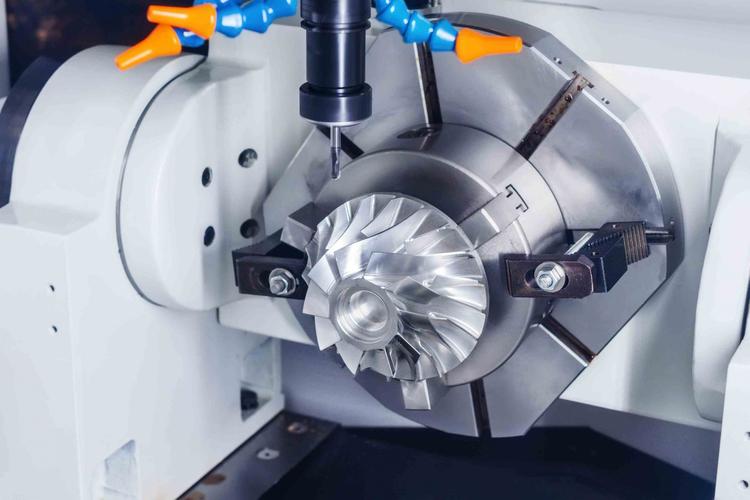
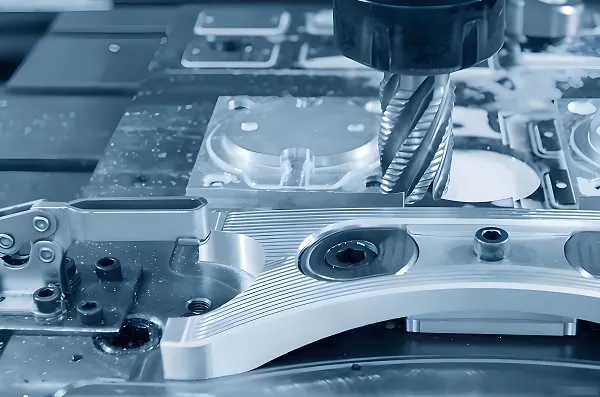
This diversity isn’t confusing—it’s a strength. A machinist running a small lathe might rely on “Compact Numerical Control,” while a large automotive plant uses “Cloud Numerical Control” to monitor 50 machines at once. Understanding all 7 full forms helps you choose the right technology for your work, not just follow trends.
Industry data underscores this: 68% of manufacturers use at least two “types” of CNC (e.g., Computer Numerical Control for production, Cloud Numerical Control for monitoring; Source: 2025 Global CNC Technology Report). These full forms aren’t just acronyms—they’re a language for talking about what CNC does and can be.
The 7 Full Forms of CNC: Depth, Applications, and Craftsman Insights
Each full form has a purpose, a history, and a place in modern manufacturing. Below is the breakdown—with the real-world context they don’t teach in basic CNC courses.
1. Computer Numerical Control (The “Foundational” CNC)
- Full Form: Computer Numerical Control
- Core Definition: The original, most universal meaning: Using a computer to execute preprogrammed numerical instructions (G-codes, M-codes) that control machine tool movements (X, Y, Z axes). It replaced manual handwheels and punch cards, turning “guesswork” into precision.
- Technical Roots: Invented in the 1950s by John T. Parsons (for aerospace part machining), it revolutionized manufacturing by cutting human error from 5% to <0.1%.
- Applications: Every CNC machine you use today—lathes, mills, routers—relies on this core definition. Example: A Haas TM-1 milling center using G-code to drill holes in an aluminum bracket.
- Craftsman’s Insight: “This is the CNC I learned on—program a part, hit ‘cycle start,’ and the machine does the rest. I still remember my first project: a simple shaft. With manual machining, it took 2 hours and had a 0.1mm error. With Computer Numerical Control? 15 minutes, ±0.005mm. It didn’t just save time—it made me a better machinist by letting me focus on design, not hand-eye coordination.”
2. Computerized Numerical Control (The “Integrated” CNC)
- Full Form: Computerized Numerical Control
- Core Definition: A subtle but important upgrade from “Computer Numerical Control”: It integrates the CNC system with other computer tools (CAD/CAM software, inventory management, quality control databases) into a single workflow. It’s not just “controlling the machine”—it’s “connecting the machine to the entire factory.”
- Key Difference: “Computer Numerical Control” is about the machine; “Computerized Numerical Control” is about the system. For example: A CAD model of a car part is automatically converted to G-code, sent to the CNC mill, and post-machining data (dimensions, cycle time) is sent back to a quality database—all without manual input.
- Applications: High-volume production (e.g., automotive plants making 10,000 door brackets/day).
- Craftsman’s Insight: “We switched to Computerized Numerical Control 5 years ago. Before, I’d spend 1 hour exporting G-code from CAD, then 30 minutes typing it into the mill. Now, the CAD/CAM software sends the code directly to the machine, and the mill logs every part’s dimensions into our QC system. I haven’t typed a G-code manually since—more time for troubleshooting, less time for data entry.”
