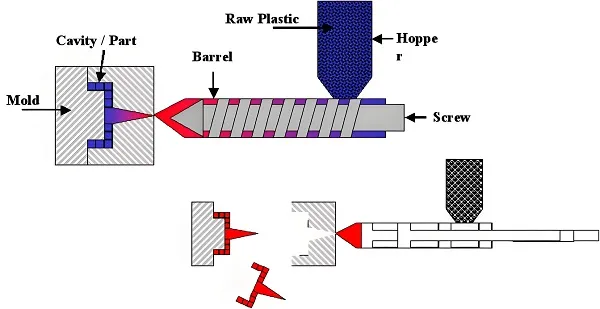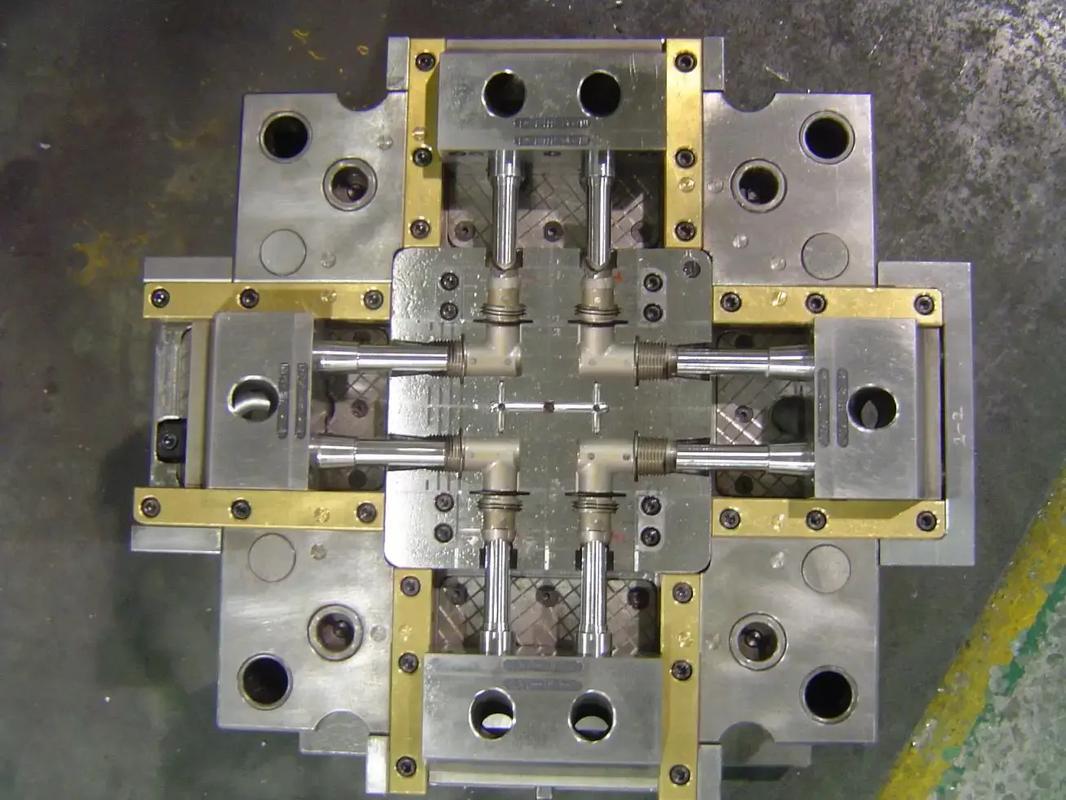
1、Answer
The core reasons for the high cost of injection molding include:
High mold costs: Molds need to be made of high – strength steel (such as H13 die steel) and undergo precision machining (such as five – axis milling and EDM forming). The cost of complex molds can reach hundreds of thousands of dollars, and they are not universal (for example, a mobile phone case mold is only suitable for a specific model).
High equipment investment: The price of injection molding machines ranges from tens of thousands to millions of dollars (for example, a large – scale automotive bumper injection molding machine requires a million – level investment), and the supporting cooling and temperature – control systems are costly.
High upfront trial – and – error costs: Multiple mold – testing and parameter adjustments (such as molten material temperature, injection pressure) are required, which wastes materials and takes time (a single mold – testing may consume thousands of yuan worth of raw materials).
2、Expansion
In – depth analysis of cost composition
Mold costs: Accounting for 50% – 70% of the total cost
Design complexity: High – precision molds (such as medical – grade transparent part molds) need to be matched with CAE simulation to analyze the runner balance, and the design fee can reach tens of thousands of dollars;
Materials and processes: Aerospace – grade molds need to use corrosion – resistant Stavax stainless steel, whose unit price is 3 – 5 times that of ordinary steel, and they need to undergo vacuum quenching (the processing cost accounts for 20% of the material cost);
Non – reusability: After product iteration, the mold is basically scrapped (for example, when a mobile phone is upgraded, the old shell mold becomes useless), and new investment is required.
Equipment and operation costs
Astounding energy consumption: A 500 – ton injection molding machine consumes about 30 kWh of electricity per hour, and the annual electricity cost exceeds 200,000 yuan (calculated based on 16 hours of operation per day);
High maintenance threshold: The seals of the hydraulic system need to be replaced every six months (the single – time cost is 5,000 yuan), and when the screw is worn, it needs to be electroplated for repair (the cost accounts for 30% of the original value of the screw);
Automation support: High – end production lines need to be equipped with robots for part removal (the cost of a single robot is 100,000 – 500,000 yuan) and coordinate measuring machines (equipment with a precision of 0.001mm requires a million – level investment).
Hidden costs: Time and risks
Long delivery cycle: It takes 8 – 16 weeks from mold design to mass production (complex molds such as automotive dashboard molds take 24 weeks), and delays may lead to liquidated damages;
Ineconomical for small – batch production: When producing 100 products, the mold cost allocated to each piece can reach thousands of yuan, while 3D printing only costs a few hundred yuan (such as small – batch customized parts);
Material waste: The waste rate in the mold – testing stage can reach 20% – 40% (for example, for transparent acrylic products, the temperature needs to be repeatedly adjusted to eliminate bubbles), and high – end materials (such as PEEK) cost more than a thousand yuan per kilogram.
Cost – reduction strategies
For small – batch scenarios: Use simple aluminum molds (the cost is 1/5 of that of steel molds, and the service life is about 5,000 times) or 3D – printed silicone molds (suitable for the production of 100 – 500 pieces);
Design optimization: Reduce the number of gates through mold – flow analysis (for example, changing multi – point gating to single – point gating can reduce the mold cost by 15%), and adopt modular design (such as a universal mold base + replaceable cores);
Process innovation: Multi – material co – injection molding (such as forming soft – hard combined parts in one step, reducing secondary assembly), gas – assisted injection molding (reducing the clamping force requirement by 40% and enabling the use of a smaller – sized machine).
In conclusion, the high cost of injection molding stems from its characteristics of “high threshold and high fixed investment.” However, in mass production (such as disposable tableware, automotive lamp covers), the cost per piece can be as low as a few cents, making it the king of cost – effectiveness in industrial manufacturing.