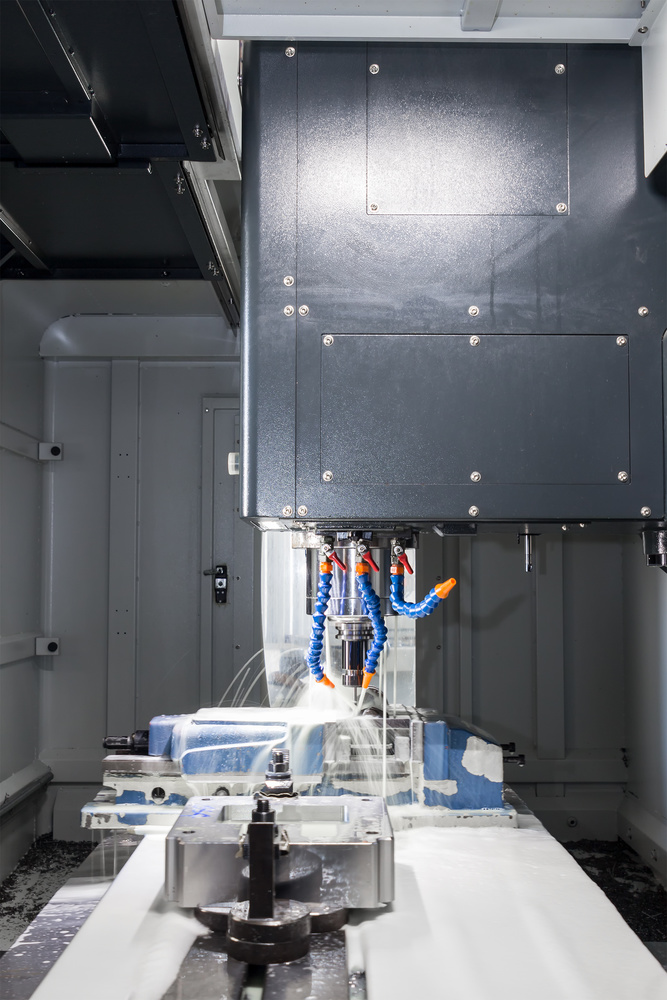
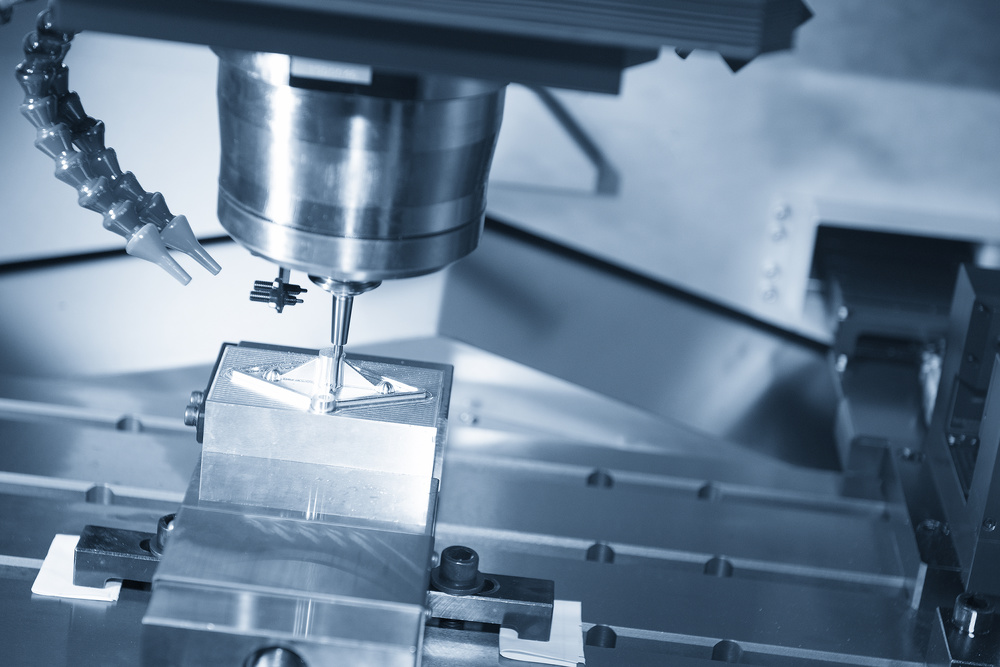
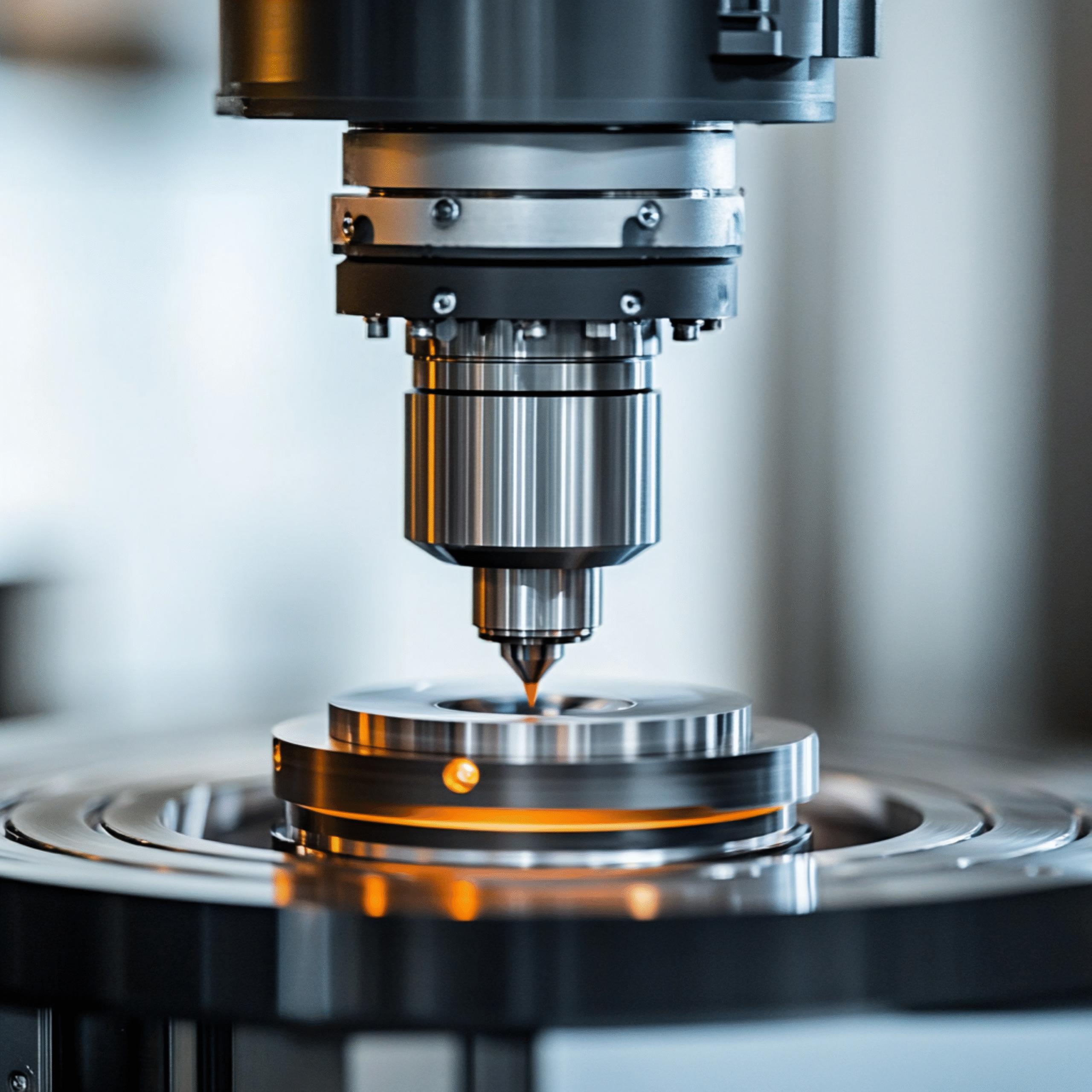
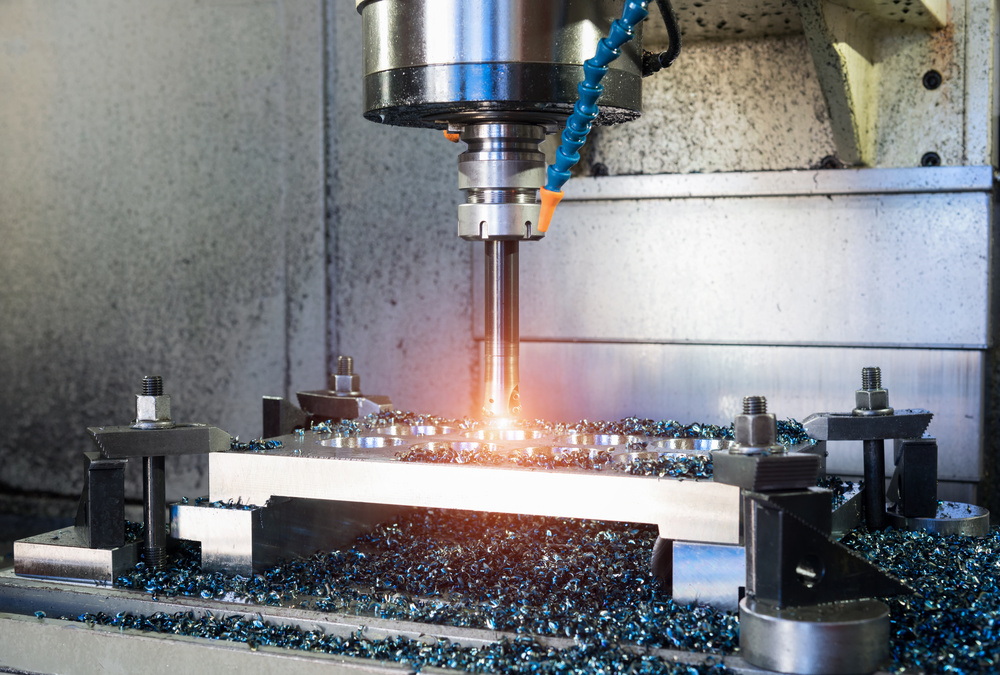
