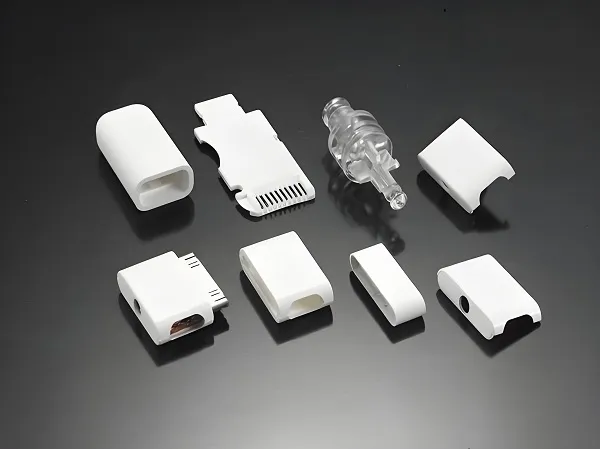
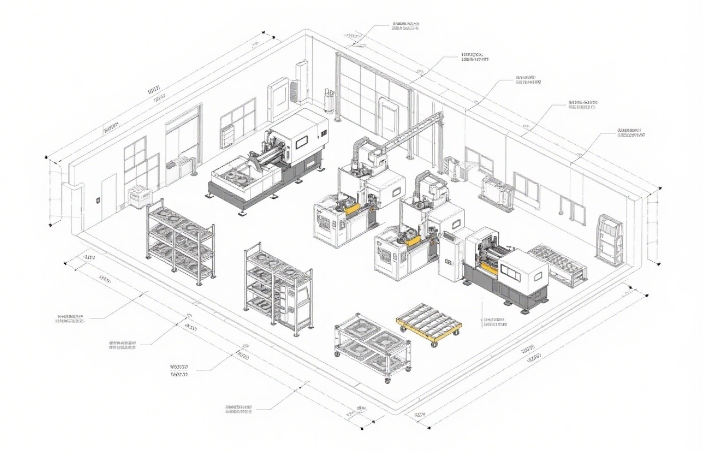
In the world of manufacturing, plastic injection molding stands as one of the most versatile and efficient processes for producing high-quality plastic parts. Whether you’re developing a new product, scaling up production, or need custom components for your business, understanding the plastic injection molding process is essential. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about this transformative manufacturing technique.
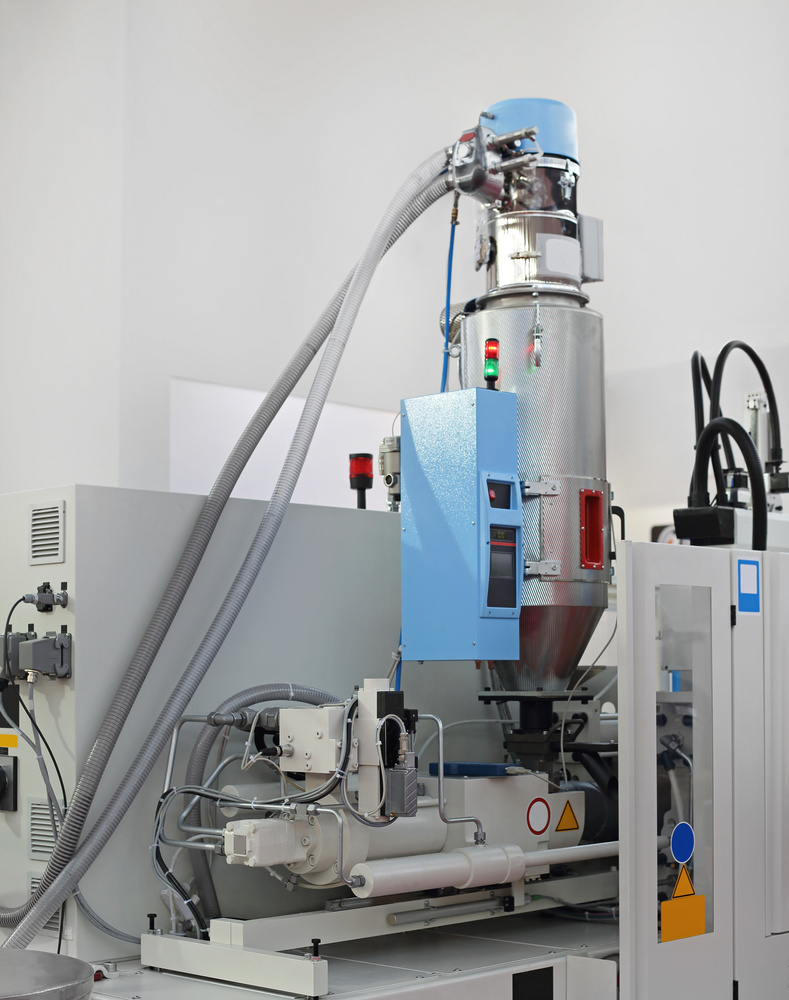
Modern plastic injection molding machine in a manufacturing facility
What is Plastic Injection Molding?
