Answer
The core differences between CNC machining and stamping are as follows:
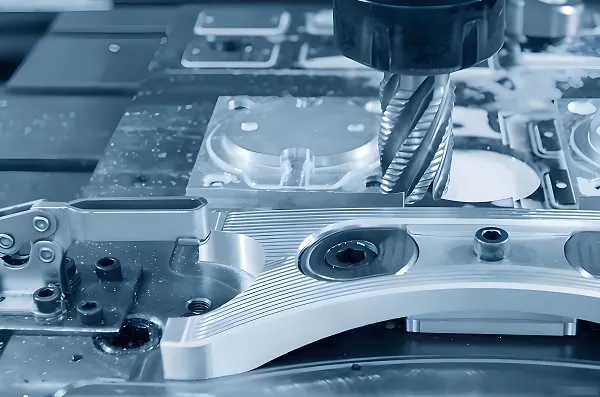
CNC machining uses computer – controlled cutting tools to cut raw materials (such as metals and plastics), achieving high – precision and complex – shaped subtractive manufacturing. It is suitable for small – batch customization, like aerospace parts.
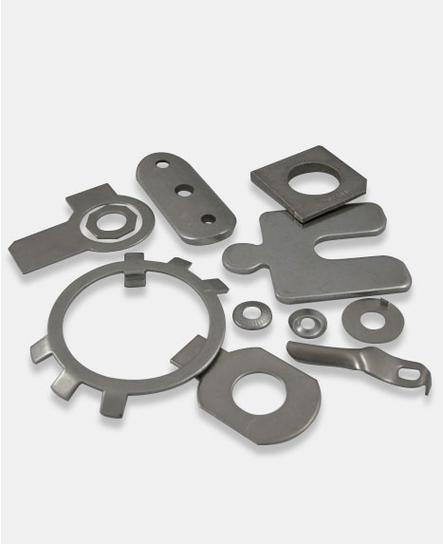
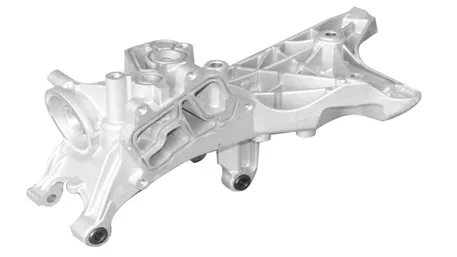
Stamping uses molds and presses to form sheet materials (such as bending and punching), which belongs to additive manufacturing and is suitable for large – scale standardized production, like automotive outer shells.
Expansion
I. Processing Principles
CNC Machining:
Technology type: Subtractive manufacturing (removing materials through milling, turning, drilling, etc.).
Core equipment: CNC milling machines, lathes, grinders, etc., relying on high – precision tool – path control.
Accuracy limit: Can reach ±0.001mm (such as the micron – level accuracy of medical implants).
Stamping Processing:
Technology type: Forming manufacturing (applying pressure to sheet materials through molds to make them plastically deform).
Core equipment: Mechanical presses, hydraulic presses, in combination with customized molds (such as blanking dies, bending dies).
Accuracy range: Usually above ±0.1mm (affected by mold wear, suitable for non – precision parts).
II. Cost Structure
CNC Machining:
Pre – production cost: Low (no need for molds, only CAD programming required).
Unit cost: High (low material utilization rate, for example, the waste rate of aluminum block processing can reach 50%).
Economies of scale: Not obvious, suitable for small batches of 1 – 1000 pieces (such as prototype verification, high – end customization).
Stamping Processing:
Pre – production cost: Extremely high (mold design + manufacturing costs range from 100,000 to 1,000,000 yuan, with a cycle of 4 – 12 weeks).
Unit cost: Extremely low (when the batch exceeds 10,000 pieces, the cost per piece can be reduced to less than 0.1 yuan).
Economies of scale: Significant, suitable for mass production in the millions (such as mobile phone casings, beverage cans).
III. Design Flexibility
CNC Machining:
Geometric complexity: Almost unlimited (can process internal threads, undercuts, thin – walled parts).
Material compatibility: Covers all materials (metals, ceramics, composite materials, etc.).
Typical cases: Aero – engine blades , customized jewelry (fine carving).
Stamping Processing:
Geometric complexity: Limited (needs to follow the principle of “formability”, such as avoiding sharp angles and high draw ratios).
Material compatibility: Mainly suitable for metals with good ductility (such as low – carbon steel, aluminum alloy).
Typical cases: Automobile door frames (one – time stamping forming), heat sinks for electronic devices (array punching).
IV. Production Efficiency
CNC Machining:
Time per piece: From minutes to hours (for example, it takes 2 hours to process a titanium – alloy aerospace part).
Difficulty of automation: High (manual loading and unloading are required, and multiple process switches are needed for complex parts).
Suitable scenarios: Urgent orders (samples can be produced within 24 hours), R & D iteration (only need to adjust the program for design modification).
Stamping Processing:
Time per piece: Second – level (high – speed presses can reach 600 times/minute, such as producing screws).
Difficulty of automation: Low (fully automated production lines can be achieved with robots).
Suitable scenarios: Long – term stable orders (such as 10 million pieces of automotive seat brackets produced annually).
V. Application Fields
CNC Machining:
Aerospace (turbine discs, landing gear parts)
Medical (dental implants, surgical instruments)
Electronics (precision connectors, heat dissipation modules)
Stamping Processing:
Automobile manufacturing (body panels, engine brackets)
Home appliances (refrigerator casings, washing machine inner drums)
Daily necessities (beverage cans, tableware)
Decision – making Guide:
Choose CNC when the demand is for small batches, high complexity, and high added – value (such as satellite parts).
Choose stamping when the demand is for large – scale, low – cost, and standardized production (such as construction – used angle steel).
Compromise solution: Rapid tooling (3D – printed molds + small – tonnage stamping), suitable for medium – sized batches of 500 – 5000 pieces, with a cost 60% lower than traditional stamping.