3. Continuous Numerical Control (The “Uninterrupted” CNC)
- Full Form: Continuous Numerical Control
- Core Definition: CNC that runs non-stop for long-duration jobs (8+ hours) without manual intervention. It uses features like automatic tool changers (ATCs), chip conveyors, and in-machine probing to handle tool changes, waste removal, and part measurement—critical for deep-hole drilling, long shaft turning, or batch production.
- Why It Matters: Manual CNC requires stopping to change tools or empty chips—losing 20-30% of production time. Continuous Numerical Control cuts that downtime to <5%.
- Applications: Deep-hole drilling (e.g., 100mm-deep holes in steel shafts) or batch machining (e.g., 500 aluminum sensor housings).
- Craftsman’s Insight: “I run a Continuous Numerical Control lathe for making long hydraulic shafts (1m long). Before, I’d stop every 10 parts to change the tool and clean chips—losing 15 minutes each time. Now, the ATC swaps tools automatically, and the chip conveyor clears waste. I start it at 8 AM, and it runs until 5 PM with just a few checks. We used to make 30 shafts/day; now we make 45.”
4. Concurrent Numerical Control (The “Parallel” CNC)
- Full Form: Concurrent Numerical Control
- Core Definition: CNC that handles multiple tasks at the same time (concurrently) instead of one after another. For example: While the machine is cutting a part, it preloads the next part’s program, checks tool wear, or sends production data to a supervisor—no waiting.
- Technical Edge: Critical for Industry 4.0, where factories need to maximize machine utilization. It increases machine “uptime” (time spent cutting) from 60% to 85% (Source: CNC Productivity Study 2025).
- Applications: Complex parts requiring multiple operations (e.g., a gear that needs turning, milling, and threading).
- Craftsman’s Insight: “Our 5-axis mill uses Concurrent Numerical Control. While it’s milling a gear’s teeth, it’s already loading the next gear’s program and checking the end mill’s wear with a probe. Before, we’d wait 2 minutes between parts—now it’s 10 seconds. For a batch of 200 gears, that saves 5.5 hours. It’s like having a second operator, but without the cost.”
5. Custom Numerical Control (The “Tailored” CNC)
- Full Form: Custom Numerical Control
- Core Definition: CNC systems designed for specific industries or parts—not one-size-fits-all. Manufacturers modify hardware (e.g., custom tool turrets) or software (e.g., specialized G-codes for aerospace parts) to solve unique problems that standard CNC can’t.
-
- Automotive: Custom CNC for making engine blocks (with large worktables and high-torque spindles).
-
- Medical: Custom CNC for machining titanium implants (with ultra-precise servo motors, ±0.001mm).
- Craftsman’s Insight: “We build Custom Numerical Control lathes for a client that makes dental implants. Standard CNCs can’t hold the ±0.002mm tolerance they need, so we added a high-precision spindle and custom software that compensates for titanium’s heat expansion. Their rejection rate dropped from 8% to 0.5%. Custom CNC isn’t cheap, but it solves problems standard machines can’t touch.”
6. Compact Numerical Control (The “Small-Space” CNC)
- Full Form: Compact Numerical Control
- Core Definition: Small, lightweight CNC systems (often tabletop size) designed for small workshops, garages, or educational settings where space is limited. They retain key features (G-code support, basic auto-tool change) but have smaller work envelopes (e.g., 300×200×150mm) and lower power requirements (110V instead of 220V).
- Why It Matters: 42% of small manufacturers cite “lack of space” as a barrier to CNC adoption (Source: Small Shop Manufacturing Report 2025). Compact CNC removes that barrier.
- Applications: Prototyping (e.g., a hobbyist making a custom phone case), small-batch production (e.g., 50 brass keychains), or training students.
- Craftsman’s Insight: “I run a small workshop out of my garage—space is tight. My Compact Numerical Control mill fits on a workbench, uses 110V power, and still cuts aluminum and brass. Before, I thought CNC was only for big factories. Now, I make custom parts for local bike shops—all from a machine that’s smaller than my refrigerator. It’s opened up a whole new business for me.”
7. Cloud Numerical Control (The “Connected” CNC)
- Full Form: Cloud Numerical Control
- Core Definition: The newest full form: CNC machines connected to the cloud, allowing remote monitoring, program sharing, and data analysis. You can check a machine’s status from your phone, send a new program from a home office, or use AI to optimize cutting parameters based on data from 100 machines.
- Key Benefits: Reduces unplanned downtime by 40% (via remote fault alerts) and cuts programming time by 25% (via cloud-shared program libraries; Source: Cloud Manufacturing Trends 2025).
- Applications: Multi-location factories (e.g., a company with mills in Detroit and Berlin sharing programs), or manufacturers using AI to improve efficiency.
- Craftsman’s Insight: “Our factory has 10 Cloud Numerical Control mills. Last month, I was on vacation when my phone got an alert: one mill had a tool break. I logged into the cloud, saw the error, and sent a backup tool program to the machine—all from my hotel room. Before, the mill would have sat idle until I got back. Now, downtime is just 15 minutes instead of 8 hours. Cloud CNC isn’t just ‘fancy tech’—it keeps the shop running when life happens.”