Plastic injection molding is a manufacturing process that involves melting plastic materials and injecting them into a precisely designed mold cavity under high pressure. Once the molten plastic cools and solidifies, the mold opens to reveal a finished part that exactly matches the mold’s shape and specifications.
This process is widely used across industries due to its ability to produce complex, high-precision parts with consistent quality and repeatability. From small electronic components to large automotive parts, injection molding offers unparalleled flexibility in design and production.
Thermoplastics vs. Thermoset Plastics
Understanding the difference between these two material types is crucial for successful injection molding:
Thermoplastics are the most commonly used materials in injection molding. They can be melted and re-molded multiple times without undergoing chemical changes. Examples include:
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Thermoset plastics, on the other hand, undergo a chemical reaction during the molding process that makes them permanently rigid. Once molded, they cannot be re-melted or re-shaped. Examples include:
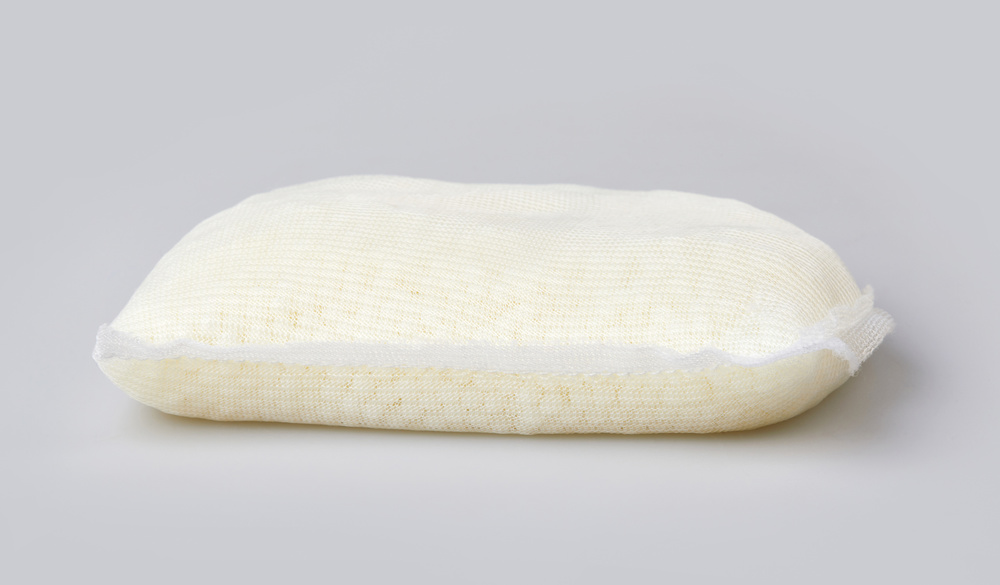
White PET plastic pellets used in the injection molding process
The Plastic Injection Molding Process Explained
The plastic injection molding process consists of several key stages, each critical to producing high-quality parts. Let’s break down each step in detail:
Step 1: Material Preparation
The process begins with the careful selection and preparation of raw materials:
- Plastic Pellets: High-quality plastic granules are chosen based on the part’s requirements
- Additives: Colorants, fillers, or reinforcements may be mixed to achieve specific properties
- Drying: Hygroscopic materials are dried to remove moisture that could cause defects
Step 2: Melting and Injection
The prepared materials are then processed through the injection unit:
- Feeding: Plastic pellets are fed into a hopper and transported into a heated barrel
- Heating: The barrel heats the plastic to its melting point (typically 150°C to 400°C)
- Mixing: A rotating screw homogenizes the molten plastic, ensuring uniform temperature
- Injection: The screw pushes the molten plastic through a nozzle into the mold cavity under high pressure (5,000 to 20,000 psi)
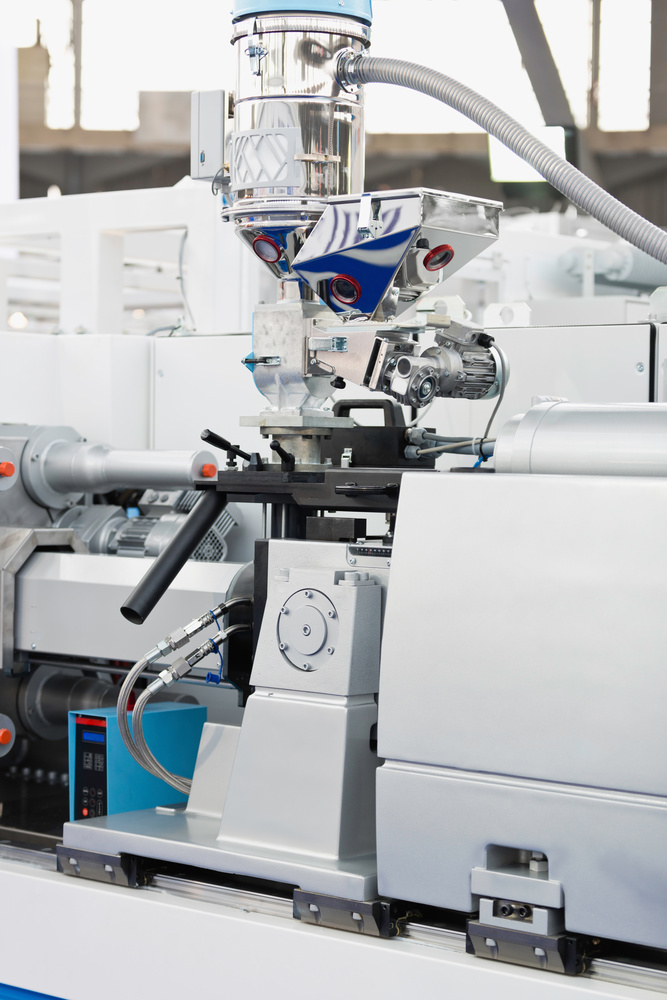
Hydraulic injection molding machine showing the injection unit
Step 3: Mold Clamping and Filling
