- Overview of CNC Wood Processing
- Common CNC Processable Wood Types
- Wood Properties and Processing Considerations
- CNC Woodworking Equipment
- Processing Techniques and Parameters
- Application Areas
- Technical Advantages and Challenges
Overview of CNC Wood Processing
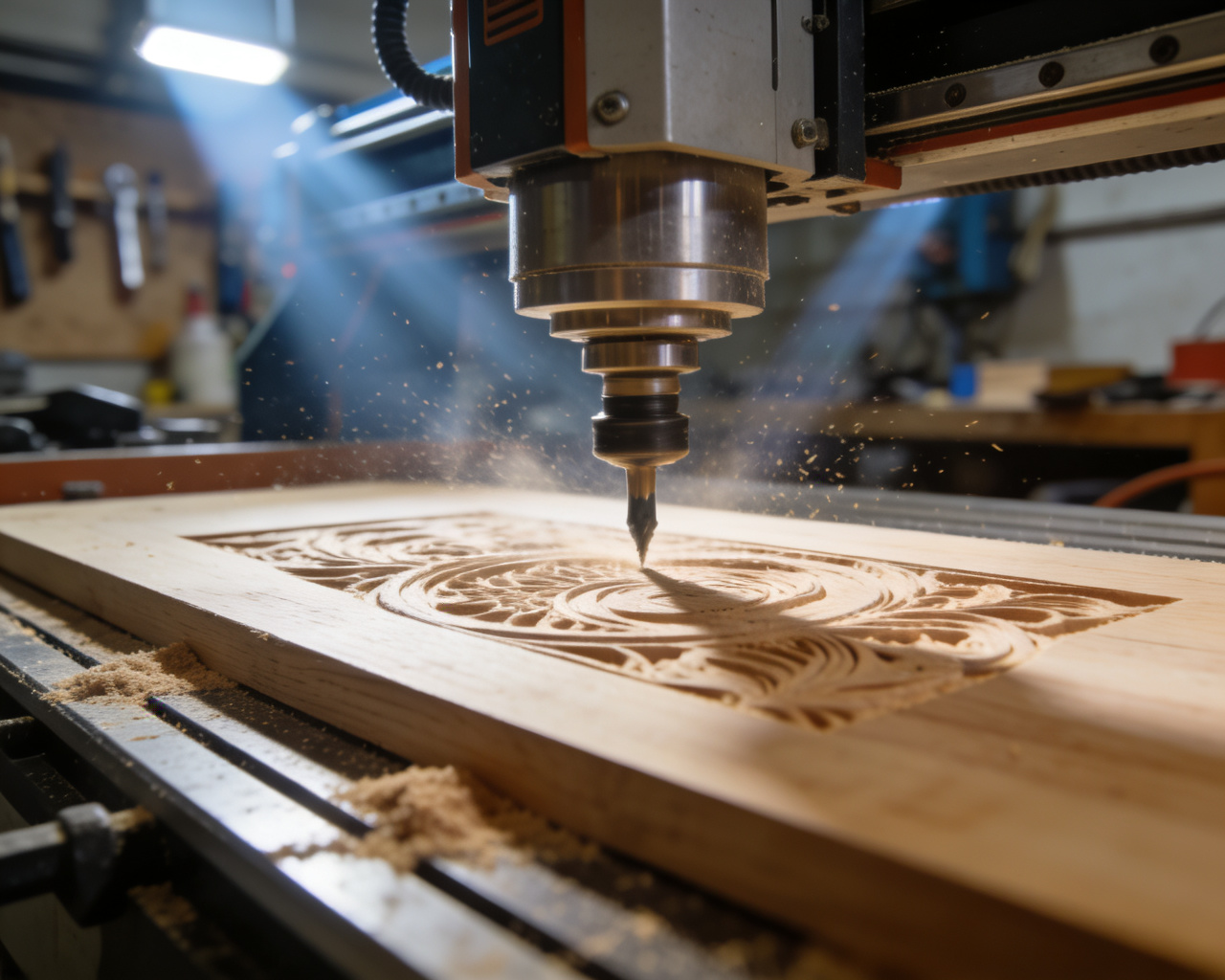

Basic Principles
- Design Modeling: Create 3D models using CAD software
- Path Generation: Generate processing paths through CAM software
- Equipment Setup: Set processing parameters according to wood characteristics
- Automatic Processing: CNC equipment completes processing automatically according to the program
- Quality Inspection: Verify processing precision and quality
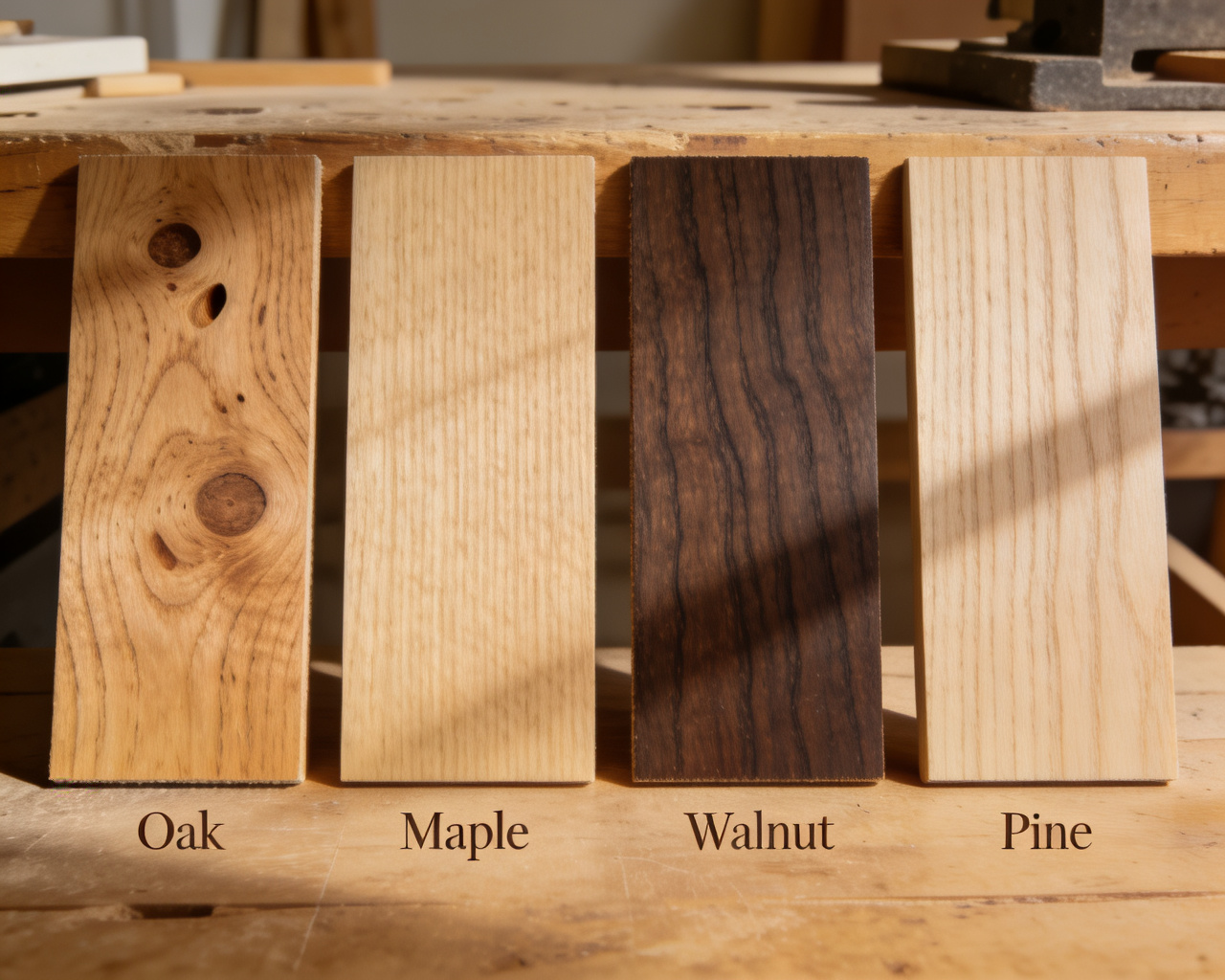
Common CNC Processable Wood Types
Hardwoods
- Oak: Hardness 1360, beautiful grain, strong corrosion resistance
- Maple: Hardness 1450, hard texture, fine grain
- Walnut: Hardness 1010, elegant color, good processing performance
