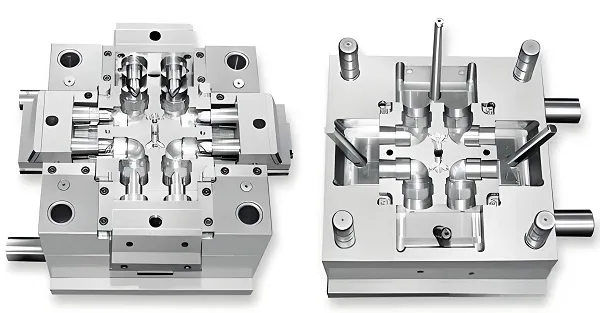
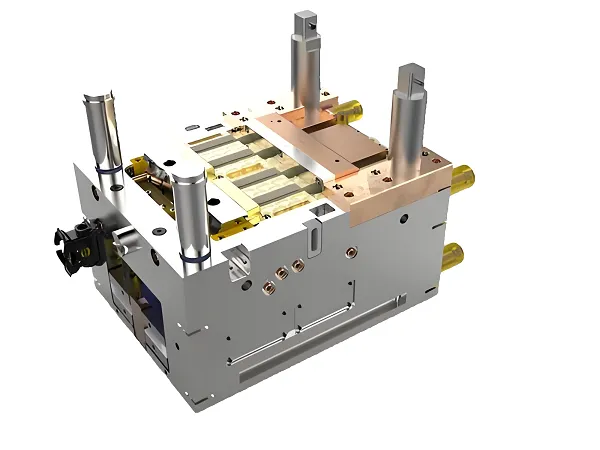
Plastic mold, as an indispensable process equipment in modern manufacturing industry, is widely used in many fields such as home appliances, automobiles, electronics, medical and so on. Its design, manufacturing and material selection directly affect the quality and productivity of products. This report will provide a comprehensive analysis of customized plastic molds from multiple dimensions such as process, flow, materials, industry knowledge, characteristics, attributes and principles.
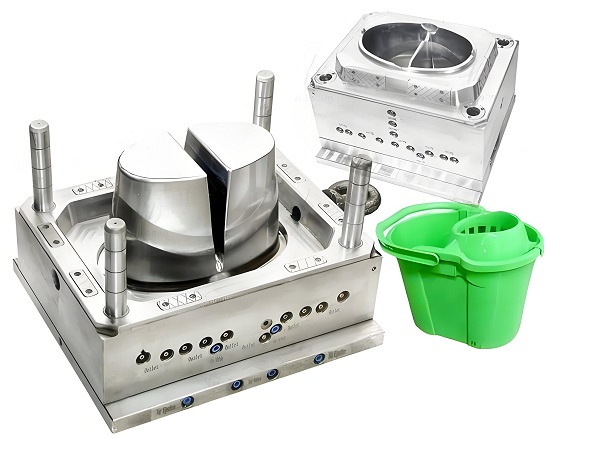

1.Process Overview
The process of customized plastic molds involves several links, mainly including design, material selection, processing and manufacturing, heat treatment and surface treatment. In the design stage, CAD (Computer Aided Design) software such as SolidWorks or UG is used for three-dimensional modeling to ensure the accuracy and structural rationality of the mold. After the design is completed, analysis of the strength, stiffness and hot runner of the mold is required to ensure that the mold design meets the production requirements.
2. The main links in the manufacturing process of customized plastic molds:
2.1 Demand analysis and design:
Demand analysis: Communicate with customers to clarify the shape, size, material, output, precision and other requirements of the product.
Conceptual design: Based on the demand analysis, carry out preliminary conceptual design, including determining the type of mold (e.g., single-cavity, multi-cavity), structural form (large spout, fine spout, hot runner, etc.) and mold materials.
Detailed design: CAD (Computer Aided Design) software is used to create a three-dimensional model of the mold, including all components such as the core, mold frame, ejector system, cooling system, and so on. After the design is completed, mold flow analysis is performed to predict the flow of plastic in the mold and optimize the mold design to improve product quality and production efficiency.
2.2 Material selection and procurement:
According to the mold design requirements, choose the appropriate mold material, such as cold work mold steel (e.g. Cr12MoV), hot work mold steel (e.g. H13) or alloy tool steel (e.g. P20).
Considering the hardness, wear resistance, toughness, heat treatment performance and cost of the material, material procurement.
2.3 Processing and manufacturing:
Rough machining: use milling machine, lathe and other machine tools to rough machining of the mold frame and mold core to remove excess material and form the basic shape.
Finishing: Use high-precision machine tools (such as machining centers, grinders) to carry out finishing of the mold to ensure the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of each part.