The mold system plays a critical role in the process:
- Clamping: The mold is securely clamped shut using hydraulic or mechanical force
- Cavity Filling: Molten plastic flows into the mold cavity through a system of runners and gates
- Packing: Additional pressure is applied to ensure complete filling and compensate for shrinkage
Step 4: Cooling and Solidification
Proper cooling is essential for part quality:
- Cooling Channels: Water or oil circulates through channels in the mold to dissipate heat
- Solidification: The plastic cools and solidifies, taking the shape of the mold cavity
- Cycle Time: Cooling time varies based on part thickness, complexity, and material type
Step 5: Mold Opening and Ejection
Once the part is fully solidified:
- Mold Opening: The clamping system releases, and the mold halves separate
- Ejection: Pins or plates push the finished part out of the mold cavity
- Part Removal: The part is removed from the machine, often by automated systems
Step 6: Post-Processing
The ejected part may undergo several finishing steps:
- Trimming: Excess material from gates and runners is removed
- Finishing: Surface treatments like painting, plating, or texturing may be applied
- Assembly: Multiple parts may be assembled into a complete product
- Quality Inspection: Parts are checked for dimensions, appearance, and functionality
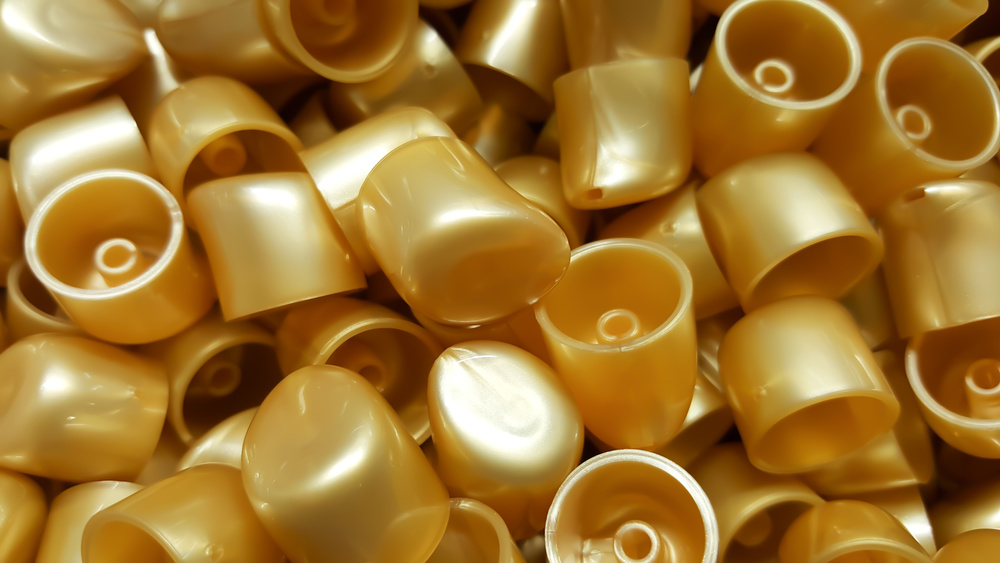
Close-up view of the injection molding process for disposable cups
Advantages of Plastic Injection Molding
The plastic injection molding process offers numerous advantages that make it the preferred manufacturing method for many applications:
High Precision and Consistency
- Tight Tolerances: Achieves tolerances as tight as ±0.0005 inches
- Dimensional Accuracy: Consistent part dimensions across large production runs
- Complex Geometries: Capable of producing intricate shapes with undercuts and threads
Cost-Effectiveness for Mass Production
- Economies of Scale: Lower per-unit costs as production volume increases
- Reduced Waste: Minimal material waste compared to other manufacturing methods
- Automation: High level of automation reduces labor costs and increases efficiency
Material Versatility
- Wide Material Selection: Compatible with hundreds of plastic materials
- Color Options: Easy color customization through pigment mixing
- Material Combinations: Ability to use multi-material molding processes
Design Flexibility
- Rapid Prototyping: Quick turnaround for design iterations
