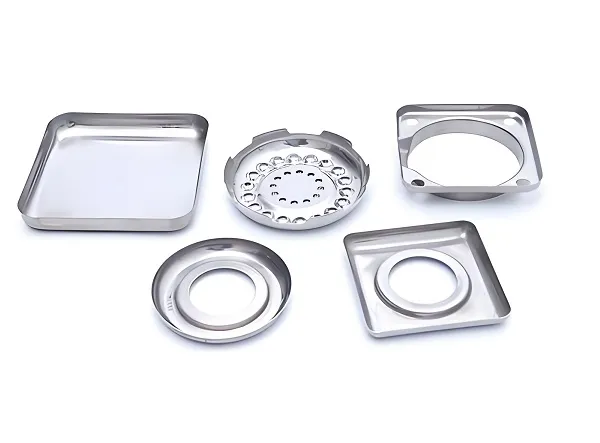
CNC Milling is a highly accurate and efficient machining process that is widely used in manufacturing. Simply put, CNC milling is the use of a computer-controlled milling machine to remove material from a workpiece by means of a rotating cutter to obtain a part or product of the desired shape.

1.The basic principle of CNC milling process
CNC milling process is the core of the “numerical control” and “milling” two concepts. CNC, that is, computer numerical control (Computer Numerical Control, CNC), refers to the process of CNC milling by means of a predefined method.
CNC), refers to the pre-programmed computer program to control the movement of the machine tool. Milling, on the other hand, is a type of cutting process that utilizes a rotating tool to cut on the workpiece and remove excess material.
2. Process Flow
Design: First, a three-dimensional model of the part is drawn using CAD (Computer Aided Design) software and its dimensions and tolerance requirements are determined.
Programming: Next, CAM (Computer Aided Manufacturing) software is used to convert the CAD model into a machine tool-recognizable G-code, which is a specially formatted set of instructions used to control every action of the machine tool, such as tool travel speed, depth of cut, etc. The G-code is used to control every action of the machine tool, such as tool travel speed and depth of cut.
Setup: On a CNC milling machine, the workpiece is fixed on the table and the required tool is installed. Then, the G-code program is loaded into the control system of the machine.
Machining: Starting the machine, the control system will drive the tool to cut and machine on the workpiece according to the instruction of G code. During the cutting process, the tool will move according to the predetermined path and speed, gradually removing the material on the workpiece until the desired shape is formed.
3.Key Technical Parameters
Spindle speed: usually measured in rpm (revolutions per minute), which determines the rotational speed of the tool. Different materials and machining requirements require different spindle speeds. For example, when machining carbide, the spindle speed may be as high as thousands of rpm.
Cutting speed: In units of m/min, it indicates the circumferential speed of the cutting edge of the tool. It is related to the spindle speed and tool diameter, and is an important factor affecting cutting efficiency and machining quality.
Feed: refers to the tool in the cutting process relative to the workpiece moving speed, usually in mm/min or mm/rev (feed per revolution) as a unit. The size of the feed directly affects the cutting force and cutting temperature, which in turn affects the machining accuracy and tool life.
Depth of cut: the depth of the tool in the cutting process into the workpiece, usually in mm. The choice of depth of cut needs to consider the rigidity of the machine tool, the strength of the tool and the material of the workpiece and other factors.
4.Application Areas
CNC milling process is widely used in many fields such as aerospace, automobile manufacturing, mold processing, electronic communications and so on because of its high precision, high efficiency and high flexibility. For example, in the aerospace field, CNC milling is used to manufacture aircraft parts with complex shapes; in the automobile manufacturing field, it is used to produce key components such as engine blocks and gearbox housings.
● Complex shapes and parts with high precision requirements
Aerospace parts, such as engine components, structural parts, etc., which require high complexity and precision, the CNC milling process can precisely control the tool path and realize the machining of complex surfaces, which meets the stringent requirements of aerospace industry on the quality of parts.
Medical equipment and instruments: such as surgical instruments, implants, etc., these products require high precision and surface finish to ensure their functionality and safety. cnc milling process can process precision medical equipment parts, to meet the high product quality requirements of the medical industry.
Precision Molds and Tooling
Mold manufacturing: CNC milling process plays an important role in mold manufacturing. It can process high-precision mold cavities and cores to meet the requirements of mold manufacturing for dimensional accuracy and shape accuracy. At the same time, CNC milling process can also realize the rapid manufacturing and repair of the mold, improve the efficiency of mold manufacturing.
Workholding: In the process of machining, workholding is used to locate and clamp the workpiece, CNC milling process can produce workholding that meets the requirements to ensure the stability and accuracy of the workpiece in the process of machining.
●Electronic products and communication equipment shell
Electronic products: such as cell phones, tablet computers, etc., the shell and internal parts, these products need to be precise size and complex shape, CNC milling process can be machined to produce a variety of shapes of the shell and internal parts, to meet the requirements of electronic products on the appearance and performance.
Communication equipment: such as base station antennas, microwave devices, etc., the shell and internal structural parts, these products require high precision and surface quality, CNC milling process can meet these requirements, to ensure the stability and reliability of communication equipment.
● Customized and personalized products
Artwork and decorations: CNC milling process can process various shapes and patterns of artwork and decorations to meet the demand for personalized customization. By controlling the movement of the machine tool through programming, precise processing of complex patterns and shapes can be realized.
Other customized products: such as car modification parts, mechanical parts, etc. These products need to be customized according to the specific needs, CNC milling process can meet the processing requirements of these customized products with its high precision and flexibility.
CNC Milling FAQ
What are the main advantages of CNC Milling?
The main advantages of the CNC milling process include:
High Accuracy: The ability to machine parts with high accuracy to meet application scenarios that require extremely high dimensional and shape accuracy.
High efficiency: High degree of automation reduces manual operations and increases productivity.
Flexibility: Through programming control, parts of various complex shapes can be processed to meet diversified production needs.
Repeatability: once the program is determined, parts with the same accuracy can be processed repeatedly, ensuring product consistency.
What materials is CNC milling process applicable to?
CNC milling process is applicable to a wide range of materials, including but not limited to:
Metallic materials: such as aluminum alloy, stainless steel, copper, iron, etc.
Non-metallic materials: e.g. plastics, wood, composites, etc.
Specialty materials: e.g. ceramics, cemented carbide, etc. (specific tool and process parameters are required).
What are the key points of fixture design in CNC milling process?
Fixture design is a non-negligible part of CNC milling process, which directly affects the positioning accuracy and machining stability of the workpiece. Here are some design points:
Accurate positioning: The fixture should ensure the accurate positioning of the workpiece in the machining process, avoiding the movement or deflection of the workpiece leading to machining errors.
Reliable clamping: the fixture should be able to reliably clamp the workpiece to prevent the workpiece from loosening or falling off during machining, while avoiding damage to the workpiece.
Convenient operation: the fixture design should consider the convenience of the operator, easy loading and unloading of the workpiece and the adjustment of the fixture.
Good rigidity: the fixture should have good rigidity to resist the cutting force and vibration in the machining process to ensure machining stability.