- Cherry: Hardness 950, beautiful color, suitable for fine carving
- Birch: Hardness 760, uniform texture, good stability
Softwoods
- Pine: Hardness 380-560, clear grain, good processing performance
- Cedar: Hardness 900, natural preservative, aromatic scent
- Fir: Hardness 600, light and soft texture, suitable for large-scale processing
- Spruce: Uniform texture, suitable for making musical instruments
Engineered Woods
- Plywood: Multi-layer veneer bonding, good stability
- Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF): Uniform density, suitable for fine carving
- Particleboard: Low cost, suitable for basic structures
- Oriented Strand Board (OSB): High strength, suitable for construction applications
Wood Properties and Processing Considerations
Key Property Parameters

|
Wood Type
|
Janka Hardness
|
Density (g/cm³)
|
Processing Difficulty
|
Main Applications
|
|
Oak
|
1360
|
0.75
|
Medium
|
Furniture, Flooring
|
|
Maple
|
1450
|
0.70
|
High
|
High-end Furniture, Musical Instruments
|
|
Walnut
|
1010
|
0.64
|
Medium
|
Decoration, Crafts
|
|
Pine
|
380-560
|
0.45
|
Low
|
Construction, Furniture
|
|
MDF
|
–
|
0.70
|
Low
|
Carving, Decoration
|
Processing Considerations
- High-density woods require greater cutting force
- Low-density woods can be processed at faster speeds
- Tool selection needs to be adjusted according to wood hardness
- Ideal processing moisture content: 8-12%
- Excessively high moisture content reduces processing precision
- Excessively low moisture content It is prone to cracking.
- Processing along the grain is smoother
- Cross-grain processing requires reduced feed rate
- Special attention to tool wear in knot areas
CNC Woodworking Equipment
Equipment Types
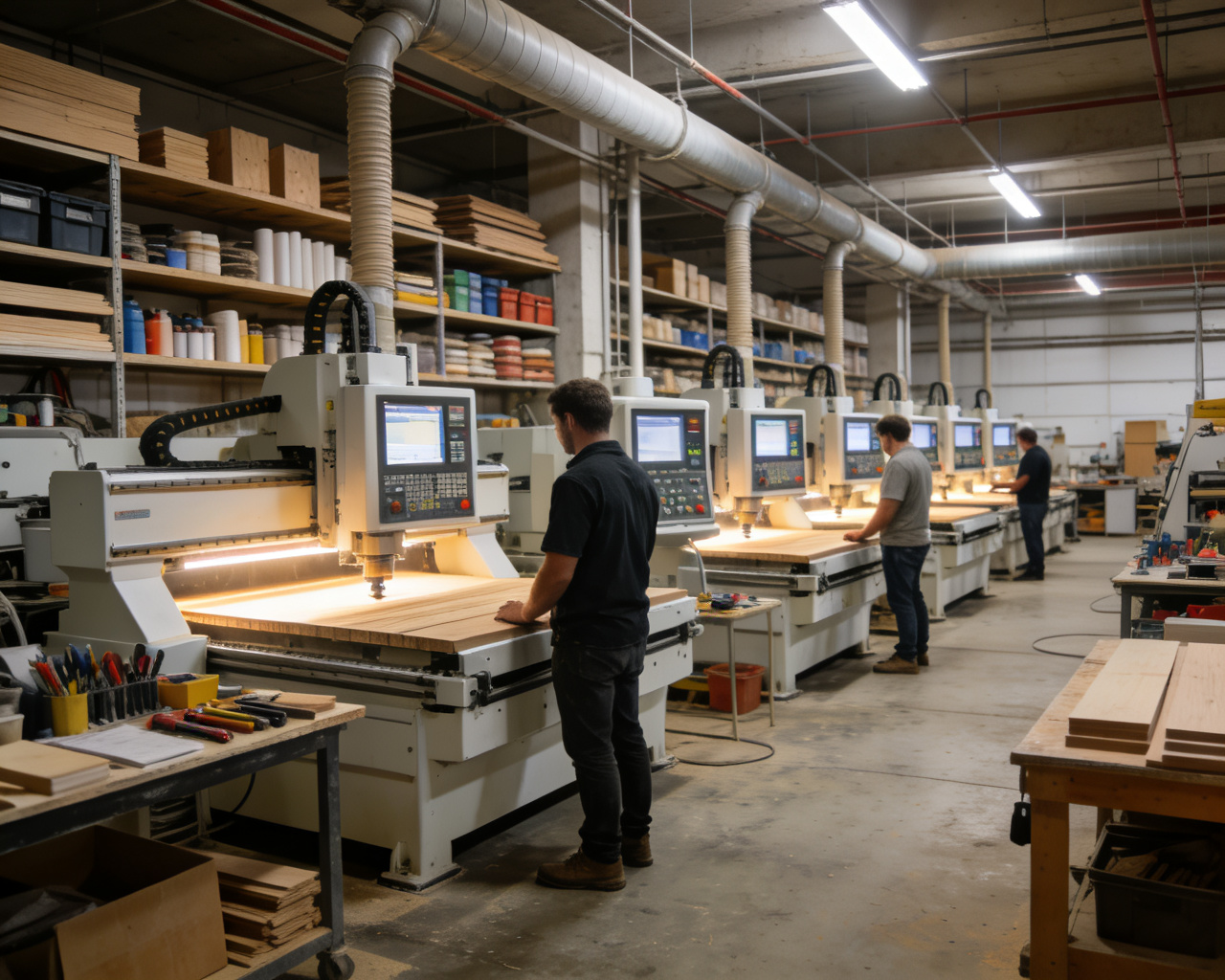

- Suitable for flat engraving and 3D modeling
- Equipped with automatic tool change system
- Working area ranges from desktop to industrial grade
- Multi-axis linkage, complex curved surface processing