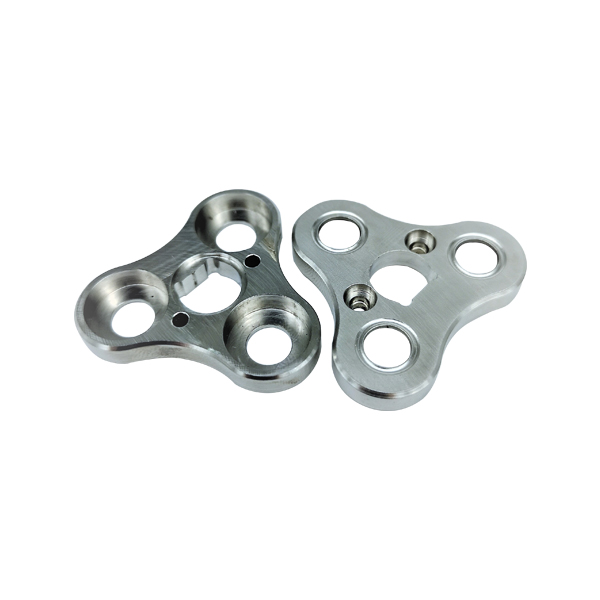
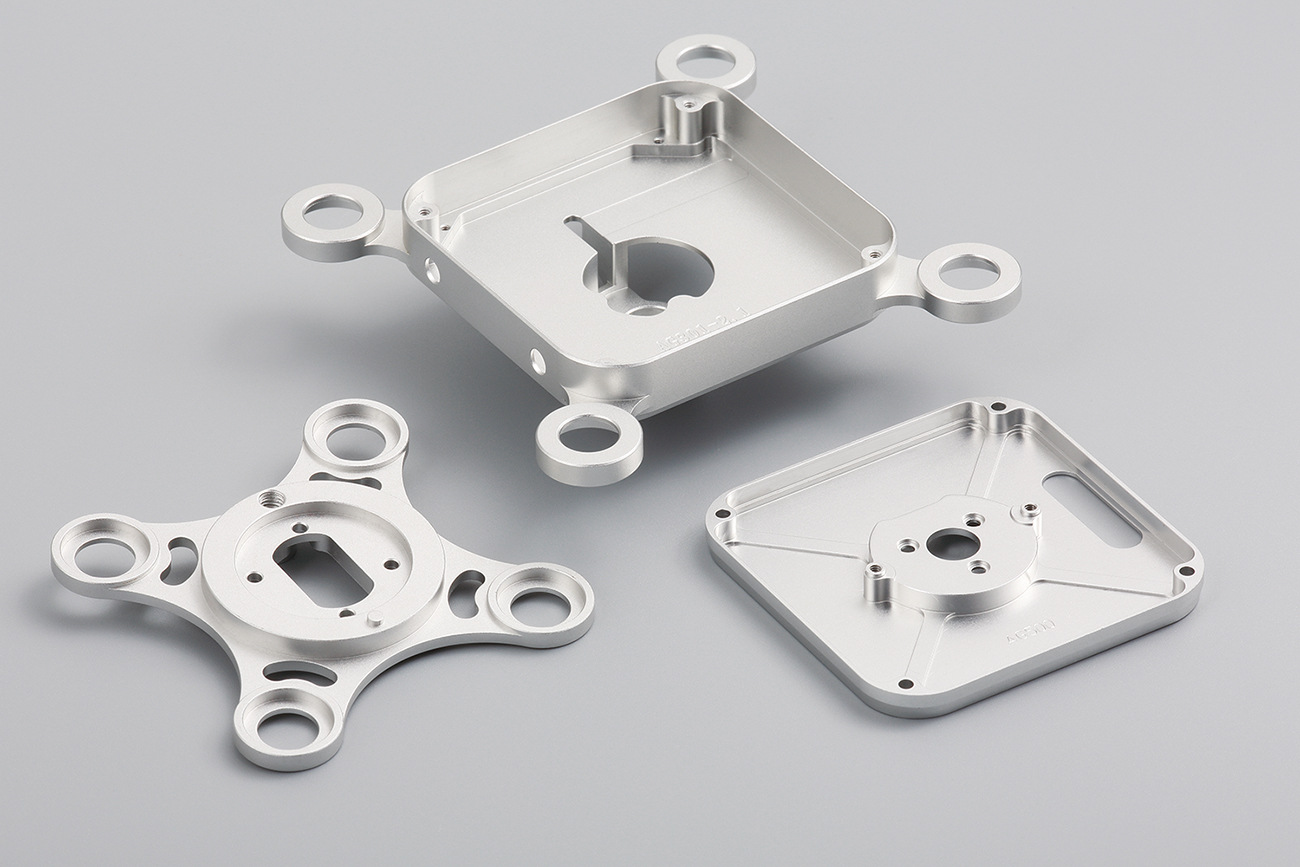
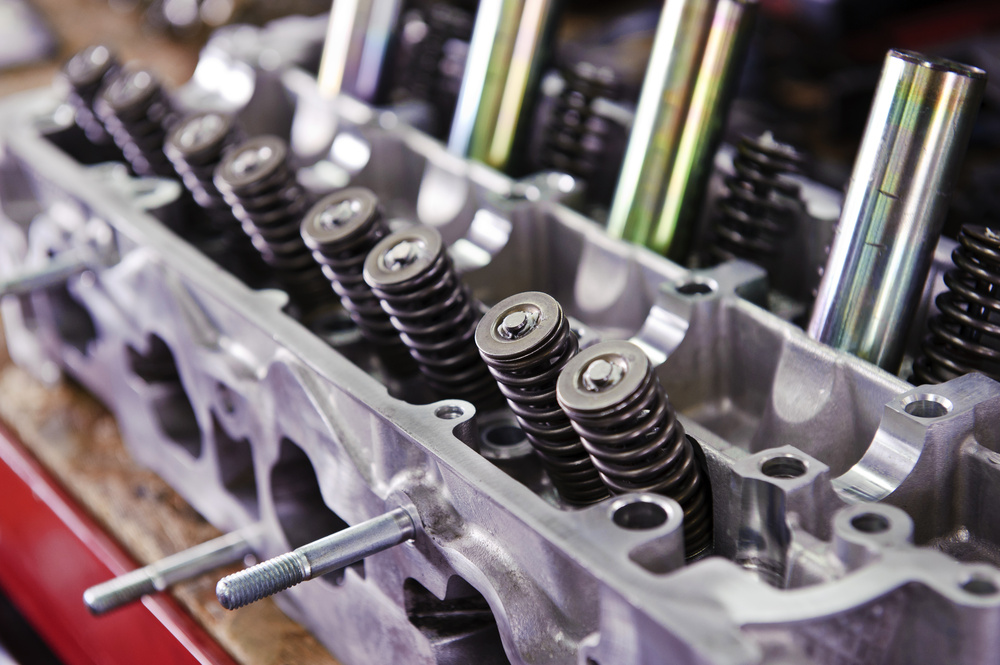
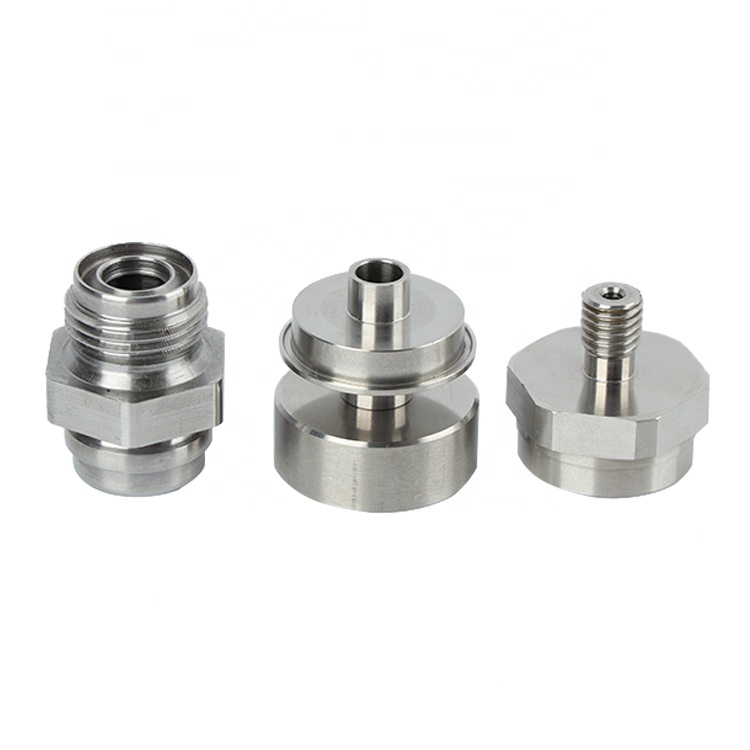
