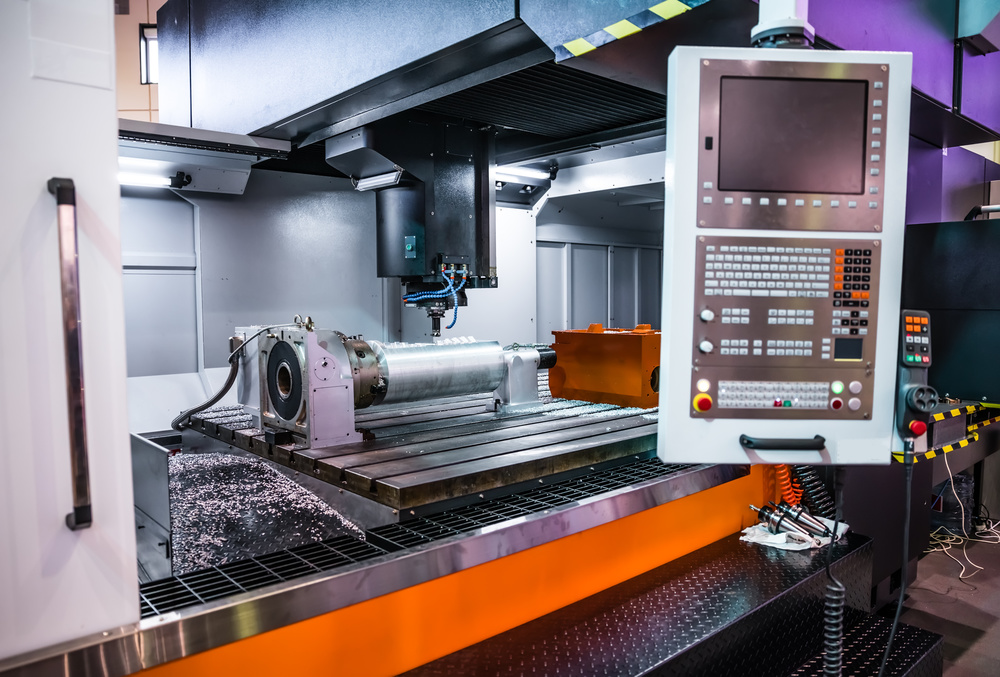
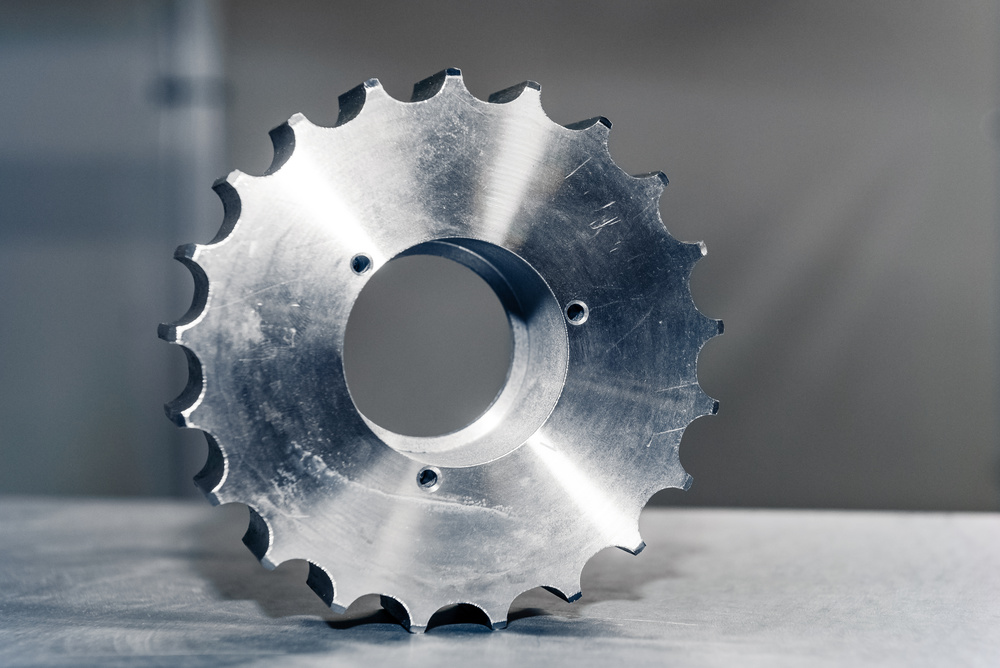
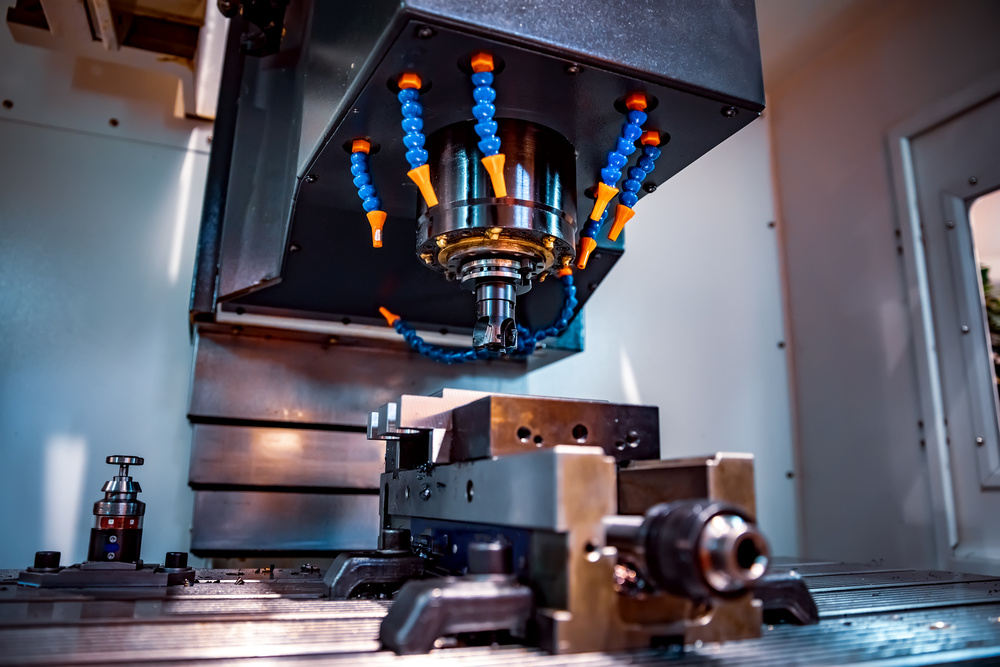
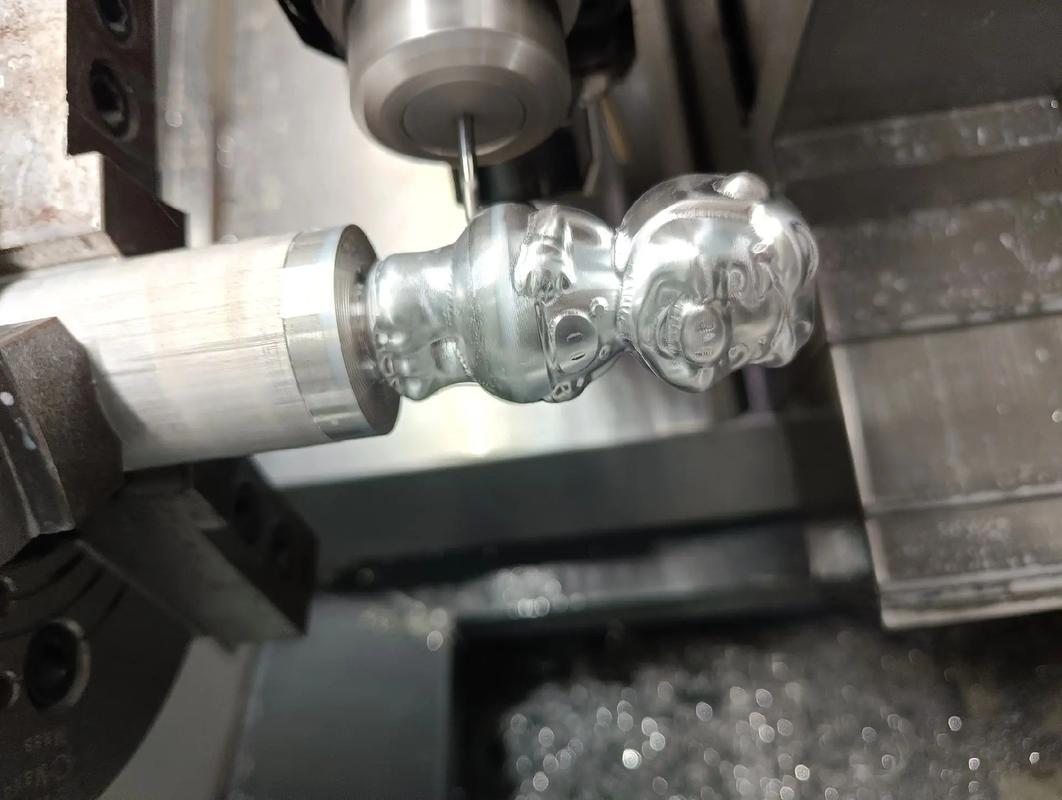
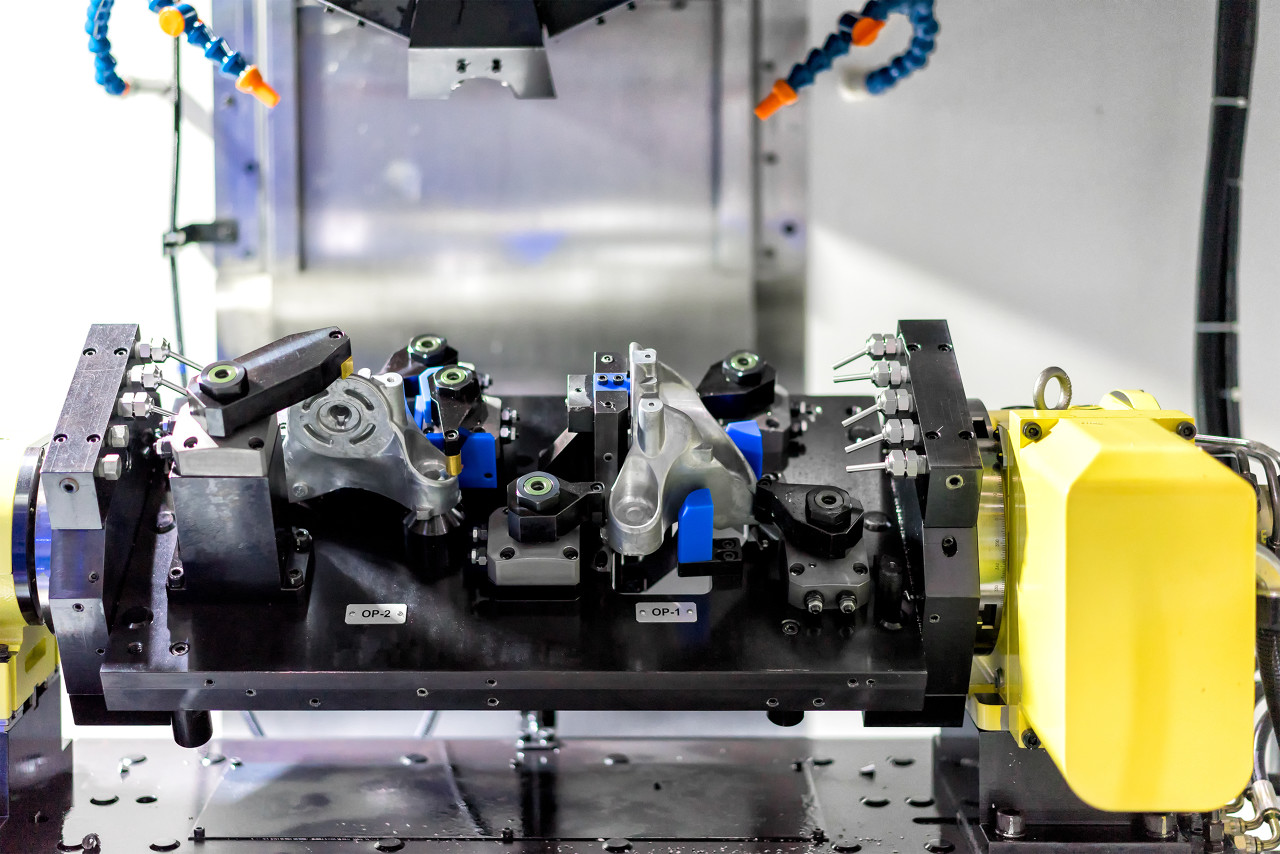
Introduction
In the world of modern manufacturing, CNC milling parts have become the foundation of precision component production across countless industries. From aerospace to automotive, medical to electronics, these computer-controlled machining processes enable the creation of complex, high-precision parts that were once thought impossible to manufacture.