- Design Optimization: Support for complex part designs and features
- Tooling Efficiency: Long-lasting molds that can produce millions of parts
Custom P20 steel injection mold for auto parts
Applications of Custom Injection Molding
Custom injection molding is used across virtually every industry to produce a wide range of components:
Automotive Industry
- Engine components and housings
- Interior trim and dashboard parts
- Exterior body panels and bumpers
- Electrical connectors and wiring harnesses
Electronics and Technology
- Smartphone and tablet casings
- Computer components and peripherals
- Cable connectors and switches
Medical Devices
- Surgical instruments and tools
- Diagnostic equipment components
- Implantable devices (using biocompatible materials)
- Disposable medical supplies
Consumer Products
- Household appliances and components
- Toys and recreational equipment
- Packaging materials and containers
Industrial and Construction
- Machinery parts and components
- Pipes, fittings, and valves
- Electrical enclosures and junction boxes
- Safety equipment and protective gear
Common Issues in Injection Molding and Solutions
Even with proper planning, issues can arise during the plastic injection molding process. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
1. Air Bubbles and Voids
Causes:
- Trapped air in the mold cavity
- Moisture in the plastic material
- Insufficient injection pressure
Solutions:
- Proper material drying before processing
- Optimizing gate location and size
- Increasing injection pressure and speed
- Using vacuum degassing systems
2. Shrinkage and Warping
Causes:
- Incorrect packing pressure
- Material shrinkage characteristics
Solutions:
- Optimizing cooling system design
- Adjusting packing pressure and time
- Using uniform wall thickness in part design
- Implementing proper mold temperature control
3. Flash Formation
Causes:
- Insufficient clamping force
- Excessive injection pressure
Solutions:
- Increasing clamping force
- Improving mold alignment and maintenance
- Reducing injection pressure
- Optimizing process parameters
4. Short Shots
Causes:
- Insufficient material to fill the mold
- Injection pressure too low
Solutions:
- Adjusting injection pressure and speed
- Raising mold and melt temperatures
- Optimizing gate and runner design
Finished plastic injection molded parts ready for assembly
Frequently Asked Questions About Injection Molding
How long does the plastic injection molding process take?