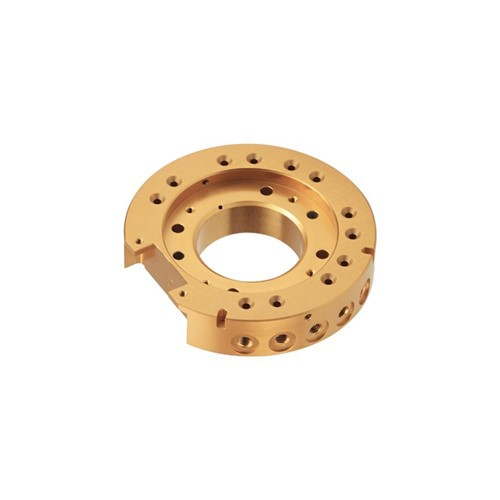
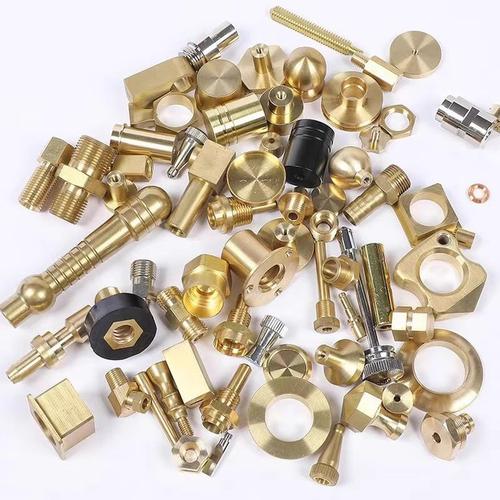
Machined parts are precision components created by carefully removing material from solid workpieces.
These parts are produced using various subtractive manufacturing processes to achieve exact specifications.