EDM: For complex shapes or parts that are difficult to be machined by traditional machinery, EDM technology is used for fine machining.
Assembly: The processed mold parts are assembled, including mold core, mold frame, ejector system, cooling system, etc., and preliminary debugging is carried out.
2.4 Heat treatment:
Heat treat the mold material, such as quenching and tempering, to improve the hardness, wear resistance and toughness of the mold. The heat treatment process needs to strictly control the temperature and time in order to obtain the ideal microstructure and performance.
2.5 Surface treatment:
Surface treatment such as sandblasting and polishing is performed on the mold to improve the surface finish and wear resistance of the mold. For molds that need to be corrosion-resistant, electroplating treatment can also be carried out.
2.6 Trial mold and debugging:
Use the injection molding machine to conduct a trial mold to observe the flow of plastic in the mold and the molding quality of the product.
According to the results of the trial mold debugging and optimization of the mold, including adjusting the mold temperature, injection pressure, injection speed and other parameters, as well as correcting the deficiencies in the mold structure.
2.7 Acceptance and delivery:
Acceptance is carried out after the mold debugging is completed to ensure that the mold can stably and efficiently produce products that meet the quality requirements.
After acceptance, the mold will be delivered to the customer to use or help to produce the corresponding products on behalf of processing.
3.Manufacturing process
3.1 Drawing review and material preparation: According to the product drawings and technical requirements, conduct a detailed drawing review and prepare the required materials. Commonly used mold materials include high-quality cold working die steel, hot working die steel and alloy tool steel, etc. These materials have high hardness, good machinability and wear-resistant, impact-resistant and other characteristics.
3.2 Processing and manufacturing: including mold frame processing, mold core processing, electrode processing and mold parts processing and other steps. Machining is the core link, using a variety of processes such as milling, turning, grinding and EDM. Among them, EDM is suitable for complex shapes and mold parts that are difficult to be processed by traditional methods.
3.3 Heat treatment: improve the hardness and wear resistance of the mold through quenching, tempering and other heat treatment methods. After quenching, the microstructure of the mold material changes and the hardness is significantly increased, while tempering helps to eliminate quenching stress and improve the toughness of the mold.
3.4 Surface treatment: the use of sandblasting, polishing, plating and other surface treatment methods to increase the mold’s wear resistance, corrosion resistance and aesthetics. The surface finish of the mold after surface treatment can reach Ra<0.8μm to meet the requirements of high-precision production.
3.5 Assembly and debugging: After the processing of each component is completed, assembly is carried out to ensure the precision and fit relationship. After the assembly is completed, test the mold and debug the mold to the best working condition.
4.Material Selection
The choice of material for customized plastic mold is crucial, directly related to the service life, precision and cost of the mold. Commonly used materials include:
4.1 high-quality cold working die steel: such as Cr12MoV, with high hardness, wear resistance and impact resistance, suitable for manufacturing high-precision molds.
4.2 hot work die steel: such as H13, with good thermal stability and thermal fatigue resistance, suitable for high temperature environment of the mold manufacturing.
4.3 Alloy tool steel: such as P20, the comprehensive performance is better, suitable for manufacturing medium precision and complex shape of the mold.
In addition, with the development of materials science, some new materials such as cemented carbide, ceramics, etc. are also gradually used in the field of mold manufacturing, further improving the performance and life of the mold.
5. Characteristics
Plastic mold industry has a high degree of customization and professionalism, mold design, manufacturing needs to be adjusted according to the specific product shape, size, precision and other requirements. The characteristics of the mold include high precision, high wear resistance, high corrosion resistance and good thermal stability. These characteristics ensure that the mold can operate stably and efficiently in the production process and produce high quality products.
6. Principle and Properties
The working principle of plastic molds is based on injection molding technology. During injection molding, the mold is clamped on the injection molding machine, and the molten plastic is injected into the molding cavity under high pressure and cooled and shaped in the cavity. After cooling, the upper and lower molds are separated and the product leaves the mold through an ejection system. The attributes of the mold include structural form (e.g., large spout, fine spout, hot runner, etc.), material properties (e.g., hardness, abrasion resistance, corrosion resistance), and machining accuracy, etc. Together, these attributes determine the performance of the mold. Together, these attributes determine the performance and service life of the mold.
Conclusion
Customized plastic mold is a complex and delicate process involving multiple links and expertise. Through scientific design, reasonable material selection, high-precision processing and manufacturing, as well as strict heat treatment and surface treatment processes, high-quality molds can be produced to meet a variety of production needs. With the continuous progress of science and technology and the rapid development of material science, plastic mold industry will usher in a broader space for development.