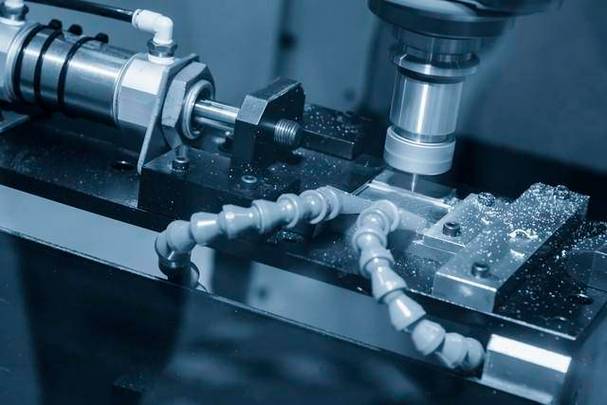
Cheapest Materials for CNC Machining in 2026 – Cost, Machinability & Trade-offs
Looking to cut CNC prototyping or production costs? The “cheapest” material isn’t always the lowest raw price – machining time & tool wear often dominate (up to 70% of total cost).
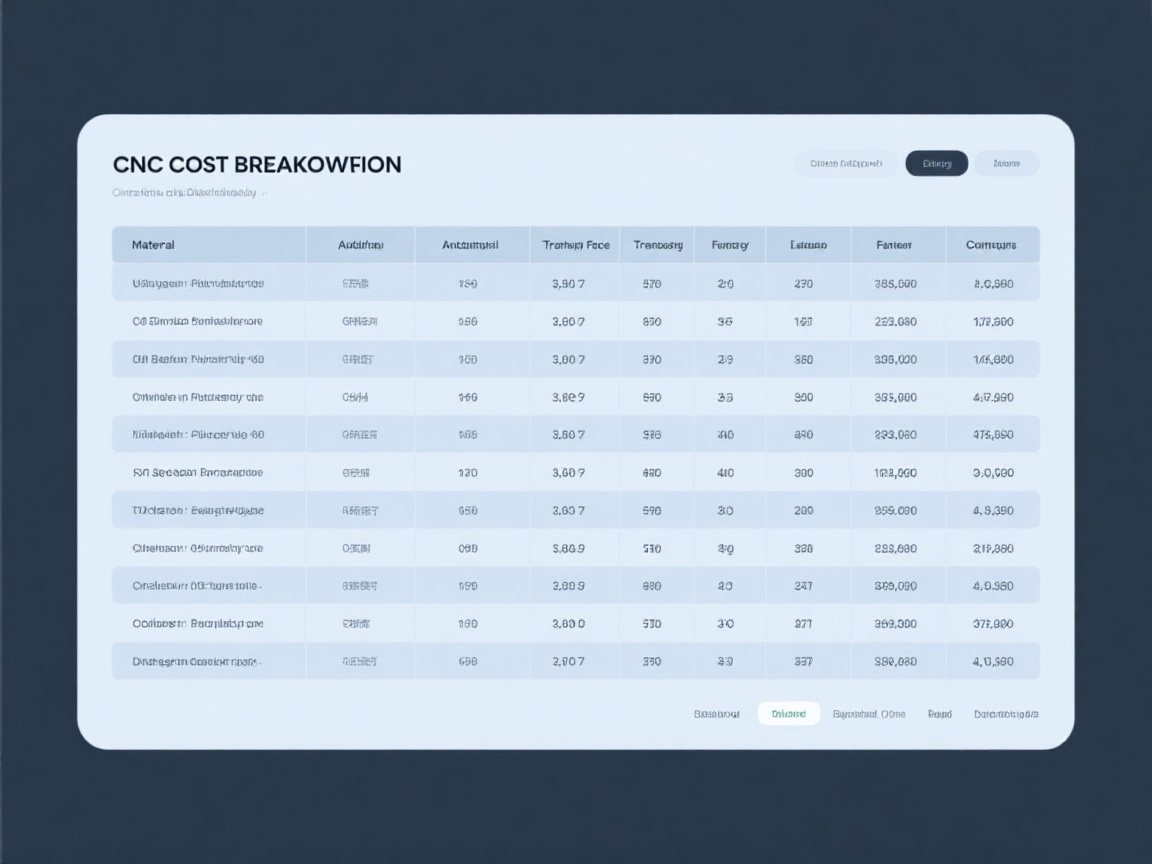
Material Comparison

Aluminum, Brass & Stainless Steel CNC Machined Parts
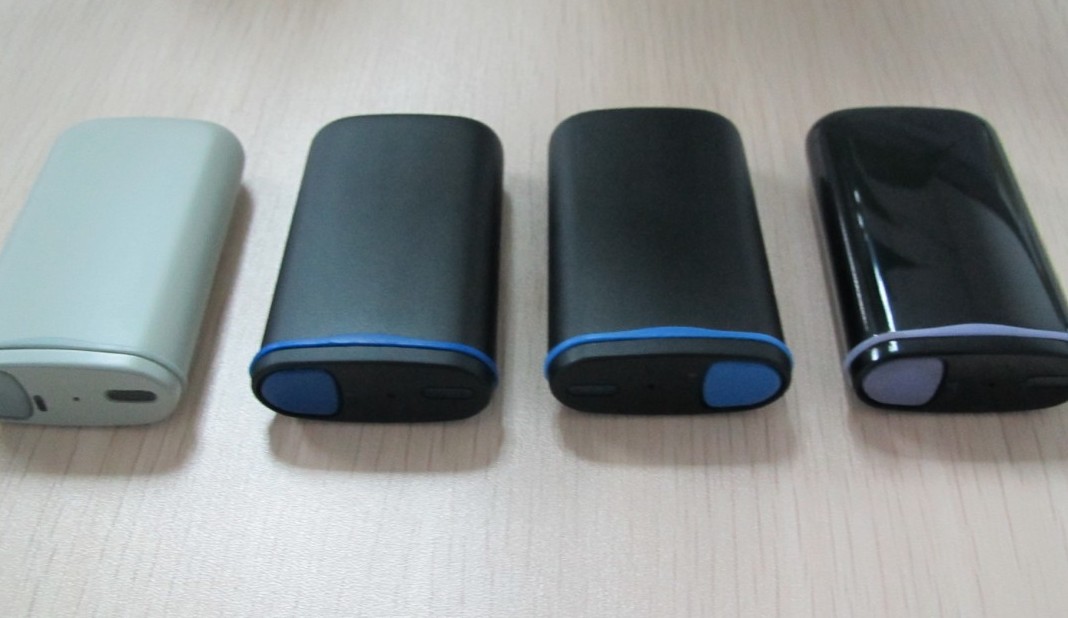
Plastic vs Metal CNC Parts
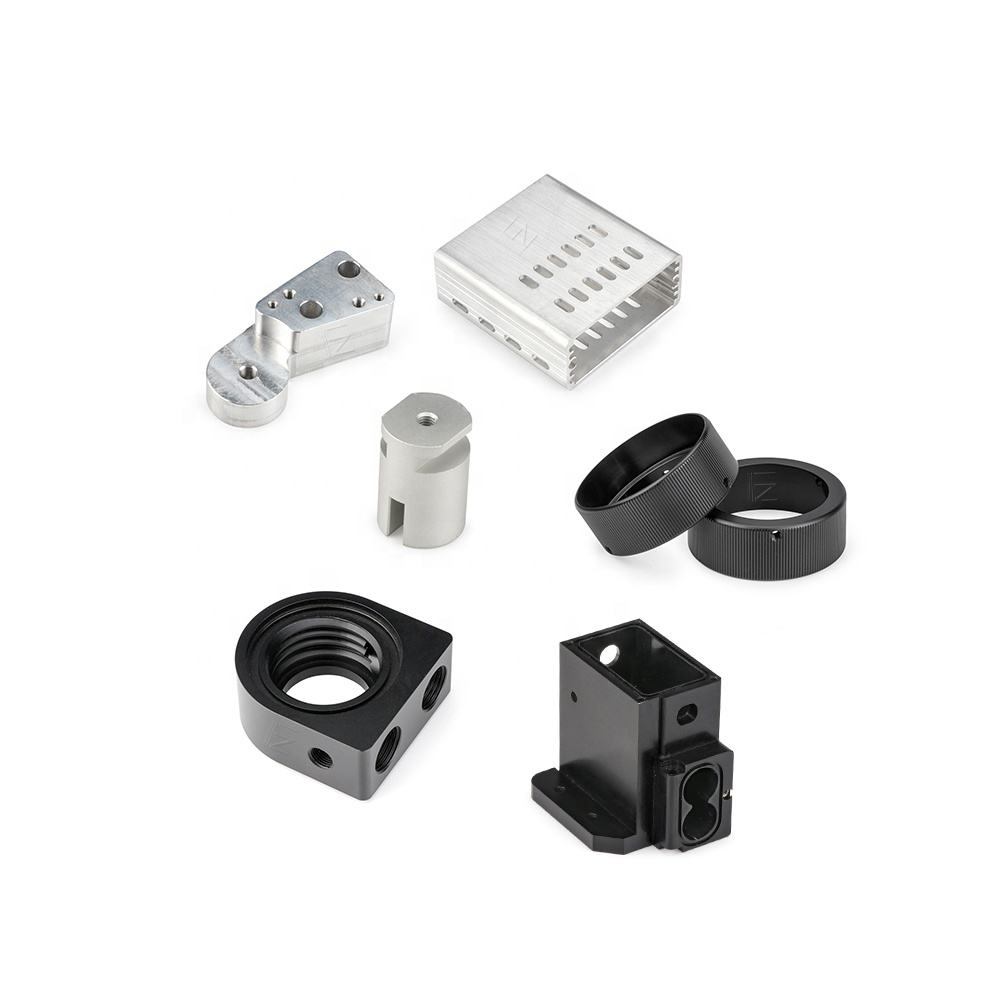

Black plastic and silver aluminum CNC machined components
CNC Cost Breakdown
Material (30%) vs Machining (50%) vs Other (20%)
2026 CNC Material Cost Comparison
Real Cost Breakdown Example
Same Part: 100×50×20mm Block
ABS Plastic
Aluminum 6061
Steel 1018
Material Deep Dive
When NOT to Choose the Cheapest
Plastic in High Temperature/Load Applications
Plastic may seem cheap upfront, but it can fail catastrophically in high temperature or load-bearing applications, leading to expensive rework and downtime.
Better choice: Aluminum or stainless steel
Steel in Corrosive Environments
Mild steel rusts quickly in humid or corrosive environments, requiring expensive plating or frequent maintenance that negates initial cost savings.
Better choice: Stainless steel or anodized aluminum
Low Strength Materials for Safety-Critical Parts
Using cheap, low-strength materials for safety-critical components can lead to failures, injuries, and liability issues that far exceed material cost savings.
Better choice: Engineering-grade materials