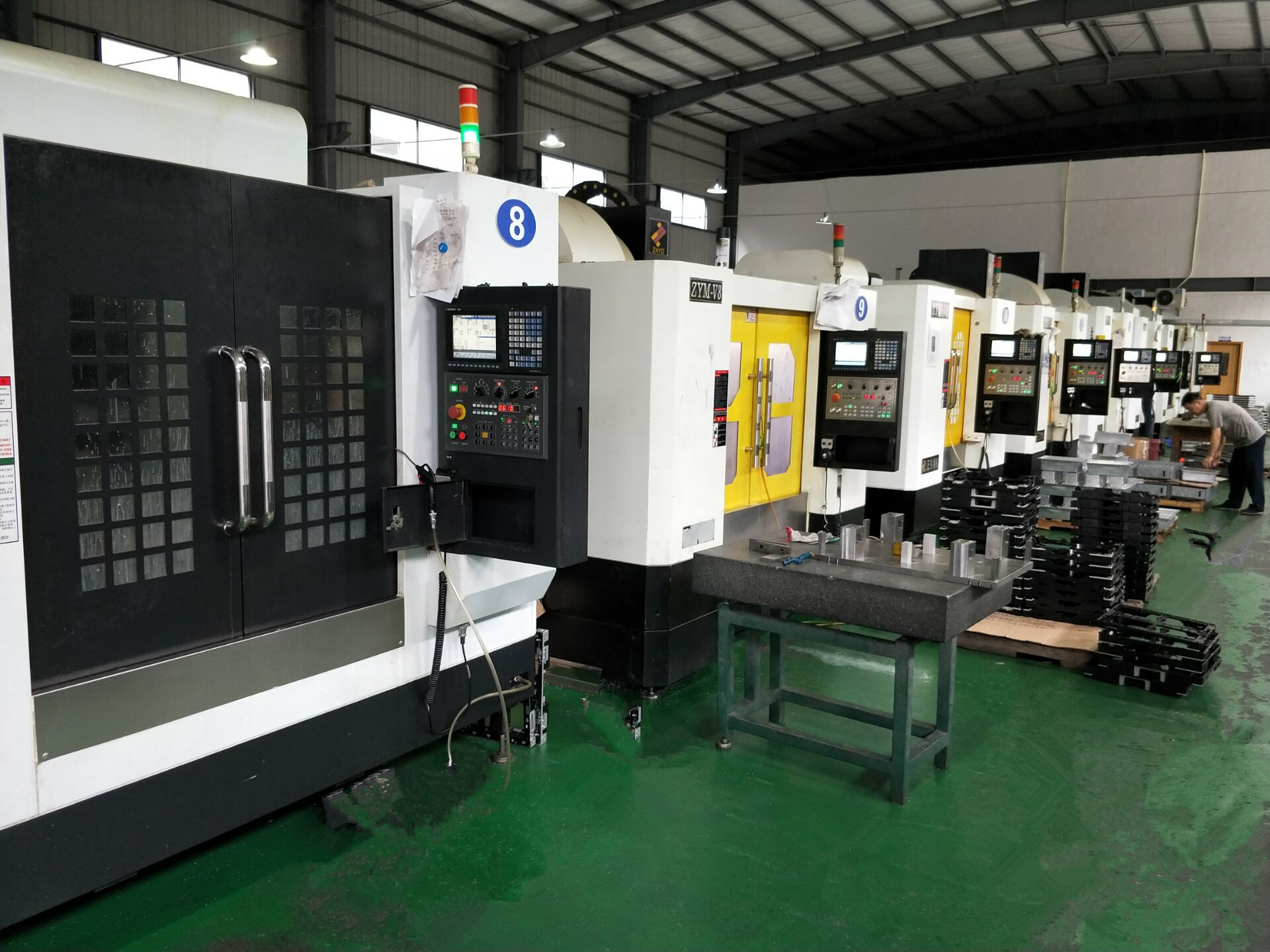
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining has become the industry standard for producing these components.
Understanding the Machining Process
The machining process begins with selecting appropriate raw materials based on part requirements.
Solid blocks or billets of metal, plastic, or composite materials serve as starting workpieces.
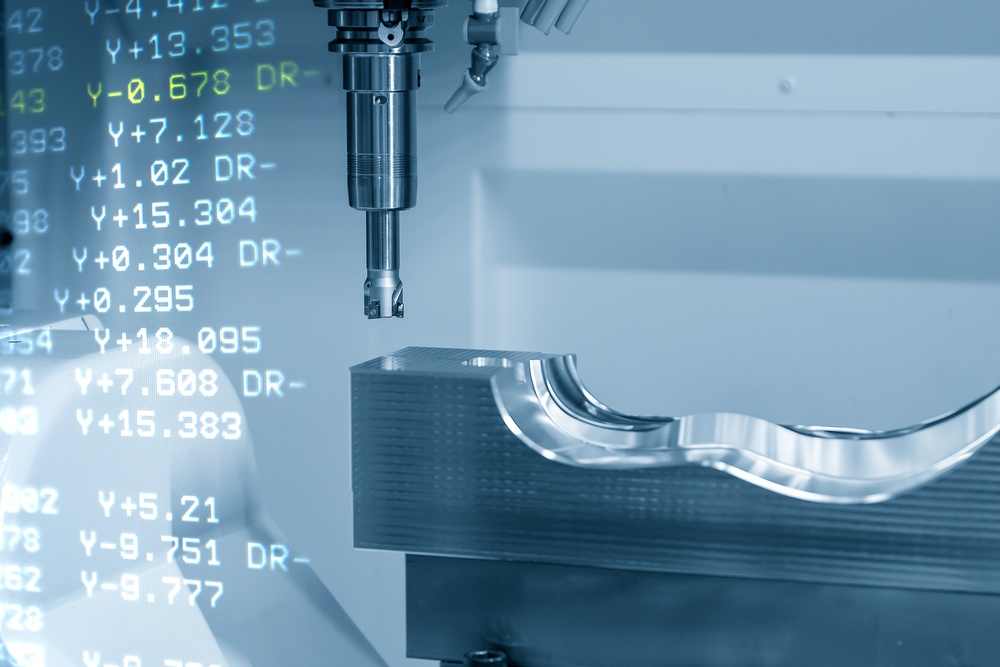
Precision cutting tools remove excess material to shape the workpiece into final form.
CNC machines use computer programs to control tool movements with extreme accuracy and repeatability.
Modern machining centers can perform multiple operations in a single setup for efficiency.
Key Machining Processes Explained
CNC Milling
CNC milling uses rotating cutting tools to remove material from stationary workpieces.
This process creates complex shapes, slots, holes, and surfaces with high precision.
Vertical and horizontal milling machines handle different types of part geometries.
CNC Turning
CNC turning rotates the workpiece while cutting tools shape its exterior surfaces.
This process excels at creating cylindrical parts like shafts, bushings, and fasteners.
Lathes and turning centers produce parts with precise diameters and lengths.
Drilling and Tapping
Drilling creates holes of various sizes and depths in machined components.
Tapping follows drilling to create internal threads for fasteners and connections.