Core Value: Why These 7 Full Forms Matter (Beyond Jargon)
You might ask: “Do I need to memorize all 7?” No—but understanding them helps you:
- Choose the Right CNC: A small workshop doesn’t need Cloud Numerical Control; a large plant wastes money on Compact Numerical Control. Knowing the full forms lets you match technology to your needs.
- Communicate Clearly: When you tell a supplier you need “Custom Numerical Control for titanium implants,” they know you’re not just asking for a standard mill—you need precision upgrades.
- Future-Proof Your Work: Cloud and Concurrent Numerical Control are the future of manufacturing. Understanding them now means you won’t fall behind when your competitors adopt them.
Example: A client once asked for “a CNC mill for making car parts.” By asking, “Do you need Computerized Numerical Control (to connect to your CAD system) or Cloud Numerical Control (to monitor it remotely)?” we saved them $15,000—they only needed the integrated (Computerized) version, not the cloud-connected one.
Common Misconceptions: Clearing Up Confusion
Even experienced machinists mix up these full forms. Here are the most frequent mistakes—and how to avoid them.
1. “Computer Numerical Control and Computerized Numerical Control are the same.”
- Reality: Computer Numerical Control is about the machine; Computerized Numerical Control is about the system. A basic mill uses Computer Numerical Control (runs G-code); a mill connected to CAD/CAM uses Computerized Numerical Control (integrates design and machining).
- Fix: Ask: “Does it connect to other software (CAD, QC)?” If yes, it’s Computerized; if no, it’s Computer Numerical.
2. “Cloud Numerical Control is only for big factories.”
- Reality: Small shops benefit too. A one-person shop can use cloud CNC to remotely start a job (e.g., run a batch of parts overnight) or share programs with a client.
- Example: A friend of mine runs a solo CNC business. He uses cloud CNC to start a milling job at 6 PM, then checks progress on his phone while eating dinner. No more staying late at the shop.
3. “Compact Numerical Control is ‘low-quality’.”
- Reality: Compact doesn’t mean cheap. Brands like Tormach make Compact Numerical Control mills that hold ±0.005mm tolerance—good enough for most small-batch parts. They’re small, not low-quality.
- Fix: Look for specs (tolerance, spindle speed) instead of size. A Compact CNC with a 10,000r/min spindle is better than a large CNC with a 5,000r/min spindle for small parts.
Q&A: Wisdom from the Shop Floor
These are the questions machinists, workshop owners, and students ask most—grounded in real needs, not just theory.
Q1: “I run a small shop (2 people). Which full form do I need?”
- My Answer: Start with Computer Numerical Control (a basic mill/lathe that runs G-code) or Compact Numerical Control (if space is tight). If you use CAD software to design parts, upgrade to Computerized Numerical Control (to connect CAD to the machine). Save Cloud or Concurrent CNC for when you grow to 5+ machines.
- Example: A two-person shop making custom brackets only needs a Computer Numerical Control lathe—they don’t need cloud monitoring or custom hardware.
Q2: “How do I know if I need Custom Numerical Control?”
- My Answer: Ask: “Can a standard CNC do this job?” If:
-
- The part needs tolerance tighter than ±0.003mm (e.g., medical implants),
-
- The material is exotic (e.g., Inconel, titanium), or
-
- The part has unique features (e.g., 10mm-deep micro-holes),
then you need Custom Numerical Control. Otherwise, a standard machine will work.
Q3: “Is Cloud Numerical Control safe? I don’t want someone hacking my machines.”
- My Answer: Yes—if you use secure cloud platforms (most reputable brands like Fanuc or Siemens use end-to-end encryption). Think of it like online banking: safe if you use trusted providers. We’ve used Cloud Numerical Control for 3 years and never had a security issue. Just avoid cheap, unbranded cloud tools—stick to the ones your machine manufacturer recommends.
Q4: “Will Concurrent Numerical Control replace operators?”
- My Answer: No—it makes operators more productive. Concurrent CNC handles repetitive tasks (preloading programs, checking tool wear), so you can focus on the hard stuff: troubleshooting, optimizing parts, and training new staff. We have 5 Concurrent CNC machines, and we haven’t laid off any operators—we’ve just moved them to more valuable work.
Final Thought
The 7 full forms of CNC aren’t just a list—they’re a story of how manufacturing has grown: from manual tools to computer control, from isolated machines to connected factories. Each full form represents a problem solved: Compact CNC for small shops, Cloud CNC for remote work, Custom CNC for unique parts.
As a machinist or manufacturer, you don’t need to master all 7 overnight. But understanding them lets you see CNC not as a “tool,” but as a set of tools that can adapt to your work—not the other way around. Whether you’re running a Compact CNC in a garage or a Cloud CNC in a factory, the goal is the same: to make better parts, faster, with less stress.
What’s your CNC story? Do you use a Compact CNC for prototyping? Has Cloud CNC changed how you run your shop? Share your experience in the comments—I’d love to hear how these full forms show up in your daily work.