This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need to know about CNC milling parts – from their definition and manufacturing process to their applications, advantages, and how to choose the right CNC milling service provider for your needs.
What are CNC Milling Parts?
Definition and Basics
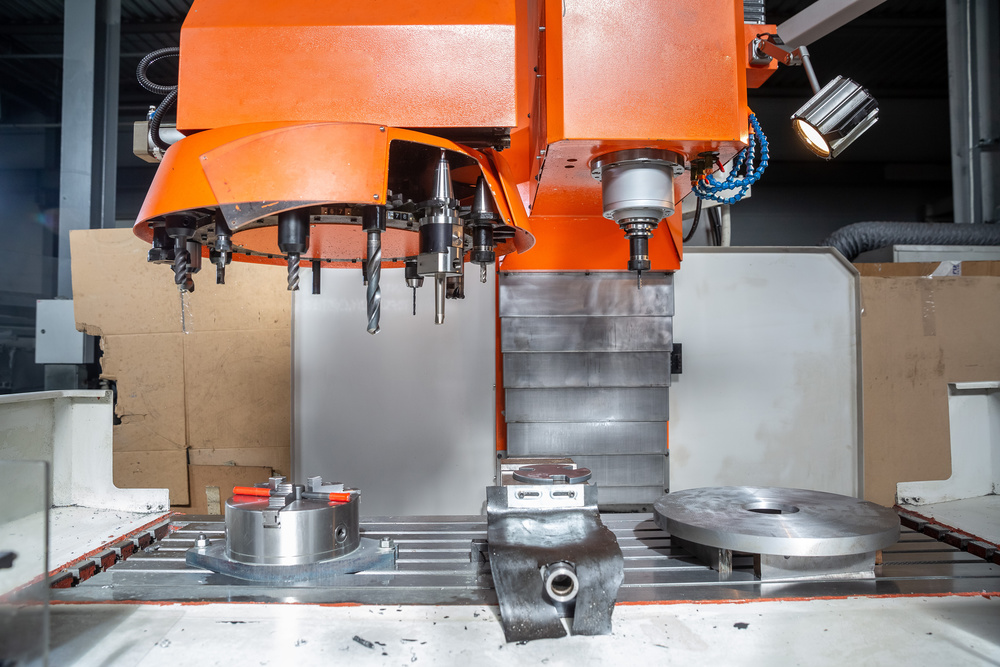
CNC milling parts are precision-machined components produced using Computer Numerical Control (CNC) milling machines. This subtractive manufacturing process involves removing material from a solid workpiece using rotating cutting tools to create complex shapes, features, and geometries with exceptional accuracy.
Unlike traditional manual milling, which relies on skilled operators to guide the cutting tools, CNC milling uses computer programming to control the machine’s movements with pinpoint precision. This automation ensures consistent quality, repeatability, and efficiency across production runs.
Key Characteristics of CNC Milling Parts
- Exceptional Precision: Tolerances as tight as ±0.005 mm (0.0002 inches)
- Complex Geometries: Ability to create intricate shapes and features
- Material Versatility: Works with metals, plastics, composites, and more
- Consistency: Identical parts across production runs
- Efficiency: Reduced production time compared to manual methods
How CNC Milling Works
The CNC Milling Process Flow
CNC milling is a sophisticated process that involves several key steps:
1. Design Creation
- The process begins with creating a 3D CAD (Computer-Aided Design) model of the desired part
- Design software such as SolidWorks, AutoCAD, or Fusion 360 is used
- The design includes all dimensions, tolerances, and features required
2. CAM Programming
- The CAD model is converted into machine-readable code using CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software
- This code, known as G-code, contains precise instructions for the machine’s movements
- The CAM software optimizes tool paths, cutting speeds, and feed rates
3. Machine Setup
- The workpiece is securely clamped to the machine’s worktable
- Cutting tools are loaded into the spindle or tool changer
- The machine is calibrated to ensure proper alignment
4. Machining Operation
- The CNC machine executes the G-code program
- The cutting tool rotates at high speed while moving along multiple axes
- Material is removed layer by layer to create the desired shape
- Coolant is used to reduce heat and improve tool life
5. Quality Inspection
- The finished part is inspected for dimensional accuracy
- Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) and other precision tools are used
- Any necessary adjustments are made for subsequent production runs
CNC Milling Machine Axes
CNC milling machines operate along multiple axes to create complex parts:
Linear Axes:
- X-axis: Horizontal movement (left-right)
- Y-axis: Horizontal movement (front-back)
- Z-axis: Vertical movement (up-down)
Rotational Axes (for multi-axis machines):
- A-axis: Rotation around the X-axis
- B-axis: Rotation around the Y-axis
- C-axis: Rotation around the Z-axis
Types of CNC Milling Machines
Based on Spindle Orientation
Vertical Milling Machines
