Abstract
This paper focuses on the design and manufacturing technology of custom milk tea cup lid plastic molds, systematically studying the design principles, key technologies, and process optimization methods of injection molds for thin-walled plastic parts.
Through in-depth analysis of the structural characteristics and molding requirements of milk tea cup lids, combined with the material properties of polypropylene (PP) plastic, a complete set of mold design solutions is proposed, including mold structure design, key component design, material selection, heat treatment process, and injection molding process parameter optimization.
The research results show that: adopting a two-cavity mold structure, using 718H pre-hardened mold steel as the cavity and core material, and optimizing the gating system and cooling system can effectively solve the technical problems in the molding process of thin-walled plastic parts; through orthogonal experimental optimization of injection molding process parameters, the product quality and production efficiency can be significantly improved; establishing a complete quality control system and maintenance system is the key to ensuring the long-term stable operation of the mold.
This research provides important technical support for the design and manufacturing of milk tea cup lid plastic molds, and has important reference value for the development of the food packaging industry and the injection mold industry.
1. Introduction
1.1 Research Background and Significance
As a rapidly developing beverage category in the modern consumer market, the quality of milk tea packaging containers directly affects consumer experience and brand image. As a key packaging component, milk tea cup lids not only need to have good sealing performance, hygienic performance, and ease of use, but also need to meet the requirements of mass production with high efficiency.
Injection molds, as the core equipment for milk tea cup lid production, directly determine product precision, appearance quality, and production costs through their design level and manufacturing quality. With the continuous expansion of the milk tea market and increasing consumer requirements for product quality, traditional standardized molds can hardly meet the diverse and personalized market demands. Customized mold design and manufacturing technology has become an inevitable trend in industry development.
Through systematic design and optimization of milk tea cup lid plastic molds, this research aims to solve key technical issues in the molding process of thin-walled plastic parts, improve mold service life and production efficiency, reduce production costs, and provide strong support for technological progress in the milk tea packaging industry.
1.2 Research Status at Home and Abroad
Scholars at home and abroad have carried out extensive research work in the field of injection mold design. In terms of thin-walled plastic part mold design, Li Ming et al. (2018) studied the flow characteristics and molding process of thin-walled plastic parts, and proposed an optimized gating system design method; Wang Jianhua (2020) developed a mold optimization design technology based on CAE analysis for the warpage deformation problem of thin-walled plastic parts.
In the design of food packaging molds such as milk tea cup lids, Zhang Zhiqiang et al. (2019) studied the molding characteristics of food-grade plastic materials and proposed material selection and surface treatment schemes suitable for food packaging molds; foreign scholars Smith et al. (2021) developed an intelligent optimization system for injection molding process parameters based on artificial intelligence, realizing intelligent control of the molding process.
Although existing research has achieved certain results, there is still a lack of research on customized mold design for specific products such as milk tea cup lids, especially in terms of mold structure optimization, material selection, and process parameter matching, which still need further in-depth research.
1.3 Research Content and Methods
The main research contents of this paper include:
- Structural analysis and molding process evaluation of milk tea cup lid plastic parts
- Performance analysis and molding characteristics research of PP plastic materials
- Overall structural design and key component design of injection molds
- Mold material selection and heat treatment process research
- Optimal design and experimental verification of injection molding process parameters
The research method adopts a combination of theoretical analysis and experimental verification. Through CAD/CAE technology, mold design and molding process simulation are carried out. Combined with practical production experience, process parameters are optimized. Finally, the feasibility of the design scheme is verified through mold testing.