The cycle time for injection molding can range from a few seconds to several minutes, depending on:
For small, simple parts, cycle times can be as short as 15-30 seconds. Larger, more complex parts may require 2-5 minutes per cycle.
What is the minimum order quantity for injection molding?
While injection molding is most cost-effective for large production runs, many manufacturers offer:
- Prototyping services: Low-volume production for testing and validation
- Bridge tooling: Cost-effective option for medium-volume production (1,000-10,000 parts)
- Production tooling: For high-volume production (10,000+ parts)
Can injection molding produce complex shapes?
Yes, one of the greatest advantages of injection molding is its ability to produce highly complex shapes with:
- Internal features and cavities
- Consistent wall thickness
How much does injection molding cost?
Cost factors include:
- Tooling costs: Initial investment for mold creation ((5,000-)100,000+)
- Material costs: Varies based on material type and part size
- Production costs: Labor, machine time, and overhead
- Post-processing costs: Finishing, assembly, and inspection
What design considerations are important for injection molding?
Key design considerations:
- Wall thickness: Uniform thickness for proper filling and cooling
- Draft angles: Facilitate easy part ejection
- Radii and fillets: Reduce stress concentrations
- Gate location: Optimize filling and minimize visible marks
- Ejection points: Strategic placement to avoid cosmetic issues
How do I choose the right material for my project?
Consider these factors when selecting materials:
- Mechanical properties: Strength, stiffness, impact resistance
- Chemical resistance: Exposure to chemicals, oils, or solvents
- Temperature requirements: Operating temperature range
- Regulatory compliance: FDA, medical, or automotive standards
- Cost considerations: Material and processing costs
Why Choose Professional Injection Molding Services?
When considering the plastic injection molding process for your project, partnering with an experienced manufacturer offers numerous benefits:
Expertise and Experience
- Technical Knowledge: Deep understanding of materials and processes
- Design Support: Assistance with part design and optimization
- Problem Solving: Ability to troubleshoot and resolve issues quickly
Advanced Technology
- Modern Equipment: State-of-the-art injection molding machines
- Quality Control: Advanced inspection and testing capabilities
- Process Monitoring: Real-time monitoring of production parameters
Quality Assurance
- Certifications: ISO 9001, ISO 13485, IATF 16949 certifications
- Traceability: Complete documentation and material traceability
- Consistency: Strict quality control throughout production
Cost Savings
- Efficiency: Optimized processes reduce waste and improve efficiency
- Scalability: Ability to scale production as your needs grow
- Value Engineering: Design optimization to reduce costs without sacrificing quality
Get Started with Your Injection Molding Project Today
Ready to leverage the power of the plastic injection molding process for your custom parts? Here’s how to get started:
1. Define Your Requirements
- Part design and specifications
- Quality standards and certifications
2. Find a Reliable Partner
- Research potential manufacturers
- Review their capabilities and experience
- Check references and customer reviews
- Evaluate their quality control processes
3. Design and Prototyping
- Work with engineers to optimize your design
- Create prototypes for testing and validation
- Refine the design based on prototype feedback
4. Production Planning
- Finalize material selection
- Design and manufacture tooling
- Establish production parameters
- Implement quality control measures
5. Production and Delivery
- Monitor production progress
- Conduct regular quality inspections
- Provide post-production support
The plastic injection molding process offers unparalleled versatility, precision, and cost-effectiveness for manufacturing high-quality plastic components. By understanding the process, materials, and applications, you can make informed decisions to ensure the success of your project.
Contact us today to discuss your injection molding needs and discover how we can help bring your product ideas to life with precision and efficiency.
This article was created to provide comprehensive information about the plastic injection molding process. For more specific details or to request a quote for your project, please contact our technical sales team.