Stamping Machining is an important process in the field of metal processing. Combined with the specialized magazines and journals in the custom processing industry, the industry’s professional encyclopedia knowledge and industry trends, we can introduce Stamping Machining in detail from the following aspects:

1. Definition and principle
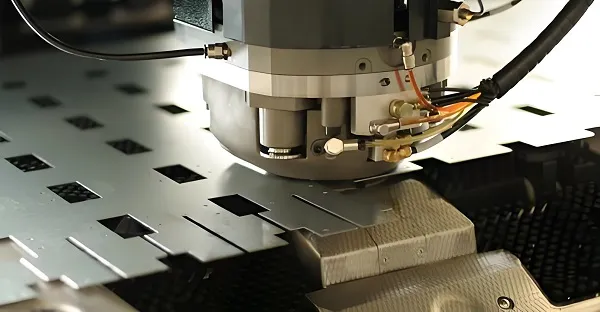
Definition: Stamping Machining, referred to as Stamping, is a metalworking process that applies pressure to a plate through a die to produce plastic deformation or fracture, so as to obtain parts of the desired shape and specifications.
Principle: In the stamping process, the plate is placed between the upper and lower dies of the mold, and through the pressure of the stamping equipment, the plate is deformed according to the specific shape of the mold, and finally the desired part is formed. This process has the advantages of high productivity, high material utilization and relatively low cost.
2.Scope of Application
Stamping Machining is widely used in a variety of industries, including but not limited to:
Automotive industry: for the production of body panels, engine parts, chassis components, etc.
Electronics industry: for manufacturing metal components such as connectors, housings, heat sinks, etc.
Home appliance industry: to produce metal housings and internal structural parts for refrigerators, washing machines, air conditioners and other home appliances.
Aerospace: manufacturing precision metal parts for aircraft, rockets and other aircraft.
3.Process Characteristics
High efficiency: stamping process can produce parts quickly and in bulk, significantly improving production efficiency.
High precision: through accurate mold design and manufacturing, it can ensure the high precision and consistency of stamped parts.
High material utilization: less material waste during stamping processing is conducive to improving material utilization.
Flexibility: by changing molds, parts of different shapes and specifications can be conveniently produced to meet diversified market demands.
4.Processing Flow
The processing flow of Stamping Machining usually includes the following steps:
Prepare plate: Select the plate that meets the requirements and carry out the necessary pre-treatment, such as cutting and cleaning.
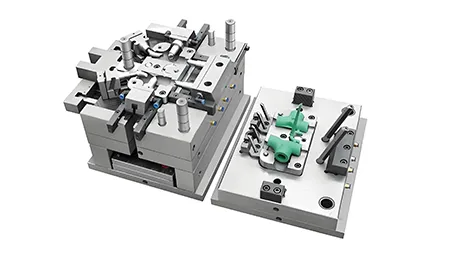
Designing the mold: According to the shape and design requirements of the part, design and manufacture the corresponding mold.
Stamping operation: Plate is placed in the mold and pressure is applied by stamping equipment to cause plastic deformation or fracture to form the required part.
Subsequent processing: deburring, cleaning, inspection and other subsequent processing of the stamped parts to ensure that their quality meets the requirements.
5. What is the difference between stamping and sheet metal fabrication?
a. Definition and Principle
Stamping Processing:
It is a metal working process in which pressure is exerted on the sheet by means of a mold to produce plastic deformation or fracture, so as to obtain parts of the required shape and specifications.
With the help of the power of conventional or special stamping equipment, the sheet is directly subjected to deformation force and deformed in the die, so as to obtain a certain shape, size and performance of the product parts.
Sheet metal fabrication:
A comprehensive cold working process mainly for thin metal sheets (usually under 6mm).
Including shearing, punching/cutting/compounding, folding, welding, riveting, splicing, molding (e.g., car body) and other process means.
b. Processing methods and precision
Stamping process:
Mainly through the mold on the plate for stamping and forming, processing precision is high.
Complex shapes and precise size control can be realized.
Sheet metal production:
More diverse processing methods, including shearing, bending, welding and other processes.
