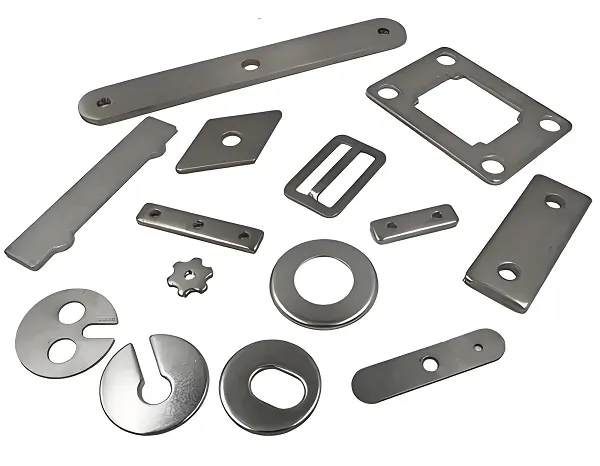
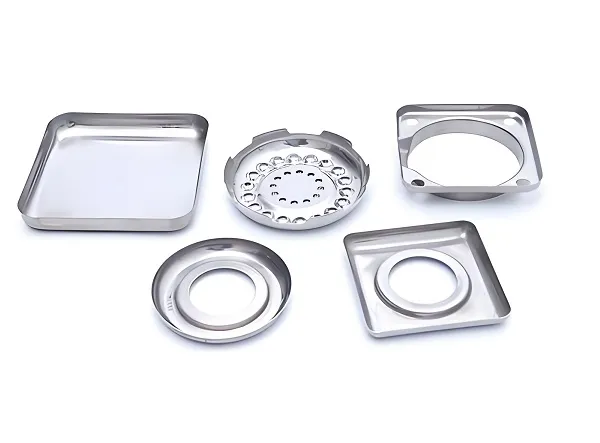
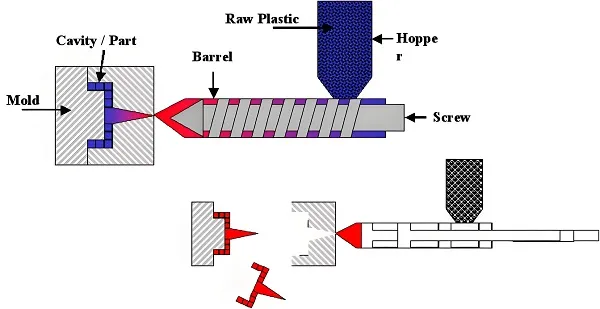
Plastic compression molding, also known as compression molding or compression molding, is a process in which solid plastics in powdered or loose granular form are added directly into a mold, softened and melted by heating and pressure, and molded according to the shape of the mold cavity. The technology is widely used in thermosetting plastics and some thermoplastic plastic molding, especially in the need for high dimensional accuracy and good surface quality of the parts production occupies an important position.
1.Plastic compression molding technology principle
The principle of plastic compression molding technology is mainly based on the thermoplastic and thermosetting properties of plastics. In the molding process, the plastic material is placed in a preheated mold, and under the dual action of heating and pressure, the plastic gradually softens to a viscous flow state and fills the mold cavity. For thermosetting plastics, this process is accompanied by a cross-linking reaction, which gradually hardens the plastic and sets the shape, while thermoplastics need to be cooled and cured after filling the cavity.
1.1 Brief description of the technical process:
Charging: Place the powdered or granular plastic raw materials in the charging chamber of the mold.
Closing and heating: the mold is closed and the plastic is softened and melted by heating.
Pressurized molding: under pressure, the molten plastic fills the mold cavity.
Curing/Cooling: Thermosets are cured by cross-linking and thermoplastics are cured by cooling.
Demolding: After molding, the plastic part is removed from the mold.
2. Plastic compression molding product customization
Plastic compression molding products are customized with a high degree of flexibility, allowing molds to be designed according to customer needs so that plastic products of various shapes, sizes and functions can be produced. The customization process usually includes:
Demand analysis: Define the requirements of product usage, size, material and performance.
Mold design: Design the mold according to the requirements to ensure the precision and efficiency of molding plastic parts.
Mold Manufacturing: Using high-precision processing equipment to manufacture molds.
Trial mold debugging: carry out trial mold, adjust process parameters to ensure product quality.
Mass production: After confirming that there is no error, carry out mass production.
3. Introduction of plastic compression molding materials
Materials: thermosetting plastics and thermoplastics can be used for compression molding, but thermosetting plastics are more common.
3.1 Thermosetting plastics:
Cross-linking reaction: cross-linking reaction occurs under heat and pressure, and cannot be re-melted after curing.
Heat resistance: high heat resistance and chemical resistance.
Mechanical properties: good strength, stiffness and wear resistance.
Typical materials: phenolic resin, epoxy resin, unsaturated polyester, etc.
3.2 Thermoplastic:
Repeatable melting: soften after heating, solidify after cooling, can be processed repeatedly.
Fluidity: good fluidity in the molten state, easy to fill the mold cavity.
Typical materials: polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride and so on.
4. Characteristics of plastic compression molding products
Products: Compression molded plastic products are widely used in electronics, automotive, home appliances, medical and other fields.
Dimensional accuracy: ±0.1mm or higher to meet the needs of precision parts.
Surface quality: good surface finish, no flow marks, shrinkage holes and other defects.
Physical properties: uniform density, stable mechanical properties, such as tensile strength up to XX MPa, impact strength up to XX kJ/m².
Production efficiency: compared with injection molding, compression molding production cycle is longer, but can produce large or complex structural components.
Environmental protection: part of the material can be recycled, in line with environmental requirements.
Plastic Compression Molding FAQ
Q1:What is the difference between compression molding and injection molding?
A1: The main difference lies in the molding principle and material adaptability. Compression molding is to add solid plastic directly into the mold, through heating and pressure molding; while injection molding is to inject molten plastic into the mold through the injection machine. Compression molding is more suitable for thermosetting plastics and less fluid thermoplastics.
Q2: What types of plastic products can be produced by compression molding?
A2: Compression molding can produce plastic products of various shapes and sizes, including but not limited to electronic equipment housings, automotive parts, home appliance accessories, medical devices, etc.
Q3: How to improve the dimensional accuracy of compression molded products?
A3: Methods to improve the dimensional accuracy of compression molded products include optimizing mold design, accurately controlling molding process parameters (e.g., temperature, pressure, and time), and adopting high-precision processing equipment to manufacture molds. Meanwhile, reasonable mold maintenance and repair is also the key to ensure product precision.