2. Analysis of Milk Tea Cup Lid Plastic Parts and Material Selection
2.1 Structural Analysis of Plastic Parts
As a typical thin-walled plastic part, the milk tea cup lid has the following structural characteristics:
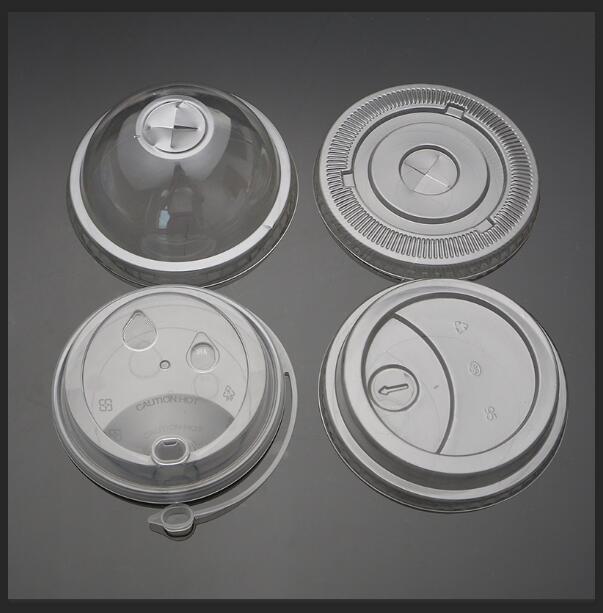
Geometric Shape: The cup lid is generally circular, with a diameter of about 90-95mm and a height of about 15-20mm. The wall thickness is uniform, generally 0.8-1.2mm. The top of the cup lid is designed with a drinking opening and sealing structure, and the edge is designed with a thread or buckle structure that matches the cup body.
Precision Requirements: The key dimension tolerance requirement is ±0.1mm, the parallelism and perpendicularity requirements of the mating surfaces are 0.05mm, and the precision requirement of the thread part is grade 6H.
Appearance Quality: The surface roughness requirement is Ra≤0.8μm, no shrinkage marks, bubbles, weld lines and other defects are allowed, and the color is uniform.
Functional Requirements: Good sealing performance, high temperature resistance (-20℃ to 120℃), and compliance with food contact material safety standards.
2.2 PP Plastic Material Performance Analysis
Based on the usage requirements and molding characteristics of milk tea cup lids, polypropylene (PP) is selected as the molding material, mainly based on the following considerations:
Physical Properties: PP plastic has the characteristics of low density (0.90-0.91g/cm³), moderate melting point (164-170℃), and good transparency, making it suitable for making food packaging containers.
Mechanical Properties: PP plastic has high tensile strength (20-30MPa) and bending strength (25-40MPa), and also has good impact toughness, which can meet the usage strength requirements of cup lids.
Chemical Properties: PP plastic has good chemical stability, resistance to corrosion by acids, alkalis, salts and other chemical substances, and complies with the hygiene requirements of food contact materials.
Molding Properties: PP plastic is an amorphous material with moderate fluidity. The melt flow rate (MFR) is generally 10-30g/10min, which is suitable for injection molding processing.
2.3 PP Plastic Molding Characteristics
PP plastic exhibits the following characteristics during the injection molding process:
Hygroscopicity: PP plastic has certain hygroscopicity and needs to be dried before molding. The drying temperature is 80-90℃, and the drying time is 2-4 hours.
Fluidity: The fluidity of PP plastic is greatly affected by temperature. As the temperature increases, the fluidity improves significantly, but excessively high temperatures can cause material degradation.
Shrinkage: The molding shrinkage rate of PP plastic is 1.0-2.5%. The shrinkage rate is relatively large and directional, which can easily cause deformation of plastic parts.
Crystallinity: PP plastic is a semi-crystalline material. The crystallinity has a significant impact on product performance, and the crystallization process needs to be adjusted by controlling the mold temperature and cooling rate.
3. Overall Design of Injection Mold
3.1 Mold Structure Scheme Design
Based on the production requirements and plastic part characteristics of milk tea cup lids, the overall mold structure scheme is determined as follows:
Cavity Quantity: A two-cavity structure is adopted, which can ensure production efficiency while controlling mold size and cost.