These processes require specialized tools and precise speed control for optimal results.
Grinding and Finishing
Grinding uses abrasive wheels to achieve ultra-precise dimensions and smooth surfaces.
This final process ensures parts meet strict tolerance requirements and surface finish standards.
Different grinding techniques handle flat surfaces, cylindrical shapes, and complex contours.
Comprehensive Classification of Machined Parts
Rotational Parts
Shafts and axles transmit rotational power between machine components in various systems.
These cylindrical parts require precise concentricity to prevent vibration during operation.
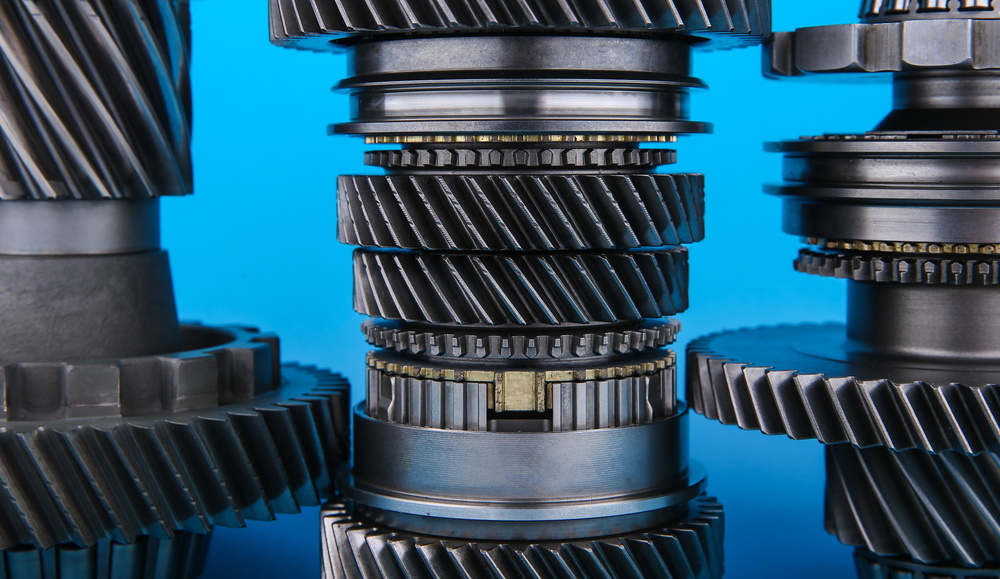
Gears and sprockets feature carefully machined teeth that mesh together to transfer motion.
Bearings reduce friction between moving parts while maintaining alignment and support.
Structural Components
Housings and enclosures provide protection and support for internal mechanical parts.
These complex parts often require multiple machining operations to create intricate features.
Brackets and supports secure components in place while maintaining proper positioning.
Flanges connect pipes, tubes, and other components with leak-proof joints.
Functional Parts
Valves control the flow of liquids, gases, and other materials in industrial systems.
Pumps move fluids through systems using precisely machined impellers and housings.
Fasteners including bolts, nuts, and screws join components securely in assemblies.
Custom components are designed for specific applications requiring unique shapes or functions.
Gear and Shaft Components
Gears are critical machine elements that transmit torque and motion between rotating shafts.
Precision gear machining ensures accurate tooth profiles for smooth and efficient operation.
Different gear types include spur gears, helical gears, bevel gears, and worm gears.
Shafts work in conjunction with gears to transfer power throughout mechanical systems.
Proper alignment between gears and shafts is essential for system efficiency and longevity.
Detailed Material Selection Guide
Metallic Materials
Aluminum alloys offer excellent strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance properties.
These lightweight materials are ideal for aerospace, automotive, and consumer products.
Carbon steel provides high strength and durability for structural and mechanical applications.
Different steel grades offer varying levels of hardness, toughness, and wear resistance.
Stainless steel combines strength with excellent corrosion resistance for harsh environments.
Titanium alloys deliver exceptional performance in high-temperature and medical applications.
Polymeric Materials
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) offers good impact resistance and machinability.
This versatile plastic is commonly used in consumer electronics and automotive components.
Nylon (Polyamide) provides excellent wear resistance and self-lubricating properties.
Delrin (Acetal) offers superior dimensional stability and low friction characteristics.
Polycarbonate combines transparency with high impact strength for visible components.
PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) delivers exceptional performance in extreme temperature environments.
Composite Materials
Carbon fiber composites offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratios for high-performance applications.
These advanced materials are used extensively in aerospace and racing industries.
Fiberglass composites provide good strength and corrosion resistance at lower costs.
Precision and Quality Control Standards
Modern machining processes achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.002 mm for critical components.
This level of precision ensures parts fit together perfectly in complex assemblies.
Surface finish requirements are measured in micrometers using Ra (Roughness Average) values.
High-quality surfaces reduce friction, improve aesthetics, and enhance performance.