- Spindle is oriented vertically
- Ideal for face milling, end milling, and drilling
- Better for tall parts and deep cavities
- More common for general-purpose machining
Horizontal Milling Machines
- Spindle is oriented horizontally
- Better for heavy-duty cutting and large workpieces
- Excellent for production machining
- Often used with rotary tables for complex parts
Based on Number of Axes
3-Axis Milling Machines
- Operates along X, Y, and Z axes
- Suitable for simple to moderately complex parts
- Most common type of CNC milling machine
- Cost-effective for many applications
4-Axis Milling Machines
- Adds rotational A-axis to 3-axis capabilities
- Can machine parts from multiple angles without repositioning
- Ideal for parts with features on multiple sides
- Reduces setup time and improves accuracy
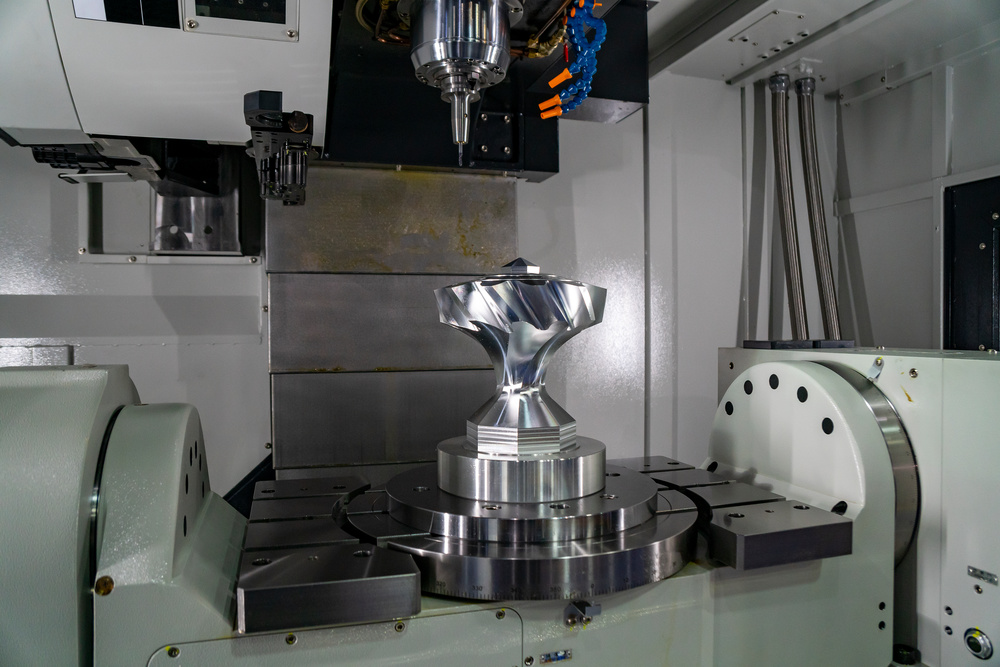
5-Axis Milling Machines
- Full 5-axis simultaneous machining (X, Y, Z, A, B or C)
- Can create extremely complex shapes and contours
- Eliminates the need for multiple setups
- Used for high-precision, complex parts in aerospace and medical industries
Specialized Milling Machines
Swiss-Type Milling Machines
- Designed for small, precision parts
- Uses guide bushings to support long workpieces
- Ideal for medical components and small mechanical parts
High-Speed Milling Machines
- Spindle speeds up to 40,000 RPM
- Used for finishing operations and hard materials
- Produces excellent surface finishes
CNC Milling Tools and Cutters
Common Milling Cutters
End Mills
- Most versatile type of milling cutter
- Used for slotting, profiling, and contouring
- Available in 2-flute, 4-flute, and multi-flute designs
- Materials: High-speed steel (HSS), carbide, cobalt
Face Mills
- Used for machining flat surfaces
- Large diameter cutters with multiple inserts
- Efficient for large surface areas
- Available with various insert geometries
Ball Nose End Mills
- Ideal for 3D contouring and curved surfaces
- Creates smooth finishes on complex shapes
- Used in mold making and prototyping
Engraving Tools
- Small diameter cutters for detailed work
- Used for engraving text and logos
- Available in various tip shapes and sizes
Tool Materials
High-Speed Steel (HSS)
- Good for general-purpose machining
- Suitable for softer materials
- Lower cutting speeds compared to carbide
Carbide
- Higher hardness and wear resistance
- Suitable for high-speed machining
- Works well with hard materials
- More expensive but longer tool life
Cermet
- Excellent heat resistance
- Suitable for high-temperature applications
- Good surface finish capabilities
Diamond-Coated
- Ultimate hardness and wear resistance
- Used for machining non-ferrous materials
- Expensive but long-lasting
- Ideal for high-precision applications
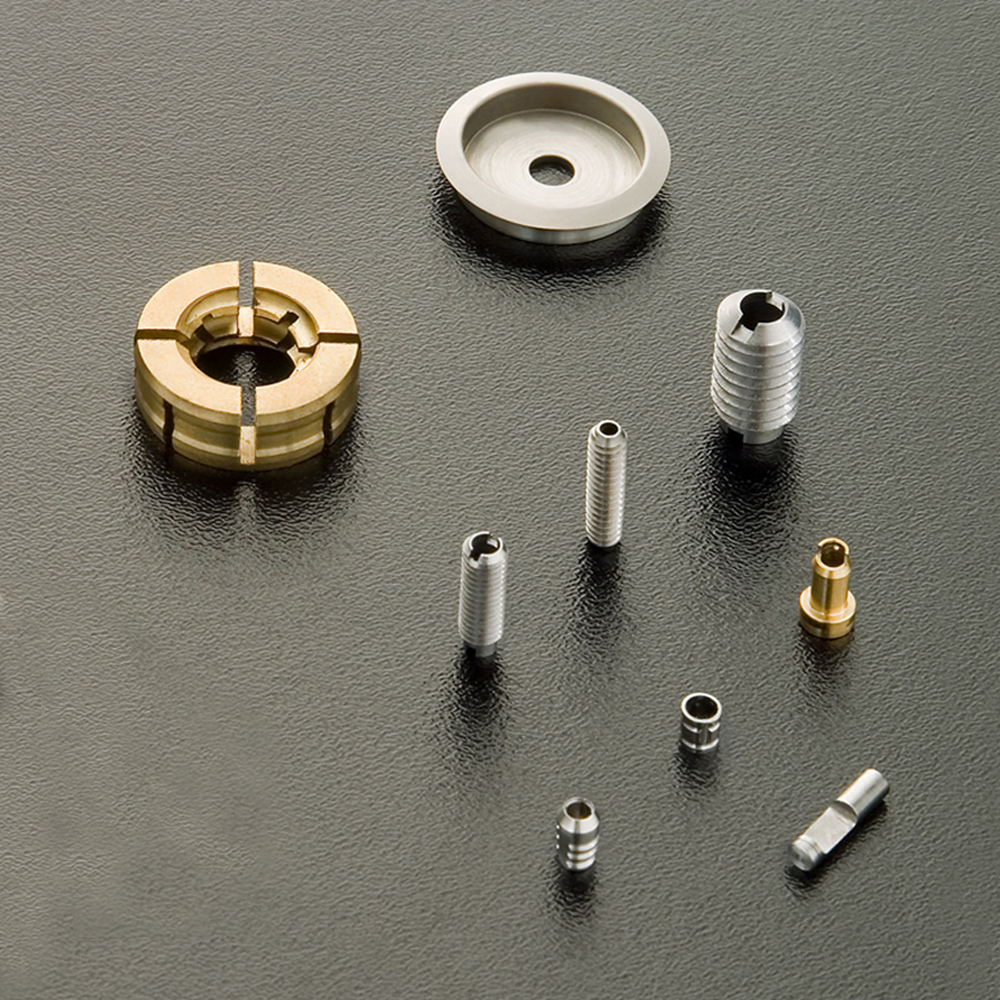
Materials Used in CNC Milling
Metal Materials
Aluminum Alloys
- 6061-T6: Excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistant
- 7075-T6: Higher strength, used in high-stress applications
- 5052: Good corrosion resistance, ideal for marine applications
- Advantages: Lightweight, good machinability, cost-effective
Steel Alloys
- Carbon Steel: 1018, 1045 for general purpose applications