- Automatic loading/unloading system
- High-precision positioning system
- Non-contact processing, extremely high precision
- Suitable for fine patterns and text engraving
- Small heat-affected zone
Tool Selection
- Low cost, suitable for softwood processing
- General wear resistance, frequent replacement needed
- High hardness, good wear resistance
- Suitable for hardwoods and engineered woods
- Long service life
- Extremely high hardness, suitable for special materials
- Higher cost, used for high-precision processing
Processing Techniques and Parameters
Processing Parameter Settings
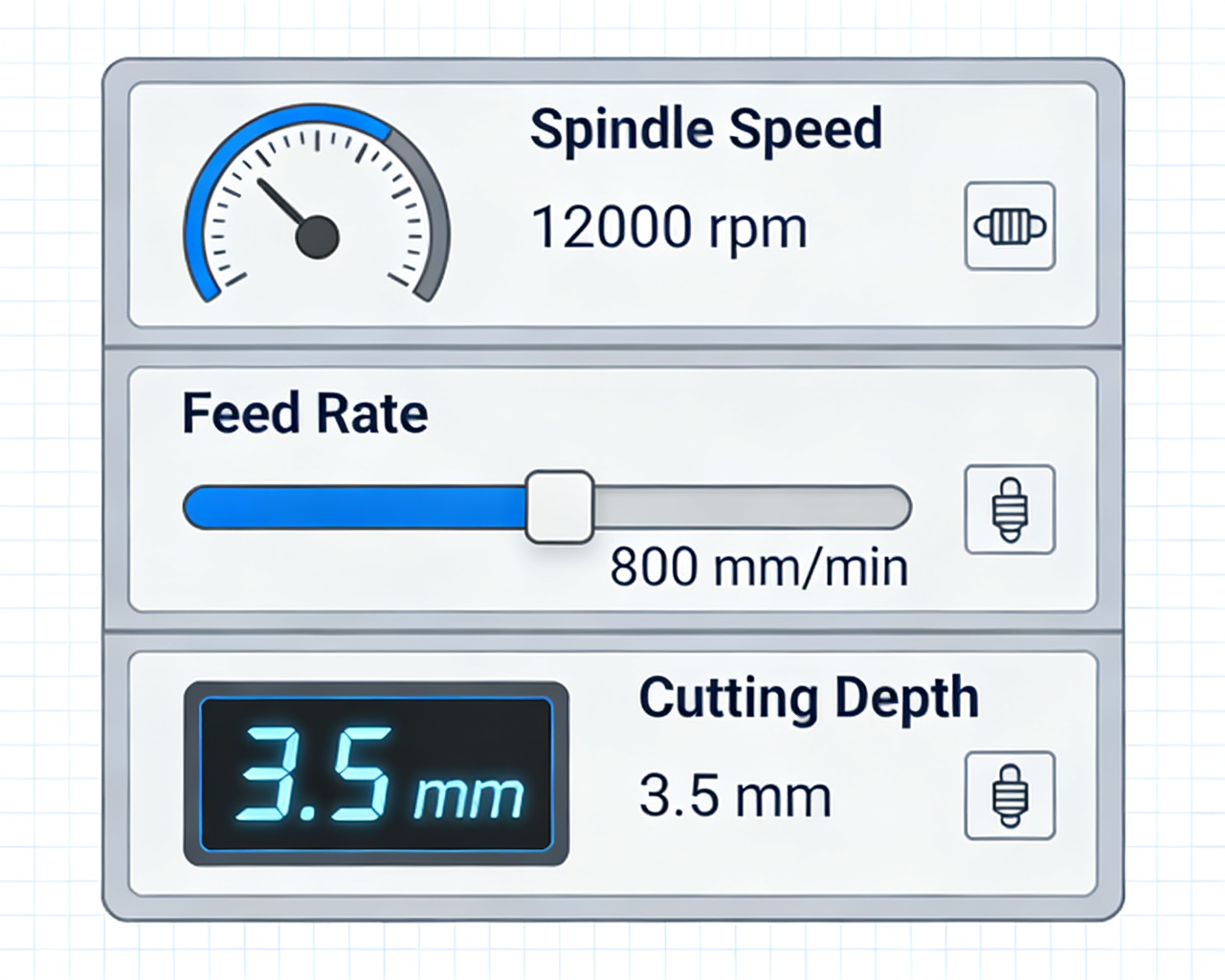
- Softwoods: 10-15 m/min
- Hardwoods: 5-10 m/min
- Engineered woods: 8-12 m/min
- Along grain: 8-12 m/min
- Cross grain: 4-6 m/min
- Engraving processing: 2-5 m/min
- Softwoods: 10,000-15,000 rpm
- Hardwoods: 8,000-12,000 rpm
- Fine processing: 15,000-24,000 rpm
Process Optimization
- Reduce empty travel time
- Optimize tool path sequence
- Adopt layered processing strategy
