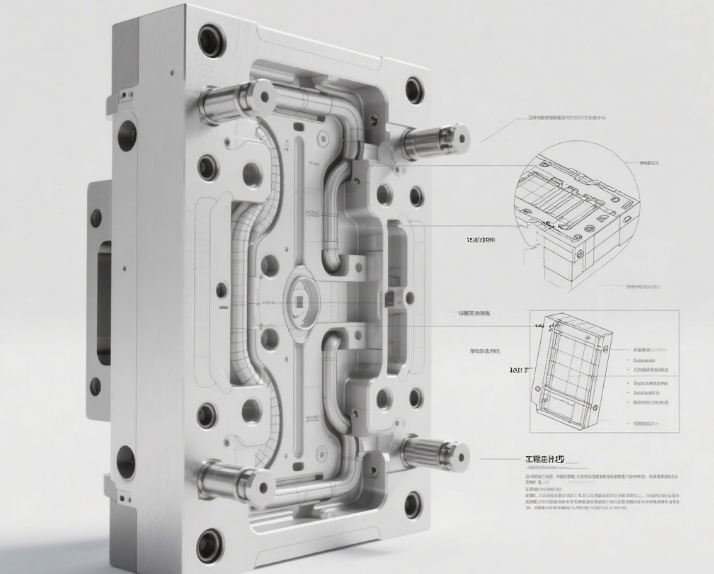
As a core component of the injection molding process, the type and characteristics of injection mold materials directly determine the performance of the mold, service life and the quality of the final product. The following will be from the types of injection mold materials, characteristics and specific value embodiment of the three aspects of a detailed introduction.

1. Types of injection mold materials
There are many types of injection mold materials, which can be roughly divided into three categories: metal materials, non-metallic materials and composite materials.
1.1 Metallic materials
1.1.1 Steel
Types: Commonly used ordinary steel, pre-hardened steel, high alloy steel and so on.
Characteristics: Steel materials are known for their high hardness, high strength, high wear resistance and good processing performance. For example, pre-hardened steel such as P20, 718, etc., which has been heat-treated before leaving the factory, has moderate hardness, is easy to process and polish, and is a commonly used material in injection molds.
Specific values: Take P20 steel as an example, its hardness range is usually between HRC 28-32, and its tensile strength can reach 550-700MPa, which is suitable for the manufacture of most injection molds.
1.1.2 Aluminum Alloy
Characteristics: Aluminum alloy material has low density, good thermal conductivity, excellent processing performance, especially suitable for the production of small injection molds and molds that require rapid heating and cooling.
Specific value: the density of aluminum alloy is about 2.7g/cm³, much lower than the steel material, the thermal conductivity is about 2-3 times of steel, which can effectively improve the heating and cooling efficiency of the mold.
1.1.3 Copper alloy
Characteristics: Copper alloy has high thermal conductivity and good corrosion resistance, especially suitable for the production of high requirements of injection molds, such as the need for rapid heat dissipation or contact with corrosive plastic molds.
Specific value: the thermal conductivity of copper alloy is much higher than that of steel, such as the thermal conductivity of brass is about 110W/(m-K), which can quickly transfer heat from the mold cavity to the cooling system.
1.2 Non-metallic materials
1.2.1 Ceramic materials
Characteristics: Ceramic materials have high hardness, high strength and excellent wear resistance, can maintain stable performance under high temperature and high pressure environment, suitable for special requirements of the injection mold.
Specific value: The hardness of ceramic materials can reach HRA 85 or more, much higher than general metal materials, and can withstand extremely high friction and wear.
1.2.2 Glass fiber reinforced plastic (GFRP) and carbon fiber reinforced plastic (CFRP)
Characteristics: These composite materials are characterized by high strength, high toughness and light weight, and are suitable for the production of complex shapes and large injection molds.
Specific values: The tensile strength of GFRP and CFRP can reach thousands of MPa, and the density is much lower than that of metal materials, which can effectively reduce the weight of molds and improve production efficiency.
1.2.3 Composite material
Composite materials are made of two or more materials composite, with the advantages of a variety of materials. Such as metal-based composites combined with the strength of metal and composite lightweight characteristics; ceramic-based composites have high hardness, high wear resistance and excellent high temperature performance.