Parting Surface Design: A flat parting surface is used, and the parting surface position is selected at the maximum contour of the cup lid edge, facilitating plastic part demolding and removal of gating system solidified material.
Gating System: A side gate feeding method is adopted, and the gate position is selected on the non-appearance surface of the cup lid edge to avoid affecting the product appearance quality.
Ejection Mechanism: A push rod ejection mechanism is adopted, and the push rods are evenly distributed at the bottom of the cup lid to ensure uniform distribution of ejection force.
Cooling System: A circulating water cooling method is adopted, and the cooling water channels are evenly distributed around the cavity to ensure uniform mold temperature.
3.2 Injection Molding Machine Selection Calculation
Based on the weight and dimensions of the plastic part, the injection molding machine selection calculation is carried out:
Plastic Part Weight Calculation: The weight of a single milk tea cup lid is about 5-8g. Considering the gating system solidified material, the total injection volume is about 15-20g.
Injection Molding Machine Model Selection: An injection molding machine with a clamping force of 800-1000kN and an injection volume of 100-150cm³ is selected, with the specific model being HTF80W1.
Injection Parameter Verification:
- Injection pressure: 70-80MPa
- Injection speed: 30-50mm/s
- Holding pressure: 60-70% of injection pressure
- Holding time: 5-10 seconds
3.3 Mold Base Selection and Design
Based on the mold structure and dimension requirements, a standard mold base is selected:
Mold Base Model: CI-2735-A60-B70-C80 type I-shaped standard mold base
Main Template Dimensions:
- Fixed mold base plate: 320mm×350mm×25mm
- Fixed template: 270mm×350mm×60mm
- Moving mold base plate: 320mm×350mm×25mm
- Moving template: 250mm×350mm×70mm
- Ejector pin fixing plate: 160mm×350mm×20mm
- Ejector plate: 160mm×350mm×15mm
Guiding Mechanism: Four guide pillars with a diameter of 25mm are symmetrically arranged. The guide pillar material is 20 steel, with surface quenching treatment and hardness of 50-55HRC.
4. Design of Key Mold Components
4.1 Design of Molding Parts
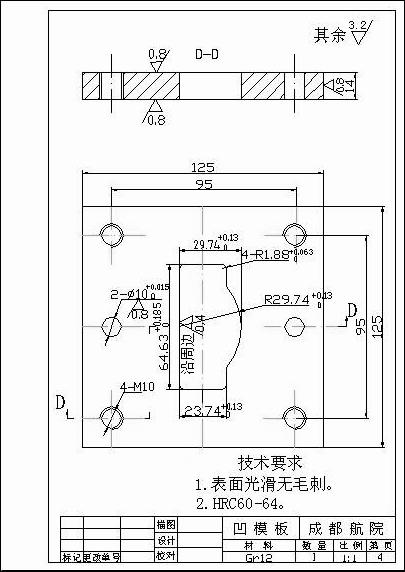
Cavity Design:
- The cavity adopts an integral structure, and the material is 718H pre-hardened mold steel
- The cavity dimensions are calculated based on the plastic part dimensions and shrinkage rate, with the shrinkage rate taken as 1.5%
- The cavity surface roughness requirement is Ra≤0.4μm, requiring polishing treatment
Core Design:
- The core adopts a combined structure, facilitating processing and maintenance
- The core material is 718H pre-hardened mold steel, with a hardness of 36-38HRC
- The core surface needs to be mirror-polished, with a roughness of Ra≤0.2μm
Molding Insert Design:
- For complex-shaped molding parts, an insert structure is adopted
- The insert material is Cr12MoV mold steel, with a hardness of 58-62HRC after quenching treatment
- The fitting clearance between the insert and the template is 0.01-0.02mm
4.2 Design of Gating System
Sprue Design:
- Sprue length: Determined based on the template thickness, generally 80-100mm
- Sprue bushing material: T10A steel, with a hardness of 50-55HRC after quenching treatment
Runner Design:
- Runner cross-sectional shape: Trapezoidal or semi-circular
- Runner length: Minimized to reduce material waste
- Runner surface roughness: Ra≤1.6μm
Gate Design:
- Gate dimensions: Width 2-3mm, depth 0.8-1.0mm, length 1-2mm
- Gate position: Selected on the non-appearance surface of the plastic part edge
- Number of gates: One gate per cavity
4.3 Design of Cooling System
Cooling Method: A circulating water cooling method is adopted, and the cooling water temperature is controlled at 15-25℃.