- Alloy Steel: 4140, 4340 for high strength requirements
- Stainless Steel: 304, 316 for corrosion resistance
- Tool Steel: H13, S7 for mold applications
Specialty Metals
- Titanium: Ti-6Al-4V for aerospace and medical applications
- Inconel: High temperature resistance for engine components
- Brass: Excellent machinability for precision parts
- Copper: Good conductivity for electrical components
Plastic Materials
Thermoplastics
- Acetal (Delrin): Excellent dimensional stability
- PEEK: High temperature resistance, biocompatible
- Nylon: Good wear resistance and strength
- PTFE (Teflon): Chemical resistance, low friction
- ABS: Impact resistant, used in consumer products
Composite Materials
- Carbon Fiber: High strength-to-weight ratio
- Fiberglass: Good strength and corrosion resistance
- G10/FR4: Electrical insulation properties
- Advantages: Lightweight, strong, corrosion resistant
Applications of CNC Milling Parts
Aerospace Industry
CNC milling parts are critical in the aerospace industry where precision and reliability are paramount:
- Engine Components: Turbine blades, housings, manifolds
- Structural Parts: Wing fittings, landing gear components
- Avionics: Enclosures and mounting brackets
- Fuel System: Valves, pumps, and connectors
Key Requirements:
- Tolerances as tight as ±0.001 mm
- Material traceability and certification
- Compliance with AS9100 standards
- Lightweight yet strong materials
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry relies heavily on CNC milled parts for both performance and safety:
- Engine Parts: Cylinder heads, blocks, crankshafts
- Transmission: Gears, shafts, housings
- Suspension: Control arms, knuckles, brackets
- Brake System: Calipers, rotors, master cylinders
Automotive Standards:
- JIT delivery capabilities
- Cost-effective high-volume production
Medical Industry
Medical applications require the highest precision and biocompatibility:
- Surgical Instruments: Scalpels, forceps, retractors
- Implants: Hip replacements, dental implants
- Medical Devices: Housings, brackets, connectors
- Diagnostic Equipment: Precision components
Medical Requirements:
- Ultra-precision machining (±0.0005 mm)
- Cleanroom manufacturing capabilities
Electronics Industry
CNC milled parts are essential for the electronics sector:
- Heat Sinks: Thermal management solutions
- Enclosures: Electronic device housings
- Connectors: Precision electrical components
- PC Board Fixtures: Manufacturing aids
Industrial Equipment
Industrial machinery relies on CNC milled parts for reliability and performance:
- Gearboxes: Gears, shafts, housings
- Hydraulic Components: Valves, cylinders, pumps
- Robotics: Arms, joints, end effectors
- Machine Tools: Precision components for manufacturing equipment
Advantages of CNC Milling
Precision and Accuracy
- Tight Tolerances: Can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.005 mm
- Consistency: Every part is identical to the last
- Repeatability: Same results across production runs
- Complex Geometries: Ability to create shapes impossible with manual methods
Efficiency and Productivity
- Reduced Setup Time: Quick changeovers between jobs
