Metal 3D Printing Types: Understanding the Core Technologies
Metal 3D printing has evolved into a diverse ecosystem of technologies, each tailored to specific industrial needs—from intricate medical implants

Metal 3D printing has evolved into a diverse ecosystem of technologies, each tailored to specific industrial needs—from intricate medical implants
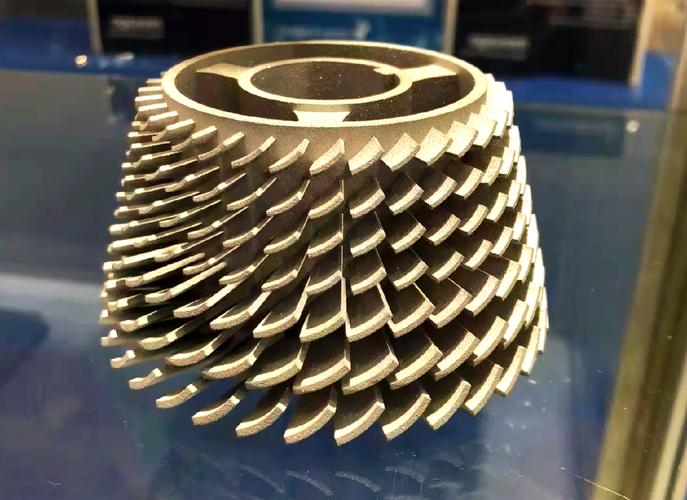

Yes, 3D printers can print metal—but only with specialized metal 3D printers (not consumer-grade FDM/PLA printers). These printers use advanced
Turning a picture into a 3D model is achievable with 3 main methods—the right choice depends on your: Picture type
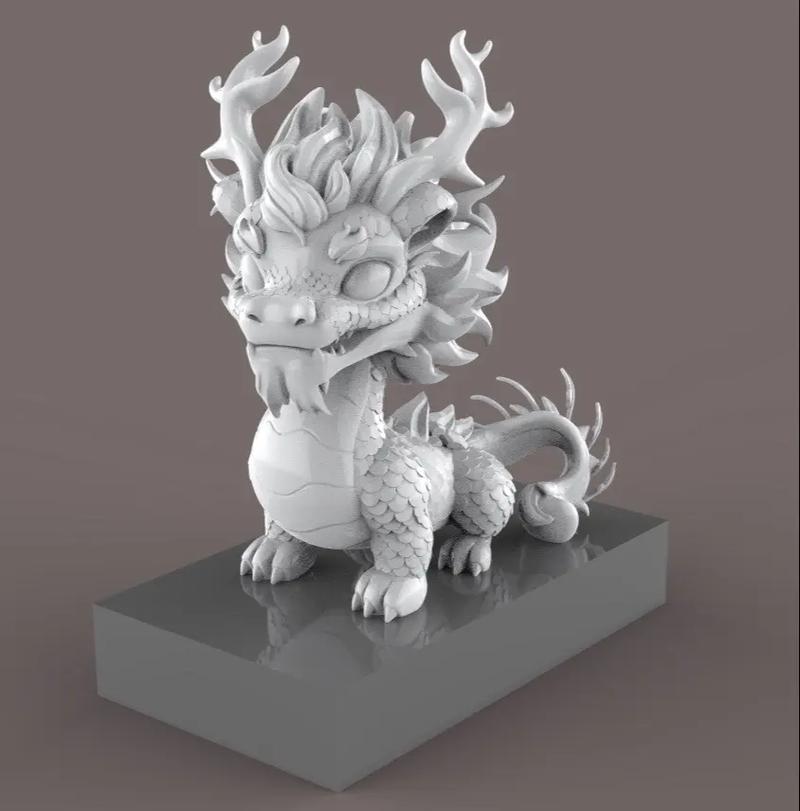

A 3D model is a digital representation of a physical object, space, or concept constructed in three-dimensional virtual space. Unlike
3D printing (additive manufacturing) is a layer-by-layer fabrication process that transforms digital 3D models into physical objects—unlike subtractive methods (e.g.,
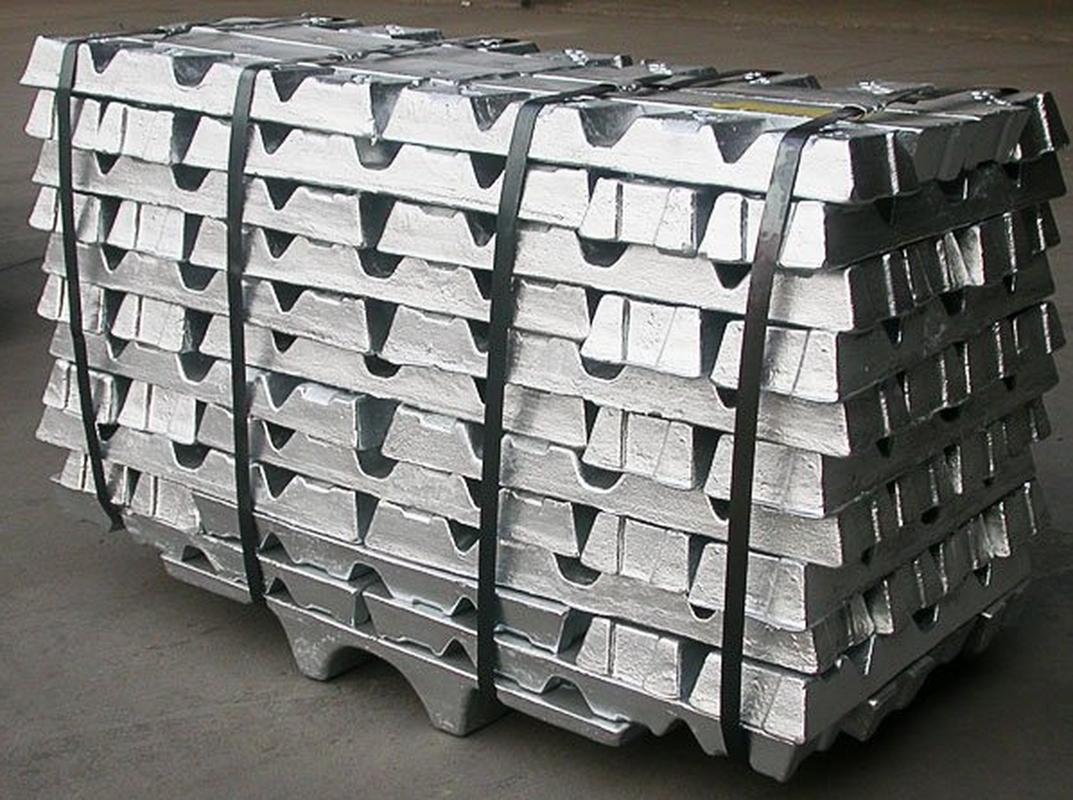