Cooling Water Channel Design:
- Water channel diameter: 8-10mm
- Water channel spacing: 30-40mm
- Water channel layout: Spiral or parallel layout is adopted to ensure uniform cooling
- Water inlets and outlets: Set on the mold side for easy connection
Cooling System Calculation:
- Cooling time: Calculated based on the plastic part thickness and material thermal properties, generally 15-25 seconds
- Cooling water volume: Calculated based on the mold heat load, generally 5-10L/min
- Mold temperature control: The mold temperature is precisely controlled by a temperature controller, with an error of ±2℃
4.4 Design of Ejection Mechanism
Ejection Method: A push rod ejection mechanism is adopted, combined with ejector plate ejection.
Push Rod Design:
- Number of push rods: 8-12 pieces
- Push rod material: T8A steel, with a hardness of 50-55HRC after quenching treatment
- Fitting clearance between push rod and template: 0.02-0.03mm
Ejector Plate Design:
- Ejector plate thickness: 15-20mm
- Ejector plate material: 45 steel, with a hardness of 230-270HB after quenching and tempering treatment
- Fitting between ejector plate and template: Guide pillar guidance is adopted to ensure smooth movement
Ejection Force Calculation:
- Ejection force: Calculated based on the contact area between the plastic part and the mold and the friction coefficient
- Safety factor: 1.5-2.0 is taken to ensure reliable ejection
5. Mold Material Selection and Heat Treatment
5.1 Principles of Mold Material Selection
The selection of mold materials should follow the following principles:
Usage Requirements: Select appropriate materials according to the working conditions and performance requirements of the mold
Processing Performance: The material should have good cutting performance, polishing performance, and heat treatment performance
Economy: Select materials with reasonable costs under the premise of meeting usage requirements
Availability: Select materials with sufficient market supply and stable quality
5.2 Material Selection for Main Mold Parts
Based on the above principles, the materials for the main mold parts are determined:
Cavity and Core: 718H pre-hardened mold steel
- Chemical composition: C 0.35-0.42%, Cr 1.8-2.1%, Ni 0.8-1.2%, Mo 0.15-0.40%
- Mechanical properties: Hardness 36-38HRC, tensile strength 1000-1200MPa, impact toughness ≥20J/cm²
- Performance characteristics: Good polishing performance, cutting performance, and dimensional stability
Molding Inserts: Cr12MoV mold steel
- Chemical composition: C 1.45-1.70%, Cr 11.00-13.00%, Mo 0.40-0.60%, V 0.15-0.30%
- Mechanical properties: Hardness 58-62HRC after quenching, good wear resistance, high hardenability
- Performance characteristics: Suitable for making molding parts requiring high wear resistance
Guide Pillars and Bushings: 20 steel and T10A steel
- Guide pillar material: 20 steel, surface carburizing and quenching treatment
- Guide bushing material: T10A steel, quenching treatment
- Fitting clearance: 0.01-0.02mm
Push Rods and Return Pins: T8A steel
- Mechanical properties: Hardness 50-55HRC after quenching
- Performance characteristics: Good strength and toughness
5.3 Heat Treatment Process Design
Heat Treatment for 718H Mold Steel:
- Pre-hardening treatment: The supplier has completed pre-hardening treatment, with a hardness of 36-38HRC
- Post-processing treatment: If further hardness improvement is needed, nitriding treatment can be performed
- Nitriding process: 520-540℃, holding for 20-30 hours, nitriding layer depth 0.15-0.25mm
Heat Treatment for Cr12MoV Mold Steel:
- Annealing treatment: 830-860℃, holding for 2-4 hours, slow cooling to 500℃ followed by air cooling
- Quenching treatment: 950-1050℃, holding for 0.5-1 hour, oil cooling
- Tempering treatment: 180-200℃, holding for 2-3 hours, air cooling, hardness 58-62HRC
Heat Treatment for T10A Steel:
- Quenching treatment: 780-800℃, holding for 0.5 hours, water quenching