- Automation: Minimal operator intervention required
- 24/7 Operation: Can run unattended for extended periods
- Material Optimization: Reduced waste through precise cutting
Versatility and Flexibility
- Material Versatility: Works with metals, plastics, composites, and more
- Design Flexibility: Easy to modify designs in software
- Low Volume to High Volume: Suitable for prototypes and mass production
- Rapid Prototyping: Quick turnaround for design verification
Cost-Effectiveness
- Reduced Labor Costs: Less manual labor required
- Fewer Errors: Reduced scrap and rework
- Longer Tool Life: Modern cutting tools last longer
- Energy Efficiency: Modern machines are more energy efficient
How to Choose a CNC Milling Service Provider
Key Selection Criteria
When choosing a CNC milling service provider, consider these important factors:
Technical Capabilities
- Equipment: Ensure they have the right machines for your parts
-
- 3-axis, 4-axis, or 5-axis capabilities
-
- Machine size and capacity
- Software: Advanced CAD/CAM software for complex parts
- Tooling: Access to a wide range of cutting tools
- Quality Control: Precision measurement equipment
Experience and Expertise
- Industry Experience: Specialization in your industry
- Technical Staff: Skilled engineers and machinists
- Project Portfolio: Examples of similar work
- Years in Business: Established track record
Quality Assurance
- Certifications: ISO 9001, AS9100, IATF 16949
- Quality Control Process: Inspection at every stage
- Traceability: Material and process documentation
- Warranty: Product quality guarantee
Production Capabilities
- Lead Times: Typical delivery times for prototypes and production
- Volume Flexibility: Ability to handle small and large production runs
- Material Capabilities: Experience with your specific materials
- Secondary Operations: Assembly, finishing, and other services
Customer Service
- Communication: Responsive and clear communication
- Engineering Support: Design assistance and DFM feedback
- Project Management: Single point of contact for your project
- Problem Solving: Ability to address challenges quickly
CNC Milling Trends and Innovations
Advanced Technologies
5-Axis Machining
- Growing adoption for complex part production
- Reduces setup time and improves accuracy
- Enables the production of more complex geometries
High-Speed Machining
- Faster spindle speeds and feed rates
- Improved surface finishes
Automation and Robotics
- Automated loading and unloading systems
- Robotic cells for lights-out production
- Integration with other manufacturing processes
Industry 4.0 Integration
Digital Twin Technology
- Virtual simulation of the machining process
- Predictive maintenance and optimization
- Improved process monitoring
IoT Connectivity
- Real-time machine monitoring
- Remote diagnostics and troubleshooting
- Data-driven process improvement
Artificial Intelligence
- AI-powered tool path optimization
- Predictive maintenance algorithms
- Quality inspection automation
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between CNC milling and CNC turning?
