CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine tools, as the cornerstone of modern manufacturing, have become indispensable for processing metals, plastics, wood and other materials with their high precision, high efficiency and automation features. In this article, we will discuss in depth the components of CNC machine tools, the principle of operation and its wide range of applications in the industry, and through detailed data and cases, to show its excellent performance and advantages.

1.Key components of CNC machine tools
The complexity of CNC machine tools is reflected in its many precision components work together, these components can be broadly divided into two categories: control system and machine tool system.
1.1.Control system
Input devices: These include keyboards, USB flash drives, wireless communications, etc., and are used to input CNC programs (e.g., G-codes) into the machine tool. These programs describe in detail the tool trajectory, cutting parameters, etc.
Machine Control Unit (MCU): As the “brain” of the CNC machine tool, the MCU is responsible for reading the input program and converting it into commands that can be executed by the servo motors to accurately control the movement of the machine’s axes.
Feedback system: monitoring the position and speed of each axis of the machine tool in real time through linear encoder or rotary encoder to ensure machining accuracy, MCU adjusts the motion instruction according to the feedback signal to realize closed-loop control.
Display device: shows the machine status and program running information to the operator, which is convenient for monitoring and adjusting the machining process.
1.2Machine tool system
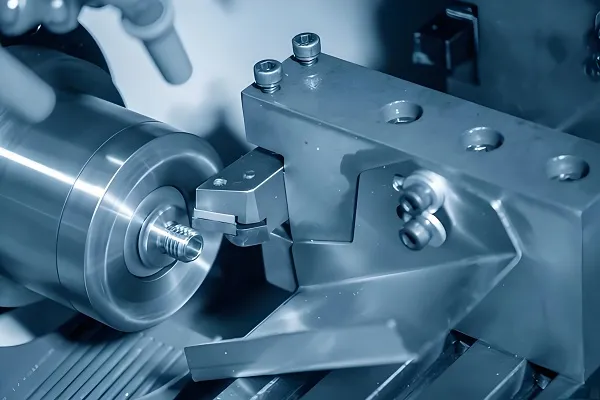
Machine tool: carries the workpiece and tool and performs cutting operations. According to the type of machine tool (e.g. CNC lathe, CNC milling machine), the structure of the machine tool is different.
Drive system: consists of servo motors, ball screws and linear guides, which are responsible for moving the tool or workpiece along each axis of the machine. The high precision control of the servo motors ensures the accuracy of the machining process.
Headstock and tailstock (CNC lathes only): The headstock contains the main drive for rotating the workpiece, while the tailstock provides axial support on the other side of the workpiece to ensure machining stability.
Chucks: used to hold the workpiece and keep it stationary during machining. Three-jaw chucks and four-jaw chucks are the two common types, the latter having higher positioning accuracy.
Coolant tank: Provides coolant to reduce friction and heat during machining to protect the tool and workpiece.
1.3Working Principle of CNC Machine Tools
The workflow of a CNC machine tool can be roughly divided into three stages: reading the program, executing the program and reducing errors.
Reading program: the CNC program is read into the MCU through the input device, and the program contains all the instructions required for manufacturing parts.
Execute program: MCU controls the drive system to move the workpiece and tool to perform cutting operation according to the program instructions. At the same time, the MCU is also responsible for controlling the tool changer, coolant and other auxiliary equipment.
Reduce error: The feedback system monitors the position and speed of each axis of the machine in real time, compares the actual value with the desired value, and adjusts the motion instruction through the MCU to reduce the machining error.
2.Advantages and disadvantages of CNC machining
Main Advantages
High precision and accuracy: CNC machine tools are capable of realizing micron-level machining accuracy to meet the production needs of high-precision parts.
High efficiency: it can run 24 hours without interruption, which significantly improves production efficiency.
Reduced labor costs: high degree of automation, requiring fewer operators.
Easy Integration: Seamless integration with CAD (Computer Aided Design) and CAM (Computer Aided Manufacturing) software simplifies the design to production process.
Ability to process complex designs: the ability to process parts with complex geometries broadens the processing range.
Main Disadvantages
High initial investment: high acquisition and maintenance costs for CNC machine tools.
High technical threshold: requires specialized personnel for programming and operation.
High cost of replacing parts: the cost of replacing some precision parts after damage is high.
Application of CNC machine tools in various industries
CNC machine tools are widely used in many industries such as aerospace, medical, consumer goods, automotive, etc. due to their high precision, high efficiency and automation characteristics. In the aerospace field, CNC machine tools are used to process high-precision parts such as engine blades and fuselage structural parts; in the medical field, they are used to manufacture surgical instruments, artificial joints and other precision medical devices.
Conclusion
As an important tool in modern manufacturing, CNC machine tools have promoted the rapid development of various industries with their excellent performance and wide range of applications. By gaining a deeper understanding of the constituent parts of CNC machine tools, their working principles and their advantages and disadvantages, we can better utilize this giant of science and technology to contribute to the transformation and upgrading of the manufacturing industry.