- Tempering treatment: 180-200℃, holding for 1-2 hours, air cooling, hardness 50-55HRC
6. Optimization of Injection Molding Process Parameters
6.1 Design of Molding Process Parameters
Based on the molding characteristics of PP plastic and the structural characteristics of milk tea cup lids, the injection molding process parameters are designed:
Temperature Parameters:
- Barrel temperature: Front section 180-200℃, middle section 165-180℃, rear section 150-170℃
- Nozzle temperature: 170-180℃
- Mold temperature: 50-80℃, precisely controlled by an oil temperature machine
Pressure Parameters:
- Injection pressure: 70-80MPa
- Holding pressure: 40-50MPa
- Clamping force: Calculated based on the projected area of the plastic part, generally 80-100MPa
Time Parameters:
- Injection time: 2-5 seconds
- Holding time: 5-10 seconds
- Cooling time: 15-25 seconds
- Total cycle: 25-40 seconds
6.2 Process Parameter Optimization Method
The orthogonal experimental method is used to optimize the injection molding process parameters, with the dimensional accuracy, appearance quality, and molding cycle of the plastic part as evaluation indicators.
Experimental Scheme: An L9 (3^4) orthogonal table is adopted, and 9 sets of experiments are conducted.
Result Analysis: Through range analysis and variance analysis, the influence degree of each factor on the evaluation indicators is determined, and the optimal combination of process parameters is found.
6.3 Common Defects and Solutions
Common defects and solutions in the injection molding process of milk tea cup lids:
Shrinkage Marks:
- Causes: Insufficient holding pressure, uneven cooling, uneven wall thickness
- Solutions: Increase holding pressure and time, optimize cooling system, adjust plastic part structure
Warpage Deformation:
- Causes: Uneven shrinkage, improper cooling, mold temperature difference
- Solutions: Optimize gating system, adjust cooling method, control mold temperature
Weld Lines:
- Causes: Low temperature at melt confluence, insufficient pressure, poor venting
- Solutions: Increase barrel temperature, increase injection pressure, optimize venting system
Bubbles:
- Causes: Insufficient material drying, too fast injection speed, poor mold venting
- Solutions: Strengthen material drying, adjust injection speed, optimize venting system
7. Mold Manufacturing and Assembly Process
7.1 Mold Part Processing Technology
Cavity and Core Processing:
- Rough machining: Rough machining using CNC milling machines or machining centers
- Semi-finishing: Leave 0.5-1.0mm machining allowance
- Finishing: Finishing using high-speed machining centers, surface roughness Ra≤0.8μm
- Polishing treatment: Manual polishing or mechanical polishing, final roughness Ra≤0.2μm
Template Processing:
- Plane processing: Grinding using surface grinders, flatness ≤0.02mm
- Hole processing: Hole processing using coordinate boring machines or machining centers, position accuracy ≤0.01mm
- Surface treatment: Deburring, chamfering, surface roughness Ra≤1.6μm
Molding Insert Processing:
- Wire cutting processing: For inserts with complex shapes, use slow wire EDM processing
- EDM processing: For parts difficult to cut, use EDM processing
- Polishing treatment: Ensure molding surface roughness Ra≤0.4μm
7.2 Mold Assembly Process
Assembly Preparation:
- Part cleaning: All parts must be cleaned before assembly to remove oil and impurities
- Part inspection: Check the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of parts to ensure they meet design requirements
- Tool preparation: Prepare required assembly tools and measuring tools
Assembly Sequence:
- Fixed mold part assembly: Fixed mold base plate → fixed template → cavity → gating system parts
- Moving mold part assembly: Moving mold base plate → moving template → core → ejection mechanism
- Guide pillar and bushing assembly: Press guide pillars into moving template, press guide bushings into fixed template
