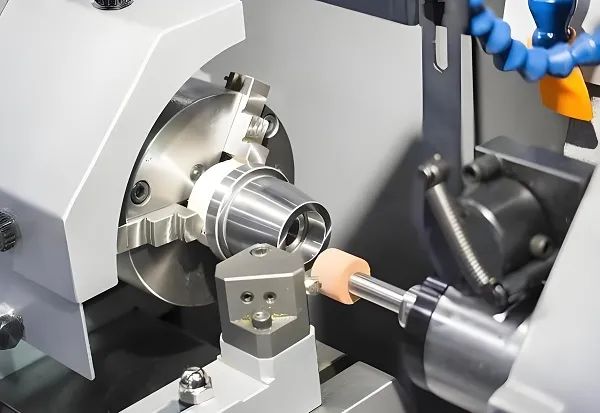
Plastic mold is a special tool used for plastic molding to process plastic materials into products of required shapes and sizes through injection, blow molding, compression molding and other processes. The design, manufacturing accuracy and material selection of the mold directly determine the quality and production efficiency of the final product.
1. What are the components of a plastic mold?
Plastic molds usually consist of several components to achieve complex molding processes. The main components include:
1.1 Mold kernel (core and cavity): directly determines the internal and external shape of the product.
1.2 Mold frame: supports and fixes the mold nut to ensure the overall structural stability of the mold.
1.3 Ejector mechanism: used to eject the molded product from the mold.
1.4 Cooling system: control the temperature of the mold by circulating the cooling medium (e.g. water or oil) to ensure the products are cooled evenly.
1.5 Pouring system: including gates, runners and cold feed wells, etc., used to introduce molten plastic into the mold cavity.
1.6 Guiding mechanism: such as guide pillar and guide sleeve, to ensure the precision and stability of the mold when it is closed.
2. Customization of plastic mold parts
The customization of plastic mold parts is based on the shape, size, material and production requirements of specific products. The customization process usually includes:
Demand analysis: Communicate with customers to clarify the specific requirements of the mold parts.
Design: Three-dimensional design according to the requirements, including the shape, size, material selection and processing technology of the parts.
Manufacturing: Using high-precision machining equipment (such as CNC machine tools, EDM machines, etc.) for manufacturing to ensure the accuracy and surface quality of the components.
Assembly and debugging: assembling the parts into molds and carrying out trial debugging to ensure smooth operation of the molds and product quality up to standard.
3. Material introduction of plastic mold parts
Commonly used materials and their characteristics:
3.1 Mold steel (such as P20, NAK80, S136, etc.):
● High hardness, high wear resistance, good corrosion resistance and thermal stability, suitable for high-precision, long-life mold parts.
● Hardness up to HRC50-60, moderate thermal conductivity, can withstand higher injection pressure and temperature.
3.2 Aluminum alloy:
●Light weight, high strength, good thermal conductivity, suitable for small and medium-sized mold parts, can shorten the molding cycle.
● The density is about 2.7g/cm³ and the thermal conductivity is about 200W/(m-K).
3.3 Non-metallic materials (e.g., resins, ceramics, etc.)
●Low cost, short processing cycle, suitable for specific applications or temporary molds.
●Performance varies depending on the type of material, but generally low cost and suitable for small-lot or quick-response production needs.
4. Role of plastic mold parts
Location and function of parts:
4.1 Die nut: Located in the center of the mold, it directly molds the shape of the product and requires high precision and high wear resistance.
The role of parts: to determine the internal and external surface quality of the product.
Requirements for the production of parts: high-precision machining, surface polishing treatment.
Characteristics of parts: high hardness, high wear resistance, corrosion resistance.
4.2 Ejector mechanism: located at the bottom or side of the mold, used to eject the product from the mold.
Role of the part: to ensure the smooth release of the product from the mold to avoid damage.
Requirements: reasonable structure, reliable action, uniform ejection force.
Characteristics of parts: wear-resistant, high strength.
Plastic Mold Parts FAQ
Q: How does the precision of plastic mold components affect product quality?
A: The precision of mold parts directly affects the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of products. High precision mold parts can ensure the consistency and stability of products and improve product quality.
Q: How to choose the right material for mold parts?
A: When choosing the material for mold parts, we need to consider the shape, size, material, production quantity, production cycle and cost of the product. Generally speaking, mold steel is preferred for high precision and long life mold parts; aluminum alloy is preferred for small and medium-sized mold parts; and non-metallic materials are preferred for specific occasions or temporary molds.
Q: What are the precautions for the maintenance of mold parts?
A: Maintenance of mold parts is essential to prolong the life of the mold and improve the production efficiency. It is necessary to clean the surface of the mold regularly, check the wear and tear of each part, and replace the damaged parts in time; at the same time, it is also necessary to pay attention to the storage environment of the mold to avoid moisture, corrosion and mechanical damage.