2. Injection mold material characteristics
2.1 High wear resistance
Mold materials need to have good abrasion resistance to resist the plastic melt in the high-pressure scouring and abrasion. For example, high hardness steel materials and ceramic materials can meet this requirement.
2.2 High corrosion resistance
Additives in the plastic and the melt itself may have a corrosive effect on the mold. Therefore, the mold material needs to have good corrosion resistance, such as the use of corrosion-resistant steel or mold surface plating treatment to improve corrosion resistance.
2.3 Good thermal conductivity
Good thermal conductivity helps the mold in the injection process to maintain a stable temperature distribution, improve product quality. Copper alloys and aluminum alloys and other materials are often used in molds that require rapid heating and cooling because of their excellent thermal conductivity.
2.4 Good dimensional stability
Molds in the molding process to withstand high temperatures and high pressures, and therefore need to have good dimensional stability to avoid mold deformation and product size instability. Through the appropriate heat treatment process and the selection of suitable materials (such as pre-hardened steel) can improve the dimensional stability of the mold.
2.5 Easy processing and polishing
Mold materials need to be easy to process and polish to meet the mold precision and surface quality requirements. Such as pre-hardened steel and other materials for its good processing performance and polishing performance and popular.
Plastic injection mold materials of various types and each has its own characteristics. In the selection of mold materials, need to consider the use of products, mold design requirements and production costs and other factors to choose the most suitable material. Reasonable material selection and processing technology control can ensure the high performance, long life and high efficiency production of injection molds.
Injection mold material FAQ
1. What are the main types of injection mold materials?
There are many kinds of injection mold materials, which can be mainly divided into the following categories:
Metal materials: including steel, aluminum alloy, copper alloy and so on. Among them, steel material has become the most commonly used material in injection molds because of its high hardness, high strength, high wear resistance and good processing performance. Aluminum alloy material is suitable for the production of small injection molds due to its low density, high thermal conductivity and good processing performance. Copper alloy materials have high thermal conductivity and good corrosion resistance, suitable for the production of high-demand injection molds.
Non-metallic materials: mainly including ceramic materials, glass fiber reinforced plastic (GFRP), carbon fiber reinforced plastic (CFRP) and so on. Ceramic materials have high hardness, high strength and excellent abrasion resistance, which are suitable for injection molds with special requirements, while GFRP and CFRP are suitable for the production of complex shapes and large-scale injection molds due to their high strength, high toughness and light weight.
Composite materials: Composite materials made of two or more materials, with the advantages of a variety of materials. Such as metal-based composites combined with the strength of metal and composite lightweight characteristics; ceramic-based composites have high hardness, high wear resistance and excellent high temperature resistance.
2. injection mold materials should have what main properties?
The selection of injection mold materials should be based on the following main performance considerations:
High abrasion resistance: molds in the use of the process need to withstand the plastic melt scouring and abrasion, so the material needs to have good abrasion resistance.
High corrosion resistance: additives in the plastic and the melt itself may have a corrosive effect on the mold, the material needs to have high corrosion resistance.
Good thermal conductivity: good thermal conductivity helps the mold in the injection process to maintain a stable temperature distribution, improve product quality.
Good dimensional stability: mold in the molding process to withstand high temperature and high pressure, the material needs to have good dimensional stability to avoid mold deformation and product size instability.
Easy to process and polish: mold materials need to be easy to process and polish to meet the mold precision and surface quality requirements.
3. What are the key steps in the processing of injection mold materials?
The processing of injection mold materials usually includes the following key steps:
Material selection and pretreatment: according to the use of mold requirements and production conditions to select the appropriate material, and the necessary pretreatment such as annealing, normalizing, etc., in order to improve the material’s organizational structure and properties.
Processing and molding: Through roughing, semi-finishing and finishing steps, the mold material is processed into the final shape and size. This process requires strict control of the processing parameters and environmental conditions to ensure that the mold processing accuracy and surface quality.
Heat treatment: quenching, tempering and other heat treatment processes to change the internal organization and properties of the mold material, improve the hardness of the mold, wear resistance, fatigue resistance and other indicators.
Surface treatment: Plating, spraying, carburizing, nitriding and other treatments on the surface of the mold to improve the mold’s wear resistance, corrosion resistance, fatigue resistance and other properties and improve the appearance of the mold quality.