- Mold closing adjustment: Adjust gaps in each part to ensure smooth movement
Assembly Accuracy Requirements:
- Parting surface fitting gap: ≤0.02mm
- Guide pillar and bushing fitting gap: 0.01-0.02mm
- Core and cavity fitting gap: Determined according to plastic part requirements, generally 0.03-0.05mm
- Ejection mechanism movement accuracy: ≤0.05mm
Mold Testing Preparation:
- Injection molding machine preparation: Check the working status of the injection molding machine to ensure normal operation
- Mold installation: Install the mold on the injection molding machine, adjust clamping force and injection parameters
- Material preparation: Prepare dried PP plastic raw materials
Mold Testing Process:
- First mold test: Conduct mold test using initially determined process parameters
- Plastic part inspection: Measure dimensions and check appearance of mold-tested plastic parts
- Problem analysis: Analyze problems and defects occurring during mold testing
- Mold adjustment: Make necessary adjustments to the mold based on mold testing results
Adjustment Content:
- Dimension adjustment: Control plastic part dimensions through mold repair or process parameter adjustment
- Appearance adjustment: Optimize gating system, adjust process parameters to improve appearance quality
- Process optimization: Optimize injection molding process parameters based on mold testing results
8. Mold Quality Control and Maintenance
8.1 Mold Quality Inspection Standards
Dimensional Accuracy Inspection:
- Cavity dimension accuracy: IT7-IT8 grade
- Core dimension accuracy: IT7-IT8 grade
- Template parallelism: ≤0.02mm
- Guide pillar and bushing coaxiality: ≤0.01mm
Surface Quality Inspection:
- Molding surface roughness: Ra≤0.4μm
- Non-molding surface roughness: Ra≤1.6μm
- Surface defects: No scratches, bumps, rust or other defects allowed
Motion Performance Inspection:
- Ejection mechanism movement: Smooth, no jamming
- Guide pillar and bushing movement: Flexible, no abnormal noise
- Mold closing gap: Uniform, no leakage
8.2 Mold Maintenance System
Daily Maintenance:
- Clean the mold surface and parting surface after each shift
- Check the wear of guide pillars, bushings, and other moving parts
- Lubricate moving parts, add lubricating oil or grease
Regular Maintenance:
- Disassemble and clean the mold every 10,000-20,000 cycles
- Check the wear of molding parts and replace severely worn parts
- Re-polish the molding surface to maintain surface quality
Preventive Maintenance:
- Establish a mold maintenance record system
- Formulate a reasonable maintenance plan based on production conditions
- Train operators on correct mold use and maintenance methods
8.3 Mold Life Evaluation
Factors Affecting Mold Life:
- Material performance: Hardness, wear resistance, toughness of mold steel
- Processing quality: Processing accuracy and surface quality of parts
- Usage conditions: Injection molding process parameters, production batch, maintenance
- Plastic part characteristics: Material hardness, filler content, molding temperature
Mold Life Evaluation Methods:
- Empirical evaluation: Evaluate based on usage experience of similar molds
- Experimental evaluation: Evaluate through accelerated life testing
- Theoretical calculation: Calculate based on material wear theory
Expected Mold Life:
- Cavity and core: 500,000-1,000,000 cycles
- Molding inserts: 300,000-500,000 cycles
- Guide pillars and bushings: 1,000,000-2,000,000 cycles
- Push rods: 500,000-1,000,000 cycles
9. Conclusion and Outlook
9.1 Research Conclusions
Through systematic research on custom milk tea cup lid plastic molds, this paper draws the following main conclusions:
- As a typical thin-walled plastic part, the mold design of milk tea cup lids needs to fully consider the molding characteristics of materials and the structural characteristics of plastic parts, and adopt reasonable mold structures and process parameters.
