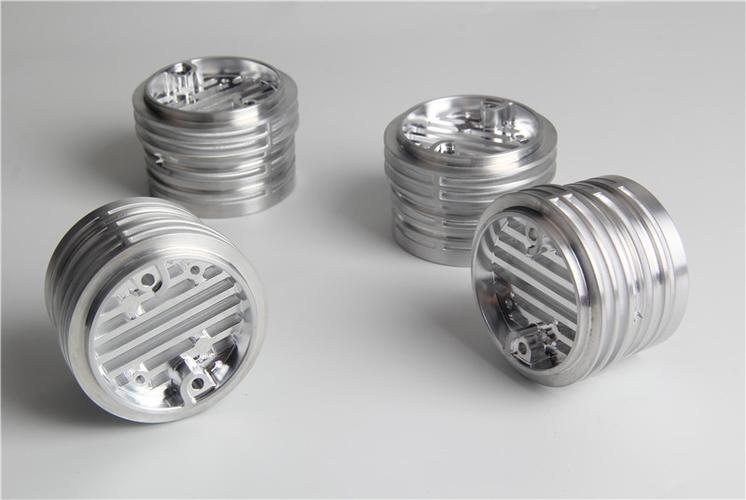
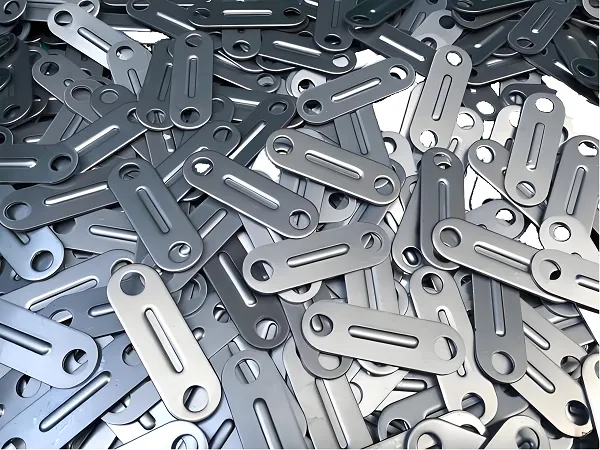
Every precision shaft, valve, or connector that powers our world starts with a machine designed for rotational excellence: the CNC turning center. More than just a tool, it’s the backbone of manufacturing, transforming raw metal, plastic, or composite bars into symmetrical, high-tolerance components with computerized precision. At Goldcattle, with 26 years of mastering these machines, we know that a top-tier CNC turning center isn’t just about cutting metal—it’s about solving engineering challenges, reducing waste, and delivering parts that fit perfectly every time. Let’s explore what a CNC turning center is, how it works, and why Goldcattle’s expertise makes all the difference in leveraging this technology.
What Is a CNC Turning Center?
A CNC turning center is a computer-controlled machine tool designed to shape rotational parts by spinning a workpiece while stationary cutting tools remove material. Unlike manual lathes (which rely on human skill), CNC turning centers use pre-programmed CAD/CAM software to guide tool movements, ensuring consistency across thousands of parts and accuracy down to ±0.001mm . These machines excel at creating cylindrical, conical, or complex shapes—think shafts, bushings, threads, and grooves—making them indispensable for industries where symmetry and precision are non-negotiable.
Modern CNC turning centers come in various configurations to handle diverse needs, from simple 2-axis models for basic parts to advanced 5-axis systems for intricate geometries. At their core, they combine mechanical precision with digital control to turn raw materials into functional components efficiently.
Types of CNC Turning Centers: Matching the Machine to the Job
Not all CNC turning centers are created equal. The right model depends on part size, complexity, and production volume. Goldcattle’s facility houses a range of specialized machines:
1. 2-Axis CNC Turning Centers
The workhorse of basic rotational parts, these machines move tools along two axes: X (radial, toward/away from the workpiece center) and Z (axial, along the workpiece length). Ideal for simple cylindrical parts like spacers, bolts, or basic shafts, they handle diameters up to 300mm with tolerances of ±0.002mm. A 2-axis center might produce 10,000 aluminum bushings for industrial machinery in a single run, maintaining consistent outer diameter (OD) and length across all parts .
2. 4-Axis CNC Turning Centers
Adding a rotational C-axis (spinning the workpiece) and live tooling (rotating tools for milling), these centers eliminate the need for secondary operations. They can machine flats, drill cross-holes, or cut slots while turning—perfect for complex parts like gear shafts or valve bodies. Goldcattle uses 4-axis centers to produce stainless steel hydraulic valve stems with integrated keyways, reducing production time by 35% compared to using separate turning and milling machines .
3. Swiss-Type CNC Turning Centers
The gold standard for small, intricate parts, Swiss-type centers feature a guide bushing that stabilizes long, thin workpieces during machining. This design minimizes vibration, enabling tolerances as tight as ±0.0005mm for parts as small as 0.3mm in diameter—critical for medical needles or microelectronics pins. With spindles reaching 40,000 RPM, they excel at precision micro-machining, producing parts like 1mm-diameter titanium surgical tools with mirror-like surface finishes (Ra 0.02μm) .