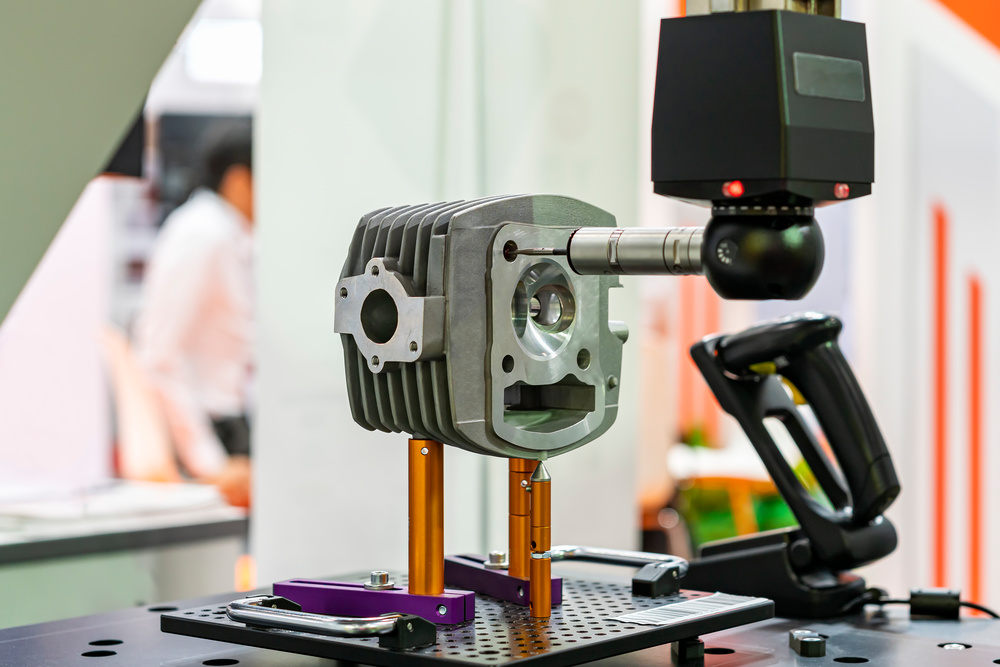
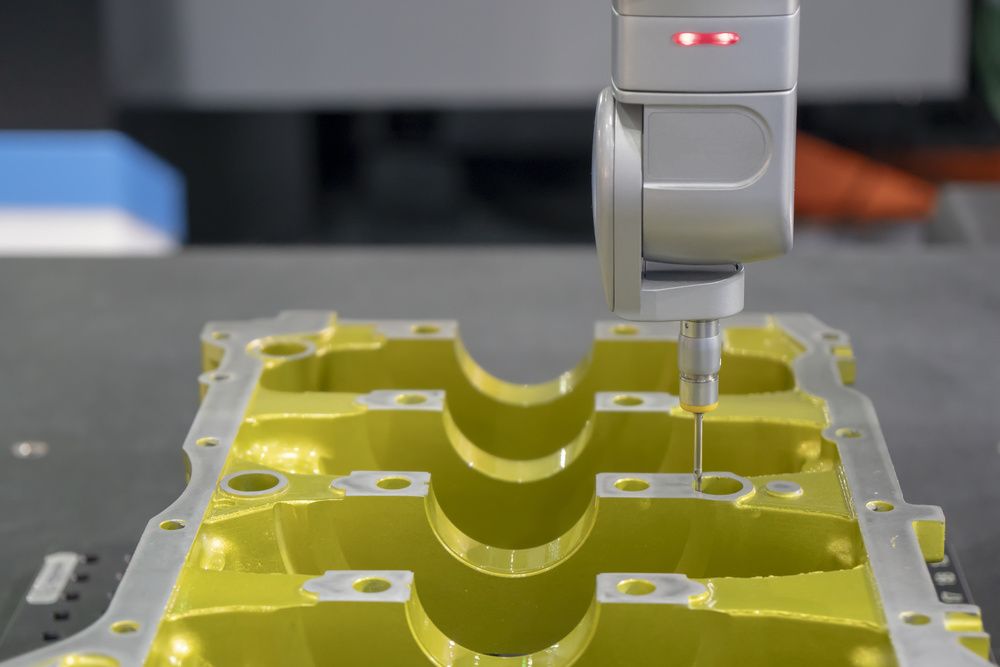
Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) verify dimensions with exceptional accuracy.
Laser scanning technology inspects complex geometries and surface profiles.
Statistical Process Control (SPC) monitors production to maintain consistent quality levels.
Advanced Machining Technologies
Multi-Axis Machining
5-axis machining centers rotate parts around multiple axes for complex geometry production.
This technology reduces setup times and improves accuracy for intricate components.
Simultaneous 5-axis machining creates complex curves and contours in single operations.
High-Speed Machining
High-speed machining uses faster spindle speeds and feed rates to improve productivity.
This technology reduces cycle times while maintaining precision and surface quality.
Advanced cutting tools withstand higher temperatures generated during 高速 operations.
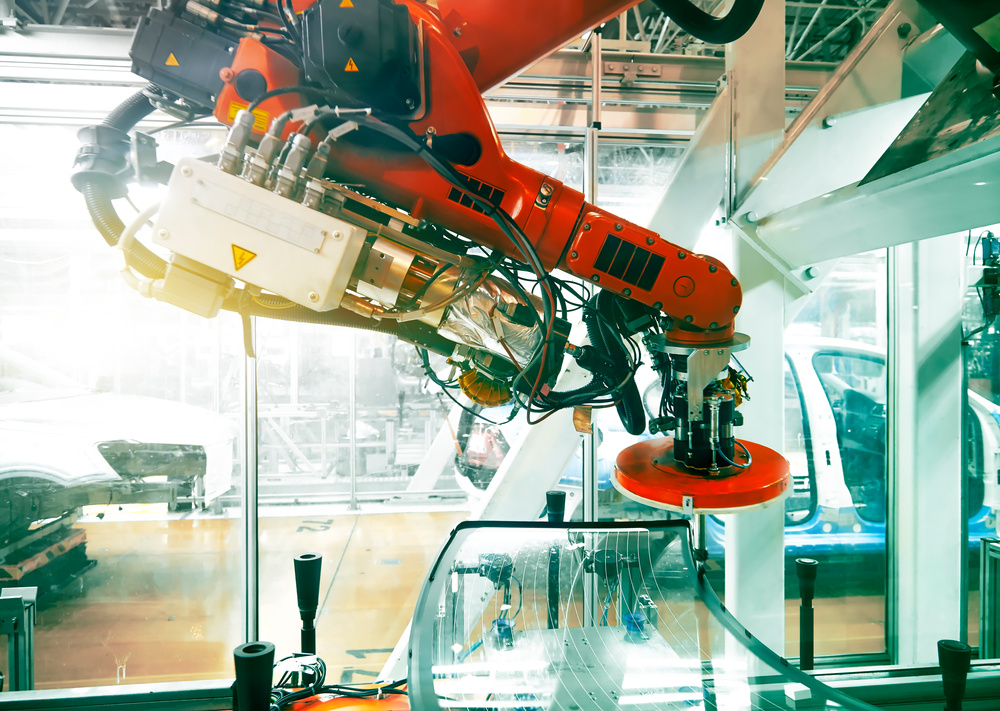
Automated Manufacturing
Robotic loading and unloading systems minimize human intervention in production.