The processing accuracy is relatively low, and it is suitable for making simpler parts or preliminary shape processing.
c. Scope of application and materials
Stamping process:
Suitable for processing smaller plates or strips, as well as making parts with complex shapes and high precision requirements.
A wide range of materials are available, including a variety of metal sheets.
Sheet metal fabrication:
Suitable for processing larger sheets or strips, as well as making parts with relatively simple shapes and low precision requirements.
Also suitable for processing a wide range of metal sheets.
d. Production efficiency and cost
Stamping Processing:
High productivity, capable of mass production of a large number of identical or similar parts.
Due to the use of molds, it makes the production cost relatively low after reaching a certain scale.
Sheet metal fabrication:
Relatively low production efficiency, especially when hand fabrication or complex welding is required.
Costs may vary depending on processing methods and materials, but are usually more flexible in small lot or customized production.
e.Areas of Application
Stamping Processing:
Widely used in many industries such as automotive, electronics, home appliances, aerospace, etc. for the production of various precision parts.
Sheet metal fabrication:
Also applicable to a number of industries, but more for the production of structural parts, shells and other larger or relatively simple shape parts.
To summarize, there are obvious differences between stamping and sheet metal fabrication in terms of definition, processing methods and precision, scope of application and materials, production efficiency and cost, as well as application areas. In practical application, the appropriate processing technology should be selected according to specific needs and conditions.
Stamping Processing Service FAQ
1. What is stamping processing?
Stamping processing is a metalworking process in which a mold is used to apply pressure to a plate to cause it to plastically deform or separate, thereby obtaining a part of the desired shape and specifications. It is widely used in many industries such as automotive, electronics, home appliances and aerospace.
2. What are the advantages of stamping?
High efficiency: It can produce parts quickly and in batch to improve production efficiency.
High precision: Ensure high precision and consistency of stamped parts through accurate mold design and manufacturing.
High material utilization: reduce material waste and improve resource utilization efficiency.
Flexibility: High adaptability, can produce parts of different shapes and specifications by changing molds.
3. What materials can be processed by stamping?
Stamping processing can handle a wide range of metal materials, including but not limited to cold rolled steel, hot rolled steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and so on. Specific material selection depends on product design requirements, usage environment and cost considerations.
4. What is the service flow of stamping processing?
Demand communication: Communicate with customers about product demand, including part shape, size, material, quantity, etc.
Mold design: Design the mold drawings according to the customer’s requirements, and review and confirm.
Mould Manufacturing: Manufacture the mould according to the mould drawings, and carry out debugging and optimization.
Trial Production Verification: Conduct trial production using the molds to verify that the quality and accuracy of the stamped parts meet the requirements.
Mass production: After confirming that the trial production is correct, carry out mass production and deliver to customers.
After-sales service: Provide necessary after-sales service, including technical support and quality problem handling.
5. How to ensure the quality of stamped parts?
Strict quality control system: establish and implement strict quality control process, including raw material inspection, mold inspection, first piece inspection, process inspection and finished product inspection.
Advanced production equipments: Adopt advanced stamping equipments and testing technology to ensure the processing precision and stability.
Professional technical team: We have an experienced technical team that can solve various technical problems and provide technical support.
Continuous improvement: continuously optimize the process and mold design to improve production efficiency and product quality.
6. How to calculate the cost of stamping processing?
The cost of stamping processing usually includes material cost, mold cost, processing cost, transportation cost and other aspects. Specific costing needs to be considered according to the specific requirements of the product, the production lot and the market price. Generally speaking, the larger the production lot, the lower the unit cost.
7. What are the common problems in stamping? How to solve them?
Wear and tear of dies: Regular inspection and replacement of worn out die parts to keep the dies in good condition.
Material deformation: Optimize die design and stamping process parameters to reduce material deformation.
Insufficient precision: Improve the precision of mold processing and stamping equipment, strengthen the process inspection and control.
Surface quality problems: choose appropriate lubricants and cleaning process to reduce surface scratches and pollution.
8. Can you provide customized stamping service?
Yes, we can provide customized stamping processing service. Whether it is production based on drawings provided by customers, or tooling design and manufacturing according to customers’ needs, we can meet customers’ individual needs. Please feel free to contact us with your specific needs and we will be happy to serve you.