology
2.1 Technology Definition and Classification
Micro injection molding technology refers to the process of injecting molten plastic into a micro mold using a precision injection molding machine, and obtaining tiny plastic parts through cooling and curing. The technology can be categorized into two types: hydraulic drive and electric drive, of which the electric drive is gradually becoming mainstream due to its advantages in energy saving, low noise and precision control.
2.2 Technical Advantages
Micro injection molding technology has the following significant advantages:
High precision: able to produce parts with dimensional tolerances at the micron level to meet the needs of precision manufacturing.
High efficiency: high degree of automation, can significantly shorten the production cycle.
Wide material adaptability: Applicable to a wide range of plastic materials, including liquid crystal polymers (LCP), polyether ether ketone (PEEK) and other high-performance materials.
Additional information: Customized services, production process and production materials for micro-injection molding
3.Customized Services
Customized services play a crucial role in the field of micro injection molding. Since different customers have different needs for their products, including special requirements in terms of size, shape, material, performance, etc., customization service becomes the key to meet these diverse needs.
3.1Design customization:
Customer demand analysis: First, communicate with customers in depth to clarify their needs, uses and expected results.
Three-dimensional modeling: Use CAD software to conduct three-dimensional modeling according to customer needs to ensure that the design meets the product requirements.
Simulation verification: Simulation analysis through CAE software to predict potential problems in the molding process and optimize the design.
3.2Mold customization:
Precision Manufacturing: Manufacture miniature molds according to the design model to ensure the precision and durability of the molds.
Rapid Iteration: Adopt rapid prototyping technology to accelerate the mold design and verification process.
3.3Production process customization:
Process Adjustment: Adjust the injection molding process parameters, such as injection pressure, speed, temperature, etc., according to product characteristics and customer needs.
Quality control: implement strict quality control measures to ensure product quality meets customer requirements.
4 Production process
The production process of micro-injection molding usually includes the following key steps:
4.1 Raw material preparation:
Select suitable plastic raw materials, and drying, mixing and other pretreatment work.
4.2 Mold Installation and Commissioning:
Install the mold to the injection molding machine, and debugging to ensure that the mold matches the injection molding machine.
4.3 Injection Molding:
Molten plastic is injected into the mold, and micro plastic parts are obtained through cooling and curing.
Monitor the parameters of the injection molding process to ensure the stability of the production process and product quality.
4.4 Post-processing:
Remove defects such as flying edges and burrs on the parts.
Perform necessary cleaning, drying and inspection work.
4.5 Packaging and shipping:
Pack the qualified micro plastic parts and ship them to customers on time.
5 Production materials
There are various production materials used for micro injection molding, which are mainly selected according to the application requirements of the product. The following are some commonly used production materials and their characteristics:
5.1 General-purpose plastics:
Polypropylene (PP): good heat resistance, chemical resistance and mechanical strength.
Polystyrene (PS): high transparency, easy to process, but poor heat resistance.
5.2 Engineering plastics:
Polycarbonate (PC): excellent light transmission, heat resistance and mechanical strength, commonly used in the manufacture of high-end electronic product shell.
Nylon (PA): wear-resistant, oil-resistant, chemical-resistant, suitable for the manufacture of high-strength, highly wear-resistant parts.
5.3 High-performance plastics:
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP): very low coefficient of thermal expansion and excellent electrical properties, suitable for the manufacture of precision electronic components.
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK): with high-temperature stability, chemical resistance and excellent mechanical properties, commonly used in the manufacture of key components in medical equipment.
When selecting production materials, it is necessary to comprehensively consider the product application environment, performance requirements, cost-effectiveness and other factors to ensure that the selected materials can meet customer needs and have a good economy and sustainability.
6 Application Areas
6.1 Medical devices
Micro-injection molding technology is particularly widely used in the field of medical devices. As the invasiveness of medical treatment continues to decrease, medical equipment is gradually developing in the direction of miniaturization and precision. Micro injection molded plastic parts are widely used in areas such as pacemakers, drug delivery devices, hearing systems, and dental applications. According to market data, the medical field is the largest downstream market for micro-injection molded plastics, holding about 8% of the market share.
6.2 Automotive Electronics
In the automotive industry, micro-injection molding technology is used to produce a variety of automotive electronic modules and devices, such as micro motors, sensors, and capacitors. These parts not only require precise dimensions, but also excellent weather resistance and electrical properties. The application of micro injection molding technology effectively improves the reliability and performance of automotive electronics.
6.3 Consumer electronics
The trend of miniaturization and multifunctionalization of consumer electronics has also promoted the development of micro injection molding technology. From smartphones, tablet PCs to wearable devices, micro injection molded plastic parts play an important role in structural support, sealing and waterproofing, electromagnetic shielding and so on.
7 Technical challenges and solutions
7.1 Mold Design and Manufacturing
The design and manufacturing of micro-injection molds is one of the technical difficulties. The precision, strength and durability of the molds have a decisive impact on product quality and production efficiency. Adopting advanced CAD/CAM technology and precision machining equipment can effectively improve the design and manufacture of molds.
7.2 Material selection and optimization
Micro injection molding has high requirements for materials, and it is necessary to choose materials with excellent fluidity, heat resistance, weather resistance and mechanical properties. At the same time, through the material modification technology, such as adding nano-fillers, tougheners, etc., can further improve the comprehensive performance of the material.
7.3 Process control and optimization
The micro-injection molding process is complex and requires precise control of parameters such as injection pressure, injection speed, and cooling time. Through the use of injection molding CAE technology (such as Moldflow) for simulation and analysis, you can predict possible problems in the molding process, and optimize the process parameters to improve product quality and production efficiency.
FAQ
How small can micro injection molding technology produce?
A: Micro injection molding technology is capable of producing tiny parts with dimensional tolerances in the micron range. How small a part can be produced depends on the accuracy of the mold and the performance of the injection molding machine. Typically, micro injection molding machines can handle part sizes in the range of a few millimeters to tens of microns.
How do I ensure the quality of my parts during the micro-injection molding process?
Answer: The key to ensuring part quality in the micro injection molding process lies in strict control of all aspects. First, select high-quality plastic raw materials and precision molds; second, optimize injection process parameters, such as injection pressure, speed, temperature, etc.; then, implement strict quality control measures, such as online monitoring, sampling inspection, etc.; and finally, carry out post-processing, such as removing defects such as flying edges, burrs, etc., and conduct final quality inspection.
What is the production cost of micro-injection molding technology?
Answer: The production cost of micro-injection molding is affected by a variety of factors, including the size and complexity of the part, the cost of materials, the cost of mold manufacturing, and production efficiency. Generally speaking, due to the small size and high precision of micro injection molded parts, the mold manufacturing cost is relatively high. However, overall production costs can be reduced by optimizing the production process, improving production efficiency, and using appropriate production materials. In addition, high volume production can also help reduce unit costs. The exact cost needs to be evaluated and calculated based on the actual situation.