CNC milling uses rotating cutting tools to remove material from a stationary workpiece, while CNC turning rotates the workpiece against a stationary cutting tool. Milling is better for complex 3D shapes, while turning is ideal for cylindrical parts.
What tolerances can CNC milling achieve?
Standard tolerances are ±0.01 mm (0.0004 inches), but high-precision CNC milling can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.005 mm (0.0002 inches) or even ±0.001 mm (0.00004 inches) for specialized applications.
How long does CNC milling take?
The time depends on the complexity of the part, material, and machine speed. Simple parts may take minutes, while complex parts can take hours or even days.
What is the minimum order quantity for CNC milling?
Most CNC milling service providers accept orders of any size, from 1 piece (prototyping) to 10,000+ pieces (mass production).
What file formats are needed for CNC milling?
Common CAD file formats include STEP, IGES, STL, DWG, DXF, SolidWorks, and Inventor files. CAM software converts these to G-code for the machine.
How much does CNC milling cost?
Cost depends on material, part complexity, tolerances, and quantity. Factors include machine time, tooling, material costs, and finishing operations.
What materials are best for CNC milling?
Aluminum alloys are the most popular due to their excellent machinability and strength-to-weight ratio. Other good choices include steel, stainless steel, brass, and various plastics.
Can CNC milling create complex 3D shapes?
Yes, especially with 5-axis CNC milling machines, which can create extremely complex 3D shapes and contours that would be impossible with traditional machining methods.
What is the surface finish quality of CNC milled parts?
Standard surface finishes range from Ra 1.6-3.2 μm. High-speed machining and proper tool selection can achieve finishes as smooth as Ra 0.4 μm.
How do I ensure quality in CNC milled parts?
Choose a reputable supplier with proper certifications, request quality documentation, and consider on-site inspections for critical components.
Disclaimer
- All information, opinions, and data contained in this article are for the purpose of information transmission only and do not constitute any advice on investment, transactions, law, medical care, or other matters.
- The content of the article is compiled based on public information or created based on the author’s personal understanding. Although every effort is made to ensure accuracy, it does not guarantee the completeness, accuracy, and timeliness of the information, nor does it bear any responsibility for any losses caused by the use of the content of this article.
- If the article involves third-party opinions, pictures, data, and other content, the copyright belongs to the original author. In case of infringement, please contact us for deletion.
- Readers should make independent decisions based on their actual situation and combined with professional opinions. The user shall bear all consequences arising from the use of the content of this article.
What is CNC Milling Parts? Comprehensive Guide to Precision Machining
Contact Information:
- For more information about CNC milling services
- Technical consultation consultation and quote requests
- Custom machining solutions