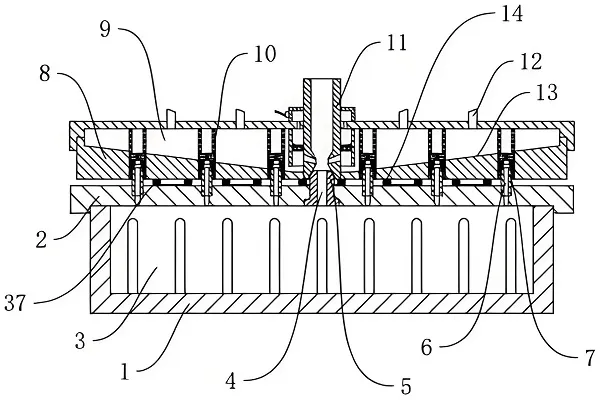
Plastic press molding is a processing method to obtain plastic products of required shape and size by applying pressure to plastic plates or prefabricated parts through presses and special molds at or near room temperature to produce plastic deformation or separation. This molding technology is widely used in many fields such as automobile, home appliance, electronics, packaging, etc. It is one of the key technologies to realize the high-volume and high-efficiency production of plastic parts.

1. Plastic press molding technology principle
The technical principle of plastic press molding is mainly based on the plasticity of plastic materials and the deformation behavior under pressure. Firstly, the plastic sheet or prefabricated part is placed in the mold, and then enough pressure is applied by the press to make the plastic material deform plastically in the cavity of the mold, filling all the corners and details of the mold. When the plastic material is cooled and cured, plastic products with precise shapes and sizes can be obtained.
2. Plastic Press Molding Product Customization
The process of customizing plastic stamping and molding products usually includes the following steps:
Demand analysis: Communicate with customers to clarify the specific requirements of the product such as shape, size, material and quantity.
Mold design: according to the product requirements, design a special stamping mold, to ensure the accuracy and durability of the mold.
Mold Manufacturing: Adopt high-precision processing equipment to manufacture stamping molds that meet the requirements.
Material Preparation: Select suitable plastic materials and carry out necessary pre-treatment, such as drying and cutting.
Stamping and molding: Placing the plastic material in the mold, stamping and molding through the press.
Post-processing: Perform post-processing operations such as deburring, cleaning, inspection, etc. on the molded products.
Delivery and Acceptance: Deliver qualified products to customers and provide necessary after-sales service.
3. Introduction of plastic press molding materials
Commonly used materials and their characteristics:
3.1 ABS plastic
Characteristics: excellent toughness and strength, good impact resistance, high surface gloss.
Data: Density of about 1.05g/cm³, heat distortion temperature of about 93°C, tensile strength of about 40MPa.
3.2 PP plastic
Characteristics: Lightweight, chemical resistance, good heat resistance and electrical insulation.
Data: Density about 0.9g/cm³, heat distortion temperature about 100°C, tensile strength about 30MPa.
3.3PC plastic
Characteristics: High transparency, high strength, superior impact resistance, suitable for making products that require transparency and durability.
Data: Density of about 1.2g/cm³, heat distortion temperature of about 135°C, tensile strength of about 60MPa.
3.4PA Plastic
Characteristics: Wear-resistant, heat-resistant, oil-resistant, with good mechanical strength and hydrolysis resistance.
Data: Density about 1.15g/cm³, heat distortion temperature about 150°C, tensile strength about 65MPa.
4. Characteristics of Plastic Stamping and Molding Products
Product examples and data:
4.1 Automotive interior parts (e.g., instrument panels, door panels, etc.)
Data: Dimensional accuracy up to ± 0.1mm, surface roughness Ra ≤ 0.8μm, impact resistance in line with automotive industry standards.
4.2 Home appliance shell (such as TV sets, washing machine shell, etc.)
Data: good dimensional stability, deformation less than 0.5%, excellent weather resistance, can be used for a long time in -40°C to +80°C environment.
4.3 Electronic components (such as connectors, sockets, etc.)
Data: High precision up to ±0.05mm, stable electrical performance, insulation resistance greater than 10^12Ω, in line with electronics industry standards.
plastic press molding FAQ
Q: What is the difference between plastic stamping and injection molding?
A: Plastic stamping molding is done at room temperature, mainly using plastic deformation of plastic, while injection molding is done at high temperature by injecting molten plastic into a mold and cooling it, which is suitable for thermoplastic plastics.
Q: What factors affect the accuracy of plastic stamping molded products?
A: The precision of the mold, the properties of the material, the parameters of the stamping process (e.g., pressure, speed, temperature), and the post-processing process all affect the precision of the product.
Q: How to improve the productivity of plastic stamping and molding products?
A: Production efficiency can be improved by optimizing the mold design, improving the automation of the stamping presses, and adopting quick mold change systems.