Automated cells operate 24/7 to maximize productivity and reduce labor costs.
Industry 4.0 technologies integrate machines, sensors, and data analytics for smart manufacturing.
Aerospace Industry Applications
Aircraft components require lightweight materials and extreme precision for safety.
Turbine blades undergo rigorous machining to maintain aerodynamic efficiency.
Structural parts must withstand high stresses and temperature variations during flight.
Avionics housings protect sensitive electronics from environmental factors.
Aerospace machining demands the highest quality standards and certification processes.
Automotive Manufacturing Applications
Engine components like cylinder heads and blocks require precise machining for performance.
Transmission parts ensure smooth power transfer between engine and wheels.
Suspension components provide stability and control while driving.
Interior and exterior trim pieces combine functionality with aesthetic appeal.
Automotive machining focuses on high-volume production with consistent quality.
Medical Device Production
Surgical instruments require exceptional precision and biocompatible materials.
Implants like hip replacements must meet strict medical standards and tolerances.
Diagnostic equipment components ensure accurate results in medical testing.
Medical device housings protect sensitive electronics and maintain sterility.
Medical machining demands traceability and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Electronics Manufacturing Applications
Heat sinks manage thermal loads in high-performance electronic devices.
Enclosures protect sensitive components from environmental damage and interference.
Precision connectors ensure reliable electrical connections in complex systems.
Custom components support miniaturization trends in consumer electronics.
Electronics machining requires tight tolerances for proper component fitting.
Design Considerations for Machined Parts
Design for Manufacturability
Simplifying part geometry reduces machining time and production costs significantly.
Adding draft angles and radii improves tool access and reduces stress concentrations.
Standardizing features across product lines streamlines production and inventory management.
Tolerance Analysis
Proper tolerance selection balances functional requirements with manufacturing costs.
Critical dimensions require tighter tolerances to ensure proper assembly and performance.
Statistical tolerance analysis optimizes design specifications for production variability.
Material Selection Factors
Mechanical properties like strength, stiffness, and toughness must match application requirements.
Environmental factors including temperature, moisture, and chemicals influence material choice.
Cost considerations balance performance needs with budget constraints for projects.
Quality Assurance and Testing Procedures
Incoming Material Inspection
Raw materials undergo rigorous testing to verify chemical composition and mechanical properties.
Material certifications ensure compliance with industry standards and specifications.
Visual inspection identifies surface defects or imperfections before machining begins.
In-Process Quality Control
Regular measurements during machining ensure parts stay within specified tolerances.
Statistical process control monitors production trends and identifies potential issues early.
Operator inspections at key process stages prevent defects from progressing through production.
Final Inspection and Testing
Coordinate measuring machines verify dimensional accuracy of finished components.
Functional testing ensures parts perform as intended in actual operating conditions.
Destructive and non-destructive testing methods evaluate material integrity and strength.
Environmental Considerations in Machining
Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
Coolant recycling systems reduce waste and minimize environmental impact of operations.
Energy-efficient machines lower carbon footprint while maintaining productivity levels.
Material recycling programs reclaim valuable metals from machining scrap and waste.
Waste Reduction Strategies
Optimizing cutting parameters reduces material waste and improves resource utilization.
Nested part layouts on raw material sheets maximize material usage efficiency.
Lean manufacturing principles eliminate non-value-added activities throughout production.
Future Trends in Machining Technology
Additive Manufacturing Integration
Hybrid machines combining additive and subtractive processes offer new production possibilities.
3D printing creates near-net shapes that require minimal machining for final dimensions.
This integration reduces material waste and enables complex geometries not possible otherwise.
Artificial Intelligence Applications
AI-powered predictive maintenance reduces machine downtime and improves reliability.
Machine learning algorithms optimize cutting parameters for maximum efficiency and quality.
Computer vision systems automate quality inspection processes with high accuracy rates.
Digital Twin Technology
Virtual replicas of machining processes enable simulation and optimization before production.
Real-time data synchronization between physical and digital models improves process control.
Digital twins facilitate remote monitoring and troubleshooting of manufacturing operations.
Conclusion: The Importance of Machined Parts
Machined parts form the foundation of modern manufacturing across all industries worldwide.
Their precision, reliability, and versatility make them indispensable in countless applications.
Advancements in technology continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible with machining.
Understanding the capabilities and limitations of machined parts helps engineers design better products.
Collaboration between designers, manufacturers, and material suppliers drives innovation in machining.
The future of machining promises even greater precision, efficiency, and sustainability in production.
Investing in advanced machining technologies ensures competitiveness in global manufacturing markets.
Continuous improvement in processes and materials will shape the next generation of machined components.