- Compressed air cooling
- Cutting fluid cooling (suitable for hardwoods)
- Dust removal system to prevent wood chip accumulation
Application Areas
Furniture Manufacturing
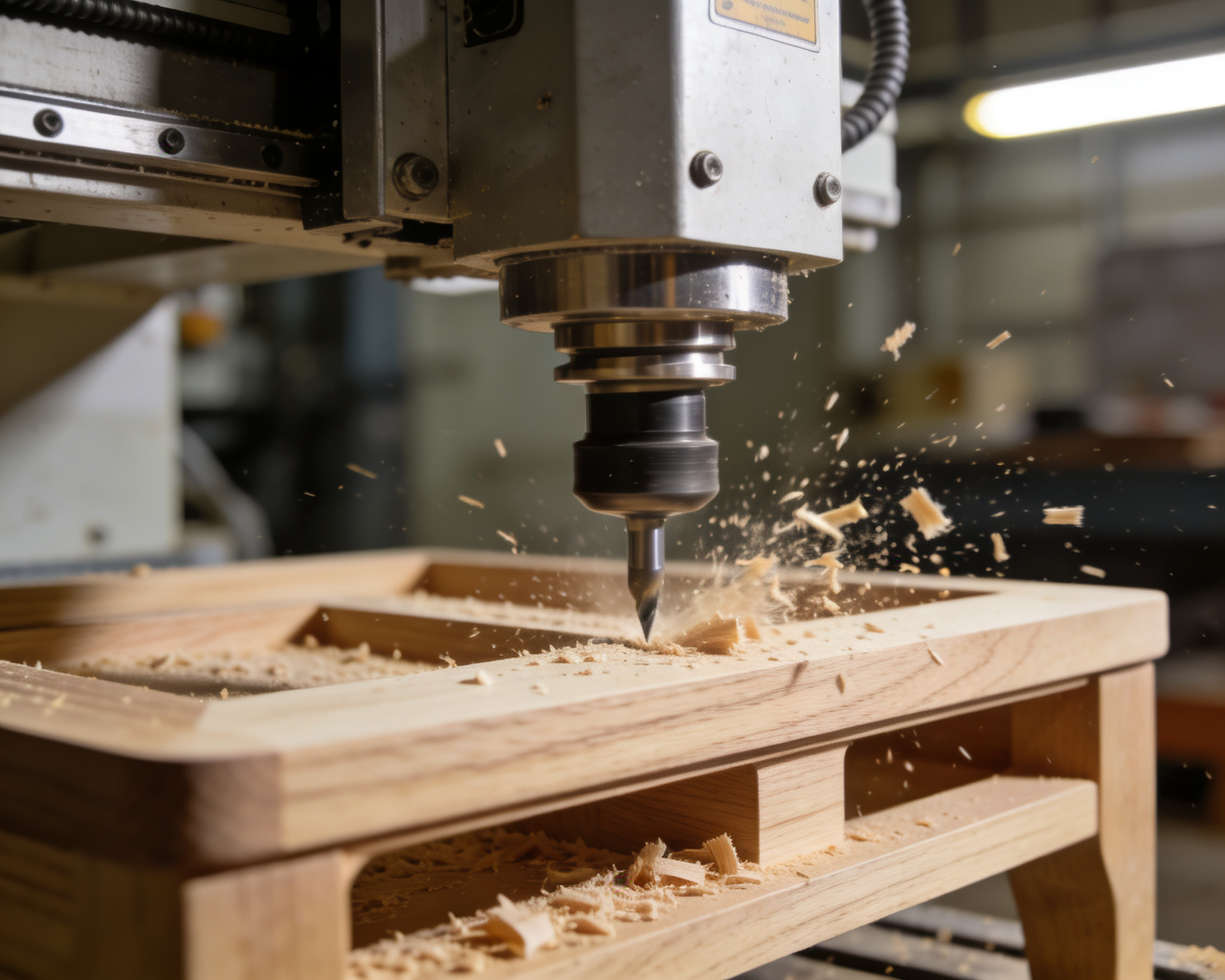


- Personalized design implementation
- Complex shape processing
- Batch production consistency
- Precise dimension control
- Complex joining structures
- Surface decoration engraving
Architectural Decoration
- Wall decorative panels
- Ceiling modeling
- Decorative moldings
- Wooden sculptures
- Landscape features
- Outdoor furniture
Craft Production
- Fine carving techniques
- Complex pattern implementation
- Personalized customization
- High-precision soundboard processing
- Complex curved surface modeling
- Sound quality optimization design
Technical Advantages and Challenges
Main Advantages
- Sub-millimeter precision control
- Accurate implementation of complex shapes
- Good consistency in batch production
- Automated processing flow
- 24-hour continuous production
- Significant reduction in labor costs
- Easy implementation of complex shapes
- Strong personalized customization capability
- Rapid prototype development
Challenges
- High-end CNC equipment is expensive
- Relatively high maintenance costs
- Technical personnel training requirements
- Natural wood properties are unstable
- Moisture content changes affect precision
- Complex knot and defect handling
- Wood chip dust treatment
- Noise control
- Adhesive environmental requirements
Development Trends
Intelligent Upgrading
- Automatic identification of wood properties
- Intelligent parameter optimization
- Predictive maintenance
- Remote monitoring and management
- Data collection and analysis
- Equipment networking collaboration
Green Manufacturing
- Recycled wood utilization
- Environmentally friendly adhesives
- Low-carbon processing techniques
- High-efficiency dust removal systems
- Noise control technology
- Waste recycling and utilization