4. Multi-Spindle CNC Turning Centers
For high-volume production, these machines feature multiple spindles (typically 6–8) that machine parts simultaneously. They’re ideal for automotive or consumer goods components, producing up to 100 parts per minute. Goldcattle uses multi-spindle centers to manufacture brass electrical connectors, achieving a 50% faster output than single-spindle machines while maintaining ±0.001mm tolerance .
How a CNC Turning Center Works: The Process Breakdown
A CNC turning center transforms raw material into finished parts through a streamlined, computer-guided workflow:
- Design & Programming: Engineers convert CAD models into machine-readable G-code, specifying tool paths, spindle speeds (3,000–40,000 RPM), and feed rates (5–500 mm/min) based on the material and part geometry. For example, machining stainless steel requires slower feed rates (10–50 mm/min) than aluminum (100–300 mm/min) to prevent tool wear .
- Material Setup: Raw bar stock (metal, plastic, or composite) is loaded into a spindle or bar feeder. Swiss-type centers use a guide bushing to support long workpieces, while larger machines use chucks to clamp material securely.
- Cutting Operations: The workpiece spins at high speed as carbide, ceramic, or diamond tools engage:
-
- Facing: Creates a flat end on the workpiece.
-
- Turning: Reduces the OD to the desired diameter.
-
- Grooving: Cuts slots or recesses (e.g., for O-rings).
-
- Threading: Creates external or internal threads (e.g., M3 to M24 for industrial parts).
-
- Drilling/Boring: Adds holes or internal diameters (ID) using live tooling on 4-axis centers.
- Quality Checks: In-process probes measure dimensions during machining, making real-time adjustments to maintain tolerance. Post-machining, parts undergo CMM inspection to verify accuracy—critical for aerospace or medical components.
- Unloading & Finishing: Finished parts are ejected automatically, while optional post-processing (anodizing, passivation, or polishing) enhances durability or aesthetics.
Materials & Applications: What a CNC Turning Center Can Produce
A versatile CNC turning center handles a wide range of materials, making it indispensable across industries:
Materials Mastered
- Metals: Aluminum (6061/7075), stainless steel (304/316), brass (C36000), titanium (Ti-6Al-4V), and alloy steel (4140).
- Plastics: PEEK, nylon, and acetal for low-friction or electrical insulation needs.
- Composites: Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (CFRP) for lightweight, high-strength aerospace parts.
Key Applications
- Aerospace: 4-axis turning centers produce titanium engine shafts with 0.002mm straightness, enduring 1,000°C temperatures in jet engines .
- Medical: Swiss-type centers craft 316L stainless steel catheter hubs with ±0.001mm concentricity, ensuring safe insertion into the human body .
- Automotive: Multi-spindle centers manufacture aluminum drive shafts for EVs, balancing lightweight design (2.7 g/cm³) with structural strength .
- Industrial: 2-axis centers produce hardened steel (58 HRC) hydraulic cylinder rods, resisting wear in heavy machinery .
Why Goldcattle’s CNC Turning Centers Stand Out
At Goldcattle, our CNC turning centers are backed by expertise that turns technology into results:
- Advanced Equipment: We invest in state-of-the-art machines, including 50+ CNC turning centers (2-axis, 4-axis, and Swiss-type) with in-process probing for real-time quality control.
- Material Expertise: Our engineers optimize cutting parameters for each material—e.g., using high-pressure coolant (70 bar) for titanium to prevent heat buildup .
- Quality Certifications: ISO 9001, ISO 13485 (medical), and AS9100D (aerospace) certifications ensure every part meets global standards.
- Efficiency: Our multi-spindle and automated systems reduce lead times by 40%, delivering prototypes in 3–5 days and production runs in 2–6 weeks.
A recent success story: A medical device client needed 10,000 micro-needles (0.5mm diameter) with ±0.0005mm tolerance. Using our Swiss-type turning centers, we delivered 100% defect-free parts in 3 weeks, meeting their critical launch timeline.
FAQs About CNC Turning Centers
Q: What’s the difference between a CNC lathe and a CNC turning center?
A: A CNC lathe is a basic version for simple turning, while a CNC turning center includes advanced features like live tooling, automatic bar feeders, and in-process probing for complex, high-volume production .
Q: What’s the maximum part size a CNC turning center can handle?
A: Our large-format 2-axis centers handle parts up to 1,000mm in length and 300mm in diameter, while Swiss-type centers specialize in parts under 50mm.
Q: How precise is a CNC turning center?
A: Our Swiss-type centers achieve ±0.0005mm tolerance, while 4-axis centers maintain ±0.001mm—critical for aerospace and medical applications .
Q: Can CNC turning centers work with soft materials like plastic?
A: Yes! We use specialized tooling (e.g., PCD diamond tools) to prevent melting or chipping, producing plastic parts with smooth surface finishes.
Q: Why choose Goldcattle for CNC turning center services?
A: With 26 years of experience, advanced machines, and a focus on quality, we turn complex designs into precision parts—on time, every time.
Ready to Harness the Power of CNC Turning Centers?
A CNC turning center is more than a machine—it’s a partner in manufacturing excellence. At Goldcattle, we combine cutting-edge technology with decades of expertise to deliver parts that meet your exact specifications, whether you need 10 prototypes or 100,000 production components.
Got a project in mind? Share your part requirements below, and our turning experts will help you choose the right CNC turning center solution!