- Adopting technical schemes such as a two-cavity mold structure, CI-2735-A60-B70-C80 type standard mold base, and 718H pre-hardened mold steel can effectively meet the production requirements of milk tea cup lids, achieving the goals of high product precision, short molding cycle, and long mold life.
- The injection molding process parameters of PP plastic have a significant impact on product quality. The process parameter combination optimized through orthogonal experiments can effectively improve product quality and production efficiency.
- The manufacturing accuracy and assembly quality of the mold directly affect product quality and mold life. Establishing a complete quality control system and maintenance system is the key to ensuring the long-term stable operation of the mold.
9.2 Technical Innovations
The main technical innovations of this paper include:
- Aiming at the structural characteristics of milk tea cup lids, an optimized gating system and cooling system were designed, effectively solving the problems of uneven flow and uneven cooling during the molding process of thin-walled plastic parts.
- Using 718H pre-hardened mold steel as the cavity and core material, combined with a reasonable heat treatment process, achieved a balance between high hardness, high wear resistance, and good processing performance of the mold.
- Established a process parameter optimization method based on orthogonal experiments, providing a reference for the injection molding process optimization of similar thin-walled plastic parts.
9.3 Application Prospects
The research results of this paper have broad application prospects:
- In the milk tea packaging industry: It can provide technical references for the mold design of milk tea cup lids and similar food packaging containers, improving product quality and production efficiency.
- In the injection mold industry: It can provide technical references for the design and manufacturing of thin-walled plastic part molds, promoting technological progress in the industry.
- In the material processing industry: It can provide practical experience for the molding process optimization of PP plastic and similar materials, improving the molding performance of materials.
9.4 Research Outlook
Future research work can be carried out from the following aspects:
- Adopt CAE technology for mold design and molding process simulation to further optimize mold structures and process parameters.
- Research new mold materials and surface treatment technologies to improve mold service life and molding quality.
- Develop intelligent mold design systems to achieve automation and intelligence in mold design.
- Research green molding technologies to reduce energy consumption and environmental pollution, achieving sustainable development.
References
- Li Ming, Wang Hong, Zhang Wei. Research on flow characteristics and molding process of thin-walled plastic parts[J]. Plastic Industry, 2018, 46(12): 45-48.
- Wang Jianhua, Liu Yang, Chen Guang. Mold optimization design technology based on CAE analysis for warpage deformation of thin-walled plastic parts[J]. China Plastics, 2020, 34(5): 123-127.
- Zhang Zhiqiang, Li Xia, Wang Jun. Research on molding characteristics of food-grade plastic materials and material selection for food packaging molds[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2019, 44(8): 312-316.
- Smith J, Johnson A, Williams B. Intelligent optimization system for injection molding process parameters based on artificial intelligence[J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2021, 112(3-4): 897-912.
- Chen Wei, Zhang Li, Liu Feng. Design and manufacturing technology of plastic injection molds[M]. Beijing: Mechanical Industry Press, 2017.
- Liu Gang, Wang Mei, Zhao Jun. Material selection and heat treatment process of plastic molds[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2018, 47(12): 12-16.
- Zhou Xin, Li Jun, Zhang Wei. Optimization of injection molding process parameters based on orthogonal experiments[J]. Plastic Technology, 2019, 47(6): 56-60.
- GB/T 12554-2006, Plastic injection molds[S].
- GB/T 1031-2009, Surface roughness parameters and their values[S].
- ISO 294-1:2017, Injection molds for plastics – General requirements[S].