There is no single “best” metal for die casting—only the most suitable metal for your specific application. The choice depends

Pouring resin into a mold is a precision-driven process for creating high-detail parts—from decorative crafts (e.g., epoxy resin coasters) to
Making a die casting mold (often called a “die”) is a high-precision, multi-stage process that requires tight control over material
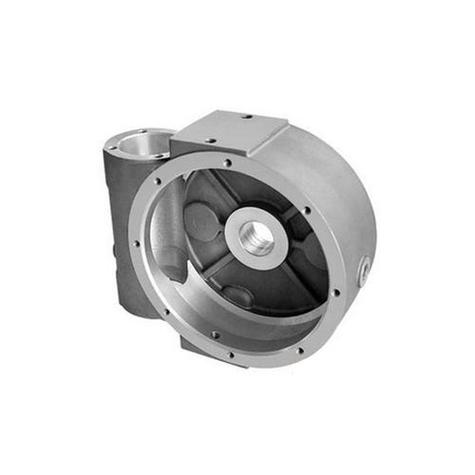

In die casting, the “mold” is officially called a die—a precision-engineered, reusable metal tool that shapes molten metal into the desired
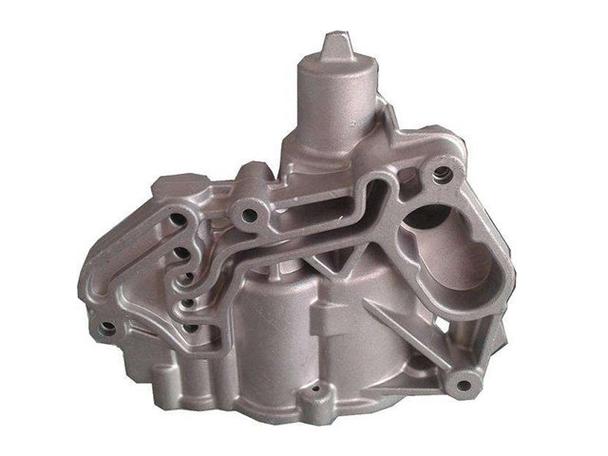

Yes—die casting can be sufficiently strong for most industrial, automotive, and consumer applications—but its strength depends on three critical factors:
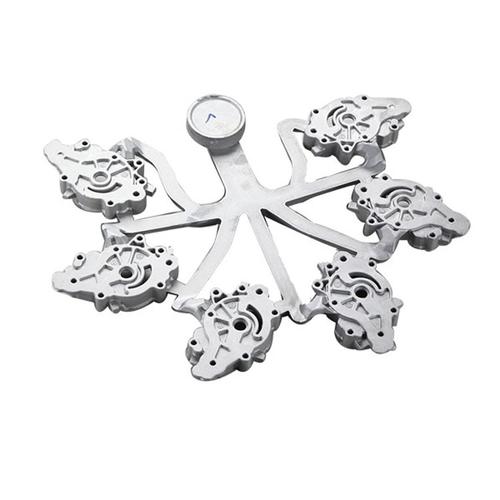

Most die cast models (e.g., 1:18 car models, aircraft replicas, toy figurines) are made of zinc-based alloys—specifically Zamak alloys (the
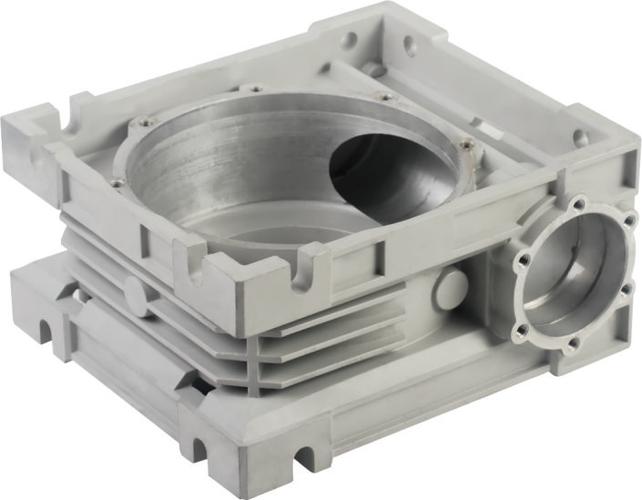
Yes—die casting is a type of permanent mold casting—but the reverse is not true. Permanent mold casting is an umbrella